Xanthorrhoea is a genus of about 30 species of flowering plants, in the family Asphodelaceae. They are endemic to Australia.

Arthropodium milleflorum, the pale vanilla lily, is a species of herbaceous perennial plants native to Australia. It occurs in various habitats including alpine areas and grows to between 0.3 and 1.3 metres high and 0.3 metres wide. The fleshy tubers were eaten by Aboriginal Australians. The plant has a strong vanilla fragrance, especially noticeable on warm days.

Centipeda cunninghamii is a species of flowering plant in the Asteraceae family. It is referred to by the common names old man weed, being the literal translation of its Koori name gukwonderuk, common sneezeweed and scent weed which were given by European settlers but are increasingly falling out of use. The plant was used by indigenous Australians for its purported medicinal properties. It grows along the Murray River, or generally anywhere there is water, especially low lying or swampy areas. It can be identified by its unique shaped leaf and its pungent scent which is pine-like and minty.

Ruppia, also known as the widgeonweeds, ditch grasses or widgeon grass, is the only extant genus in the family Ruppiaceae, with eight known species. These are aquatic plants widespread over much of the world. The genus name honours Heinrich Bernhard Rupp, a German botanist (1688-1719). They are widespread outside of frigid zones and the tropics.

Banksia telmatiaea, commonly known as swamp fox banksia or rarely marsh banksia, is a shrub that grows in marshes and swamps along the lower west coast of Australia. It grows as an upright bush up to 2 metres tall, with narrow leaves and a pale brown flower spike, which can produce profuse quantities of nectar. First collected in the 1840s, it was not published as a separate species until 1981; as with several other similar species it was previously included in B. sphaerocarpa.

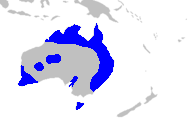
Exocarpos cupressiformis, with common names that include native cherry, cherry ballart, and cypress cherry, belongs to the sandalwood family of plants. It is a species endemic to Australia. Occasionally the genus name is spelt "Exocarpus" but it appears to be mostly no longer in use.

Potamogeton crispus, the crisp-leaved pondweed, curly pondweed, curly-leaf pondweed or curled pondweed, is a species of aquatic plant (hydrophyte) native to Eurasia but an introduced species and often a noxious weed in North America.

This is a list of plants commonly found in Kakadu National Park, Northern Territory of Australia. Where known, common names are given in English and in Gun-djeihmi, a commonly spoken indigenous language in the area, are given in parentheses.
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology, Glossary of lichen terms, and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names.

Alpinia caerulea, commonly known as native ginger or Australian ginger, is an understorey perennial herb in the family Zingiberaceae which grows in rainforest, gallery forest and wet sclerophyll forest in eastern Australia.

Ampera xiphloclada, commonly known as ‘broom spurge’, is a grass-like erect shrub in the Euphorbiaceae family.

Persicaria amphibia is a species of flowering plant in the knotweed family known by several common names, including longroot smartweed, water knotweed, water smartweed, and amphibious bistort. It is native to much of North America, Asia, Europe, and parts of Africa, and it grows elsewhere as an introduced species and sometimes a noxious weed.

Gahnia grandis is a tussock-forming perennial plant found in southeastern mainland Australia and Tasmania.

Cordyline manners-suttoniae, commonly known as the giant palm lily, is an evergreen plant found only in rainforest of northeastern Queensland, Australia.

Nymphaea gigantea, commonly known as the giant waterlily or blue waterlily, is a perennial, herbaceous plant in the family Nymphaeaceae which is native to parts of northern and eastern Australia, and it has been widely cultivated elsewhere. It is an aquatic plant whose natural habitat is permanent and semi-permanent still water bodies

Gonocarpus tetragynus is an Australian herb in the watermilfoil family Haloragaceae native to eastern Australia. Common names include common raspwort. A widespread species particularly found in dry eucalyptus forests, scrubland, and heathland.

Lomandra multiflora, also commonly known as many-flowered mat rush, mat rush and many flowered mat-lily, is a perennial, rhizomatous herb found in Australia and Papua New Guinea. The mat rush is distributed widely in the region and common within its preferred growing conditions. Its conservation status is considered not to be of concern and risk.

Podostemum ceratophyllum, commonly known as the hornleaf riverweed, is a species of submerged aquatic plant in the family Podostemaceae. It is native to eastern North America where it grows on hard bottoms in swiftly flowing rivers and streams and is considered a foundation species.

Potamogeton tepperi is a water herb, belonging to the Potamogetonaceae family in the order Alismatales.

Caesia calliantha, commonly known as the blue grass lily or blue star lily, is a species of herbaceous flowering plant. It is a member of the Asphodelaceae family, subfamily Hemerocallidoideae, native to Australia found predominantly along the East coast in Victoria, New South Wales, South Australia and Tasmania.



















