
Baculites is an extinct genus of heteromorph ammonite cephalopods with almost straight shells. The genus, which lived worldwide throughout most of the Late Cretaceous, and which briefly survived the K-Pg mass extinction event, was named by Lamarck in 1799.

Acanthohoplites is an extinct genus of ammonites in the family Parahoplitidae that lived in the Aptian and Early Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous.

Barremites is an ammonoid cephalopod genus belonging to the family Desmoceratidae, that lived during the Hauterivian and Barremian stages of the Early Cretaceous.

Gleviceras is an ammonite genus that lived during the Early Jurassic Period, found in Canada, Hungary, Mexico and the United Kingdom.

Pavlovia is an extinct genus of ammonite of the Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous.

Placenticeras is a genus of ammonites from the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils have been found in Asia, Europe, North and South America.

Vinctifer is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish erected by David Starr Jordan in 1919.

Cenoceras is an extinct genus within the cephalopod mollusc family Nautilidae, which in turn makes up part of the superfamily Nautilaceae. This genus has been described by Hyatt in 1884. The type species is Cenoceras intermedium, which was originally described by Sowerby 1816 as Nautilus intermedius.
Heminautilus is an extinct genus of nautiloids from the nautilacean family Cenoceratidae that lived during the Early Cretaceous. Fossils of Heminautilus have been registered in rocks of Barremian and Aptian age. Nautiloids are a subclass of shelled cephalopods that were once diverse and numerous but are now represented by only a handful of species.
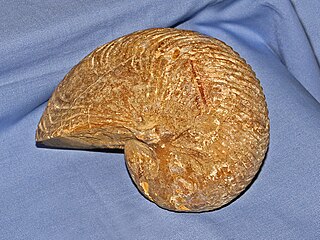
The Cymatoceratidae is a family of Mesozoic and early Cenozoic nautiloid cephalopods and the most abundant of this kind in the Cretaceous. They are characterized by ribbed, generally involute shells of varied form - coiled such that the outer whorl envelops the previous, as with Nautilus, and sutures that are variably sinuous.
Compsemys is an extinct genus of prehistoric turtles from the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene of North America and possibly Europe. The type species C. victa, first described by Joseph Leidy from the Hell Creek Formation in Montana in 1856, and another probable species C. russelli, described in 2012, from Paleocene deposits in France. Its affinites have long been uncertain, but it has recently been considered to be the most basal member of Paracryptodira, despite the clade first appearing in the Late Jurassic, and is sometimes included in its own family, Compsemydidae. A revision in 2020 found Compsemydidae to be more expansive, also containing Riodevemys and Selenemys from the Late Jurassic of Europe, and Peltochelys from the Early Cretaceous of Europe.

Phylloceras is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the family Phylloceratidae. These nektonic carnivores lived from Early Jurassic to Late Cretaceous.

Craspedites is an ammonoid cephalopod included in the Perisphinctoidea that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous, found in Canada, Greenland, Poland, and the Russian Federation.

Lytoceratinae is a subfamily of ammonoid cephalopods that make up part of the family Lytoceratidae.

Puzosia is a genus of desmoceratid ammonites, and the type genus for the Puzosiinae, which lived during the middle part of the Cretaceous, from early Aptian to Maastrichtian. Sepkoski defines the range from Albian to Santonian. The generic name comes from the Serbian words "Puž" (snail) and "oce/ose" (axis), gaining its name from the shell's snail-like appearance.

Pterotrigonia is an extinct genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Megatrigoniidae. This genus is known in the fossil record from the Jurassic period Tithonian age to the Cretaceous period Maastrichtian age. Species in this genus were facultatively mobile infaunal suspension feeders. The type species of the genus is Pterotrigonia cristata.

Phyllopachyceras is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the family Phylloceratidae. These nektonic carnivores lived in the Cretaceous, from Hauterivian to Maastrichtian to age.

Olcostephanus is an extinct ammonoid cephalopod genus belonging to the family Olcostephanidae. These fast-moving nektonic carnivores lived during the Cretaceous, from the upper Valanginian to the lower Hauterivian age.
Calamophylliopsis is a genus of extinct stony corals. They lived from the Early Jurassic to Late Oligocene.

Rastellum is an extinct genus of molluscs, which lived from the Middle Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous. This species is also known as Arctostrea carinata.

















