
Falcons are birds of prey in the genus Falco, which includes about 40 species. Some small species of falcons with long, narrow wings are called hobbies, and some that hover while hunting are called kestrels. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene.
The Sivalik Hills, also known as Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas. The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. The hills are known for their numerous fossils, and is also home to the Soanian Middle Paleolithic archaeological culture.

Sauropterygia is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. It is possible that sauropterygians are a distant relatives of turtles, uniting them under the group Pantestudines, although this is still debatable as sauropterygians might be archosauromorphs or completely unrelated to both.

A nummulite is a large lenticular fossil, characterised by its numerous coils, subdivided by septa into chambers. They are the shells of the fossil and present-day marine protozoan Nummulites, a type of foraminiferan. Nummulites commonly vary in diameter from 1.3 cm to 5 cm and are common in Eocene to Miocene marine rocks, particularly around southwest Asia and the Mediterranean in the area that once constituted the Tethys Ocean, such as Eocene limestones from Egypt or from Pakistan. Fossils up to six inches wide are found in the Middle Eocene rocks of Turkey. They are valuable as index fossils.
In geology, the Llandeilo Group is the middle subdivision of the British Ordovician rocks. It was first described and named by Sir Roderick Murchison from the neighborhood of Llandeilo in Carmarthenshire. In the type area it consists of a series of slaty rocks, shales, calcareous flagstones and sandstones; the calcareous middle portion is sometimes termed the Llandeilo limestone; and in the upper portion volcanic rocks are intercalated.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1987.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1977.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1964.

Cynarctus is an extinct genus of the Borophaginae subfamily of canids native to North America. The genus was first founded by W. D. Matthew in 1901, based from a pair of lower jaws, Cynarctus saxitilis, found in the Pawnee Creek Beds of Colorado. It lived during the Middle to Late Miocene 16.0—10.3 mya, existing for approximately 5.7 million years. Fossils have been uncovered in Colorado, California, Maryland, western Nebraska, and Texas. It was likely an omnivore, and lacked the bone-cracking adaptations found in some later borophagines. Newer findings have proved the genus to be described as a large dog-like raccoon, a result from combining characteristics from Canidae with Procyonidae.

Miocyon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from the early to late Eocene.
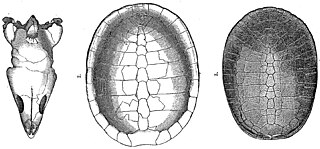
Glyptops is an extinct genus of pleurosternid freshwater turtle known from the Late Jurassic of North America.

Ptychoceratodus is an extinct genus of lungfish living from Early Triassic to Middle Jurassic. It was established by Otto Jaekel for one species, transferred from Ceratodus genus. Type species is P. serratus from the Middle Triassic of Switzerland and Germany. Ptychoceratodus had two pairs of massive dental plates, bearing 4-6 acute ridges. Its skull roof was composed from massive, plate-like bones. In the central part of skull roof was localized an unossified fenestra. Most of the Ptychoceratodus findings are isolated dental plates, some associated with jaws. Other parts of skull or postcranial skeleton are relatively rarely found as fossils. The anatomy of skull is the best recognized in P. serratus, whereas less complete cranial material is available also for P. concinuus, P. phillipsi, and P. rectangulus. Although Ptychoceratodus is known exclusively from the Triassic and Jurassic, there were also Cretaceous specimens referred to this genus. However, they are more often regarded as representants of Metaceratodus. Ptychoceratodus is the only member of the family Ptychoceratodontidae. The first named species is P. phillipsi by Louis Agassiz in 1837 as a species of Ceratodus and later moved to the genus Ptychoceratodus. Occurrences of Ptychoceratodus come mainly from Europe. However, occurrences from other continents suggest it was dispersed globally during the Triassic. After 2010, the new fossil material behind the Europe was reported from South America, India, and Greenland
Zooceras is an extinct genus of prehistoric nautiloids known from Pragian-aged fossils in the Prague Basin. The fossils were originally described by Joachim Barrande as species of Cyrtoceras. The shells are curved into a "C" shape.

Felis lunensis, or the Martelli's cat is an extinct felid of the subfamily Felinae.
Glyptodendron is a Lower Silurian westonocerid characterized by compressed cyrtocones with a narrowly rounded dorsum and greatest width in the ventrolateral region. Sutures slope forward from the dorsum which is on the longitudinally concave side. The siphuncle is slightly ventral from the center. Segments are subspherical in the young; equally broad but shorter in the adult. No endosiphuncular deposits are known. The surface of the shell is covered by obliquely intersecting rows of scale-like pits.

Calmasuchus is a genus of capitosaurian temnospondyl which lived during the middle Triassic. Fossils of Calmasuchus have been recovered from the La Mora site of the Catalan basin in Barcelona of Spain. Identified from a partial skull roof and palate, skull fragments and complete hemi-mandible, it was named by Josep Fortuny, Àngel Galobart and Carles De Santisteban in 2011. The type species is Calmasuchus acri.

Tanytrachelos is an extinct genus of tanystropheid archosauromorph reptile from the Late Triassic of the eastern United States. It contains a single species, Tanytrachelos ahynis, which is known from several hundred fossil specimens preserved in the Solite Quarry in Cascade, Virginia. Abundant fossils of Tanytrachelos are found in a series of lakebed sediments that were deposited over the course of about 350 thousand years in a lake which existed approximately 230 million years ago. Some fossils are very well-preserved and include the remains of soft tissues. Tanytrachelos is the most likely trackmaker of the ichnogenus Gwyneddichnium.

The Guelph Formation is a geologic formation in New York and in Ontario, Canada. It preserves fossils dating back to the Silurian period.

The Kilmaluag Formation is a Middle Jurassic geologic formation in Scotland. It was formerly known as the Ostracod Limestone for preserving an abundance of fossil freshwater/low salinity ostracods. Gastropods, bivalves, trace fossil burrows, and vertebrate fossil remains have also been recorded from the formation. Vertebrate fossils include fish, crocodylomorphs, mammals, small reptiles, amphibians, theropod and sauropod dinosaurs and pterosaurs.

Dipteronia brownii is an extinct species in the soapberry family (Sapindaceae) described in 2001. Fossils of D. brownii are known from stratigraphic formations in North America and Asia ranging in age between Paleocene to Early Oligocene.














