
Gamma-glutamyltransferase is a transferase that catalyzes the transfer of gamma-glutamyl functional groups from molecules such as glutathione to an acceptor that may be an amino acid, a peptide or water. GGT plays a key role in the gamma-glutamyl cycle, a pathway for the synthesis and degradation of glutathione as well as drug and xenobiotic detoxification. Other lines of evidence indicate that GGT can also exert a pro-oxidant role, with regulatory effects at various levels in cellular signal transduction and cellular pathophysiology. This transferase is found in many tissues, the most notable one being the liver, and has significance in medicine as a diagnostic marker.

Transglutaminases are enzymes that in nature primarily catalyze the formation of an isopeptide bond between γ-carboxamide groups ( -(C=O)NH2 ) of glutamine residue side chains and the ε-amino groups ( -NH2 ) of lysine residue side chains with subsequent release of ammonia ( NH3 ). Lysine and glutamine residues must be bound to a peptide or a protein so that this cross-linking (between separate molecules) or intramolecular (within the same molecule) reaction can happen. Bonds formed by transglutaminase exhibit high resistance to proteolytic degradation (proteolysis). The reaction is
In enzymology, a UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate—L-lysine ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-tripeptide—D-alanyl-D-alanine ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-glutaminase (EC 3.5.1.35) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutamin-(asparagin-)ase (EC 3.5.1.38) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a peptidyl-glutaminase (EC 3.5.1.43) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a protein-glutamine glutaminase (EC 3.5.1.44) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an agaritine gamma-glutamyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-alanine gamma-glutamyltransferase (EC 2.3.2.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase (EC 2.3.2.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutathione gamma-glutamylcysteinyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 1 (GGT1), also known as CD224, is a human gene.

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GGT7 gene.

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GGT5 gene.
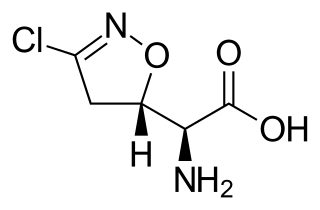
Acivicin is an analog of glutamine. It is an inhibitor of gamma-glutamyl transferase.
Glutathione hydrolase (EC 3.4.19.13, glutathionase, GGT, gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase) is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Leukotriene-C4 hydrolase (EC 3.4.19.14, gamma-glutamyl leukotrienase) is an enzyme. Gamma-glutamyltransferase 5 (GGT5) is a human gene which encodes an enzyme protein that belongs to this class of enzymes. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GGT6 gene.






