
Fungus-growing ants comprise all the known fungus-growing ant species participating in ant–fungus mutualism. They are known for cutting grasses and leaves, carrying them to their colonies' nests, and growing fungi on them on which they later feed.

Rhopalosomatidae is a family of Hymenoptera containing about 68 extant species in four genera that are found worldwide. Three fossil genera are known.

Aeolosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. Like most sauropods, it would have been a quadrupedal herbivore with a long neck and tail. Aeolosaurus is well known for a titanosaur, as it is represented by the remains of several individuals belonging to at least three species. However, like most titanosaurs, no remains of the skull are known. The holotype of Aeolosaurus rionegrinus consists of a series of seven tail vertebrae, as well as parts of both forelimbs and the right hindlimb. It was discovered in the Angostura Colorada Formation in Argentina, which dates from the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, about 83 to 74 million years ago. The species A. maximus was transferred over to the new genus Arrudatitan in 2021.
Barry Bolton is an English myrmecologist, an expert on the classification, systematics, and taxonomy of ants, who long worked at the Natural History Museum, London. He is known especially for monographs on African and Asian ants, and for encyclopaedic global works, including the Identification Guide to Ant Genera (1994), A New General Catalogue of Ants of the World, Synopsis and Classification of Formicidae (2003), and Bolton's Catalogue of Ants of the World: 1758-2005 (2007). Now retired, Bolton is a Fellow of the Royal Entomological Society and Myrmecologist, Biodiversity Division, Department of Entomology, Natural History Museum, London.

The ocellated antbird is a species of antbird in the family Thamnophilidae. It is monotypic within the genus Phaenostictus and is found in southern Central America and the northwestern part of South America. Its natural habitat is the understory of tropical moist lowland forest, foothill forest, and tall secondary growth woodlands.
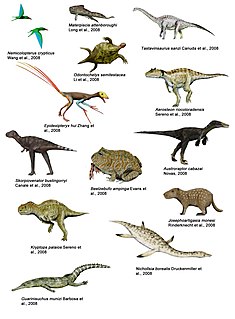
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2008.

Agroecomyrmecinae is a subfamily of ants containing two extant and two fossil genera. The subfamily was originally classified in 1930 by Carpenter as Agroecomyrmecini, a Myrmicinae tribe. Bolton raised the tribe to subfamily status in 2003, suggesting that Agroecomyrmecinae might be the sister taxon to Myrmicinae. It has since been discovered to be one of the earliest lineages of ants, a clade from the basal polytomy for all ants. In 2014, the subfamily was expanded to two tribes. The tribe Ankylomyrmini was moved from the subfamily Myrmicinae to Agroemyrmecinae.

Eulithomyrmex is an extinct genus of ant in the formicid subfamily Agroecomyrmecinae. The genus contains two described species, Eulithomyrmex rugosus and Eulithomyrmex striatus. Eulithomyrmex is known from a group of Late Eocene fossils which were found in North America.

Anomalomyrma is an Asian genus of ants in the subfamily Leptanillinae. The genus was originally described in 1990 with the type species Anomalomyrma taylori, based on a single dealate queen from Borneo. Workers were unknown until 2011, when two new species were described from Peninsular Malaysia and the Philippines.

Lordomyrma is a genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae.

Meranoplus is an Old World genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae. With over 80 valid species, it is predicted that over half of the Meranoplus diversity remains undescribed, most of these from Australia.
Daceton boltoni is a Neotropical species of arboreal ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae. The species occurs in Peru and Brazil and is similar to its sister species, D. armigerum.

Daceton armigerum is a Neotropical species of arboreal ants, distributed throughout northern South America. D. armigerum combines several traits generally noted in some other arboreal ants i.e., populous colonies, large and/or polydomous nests, intra- and interspecific aggressiveness, trophobiosis, and capturing prey by spread-eagling them.
Cyatta is a genus of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae containing the single species Cyatta abscondita. It is considered the most recent ancestor of all fungus-farming ants and a living fossil.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2009 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods that have been described during the year 2009, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to arthropod paleontology that occurred.












