
The Indomalayan realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms. It extends across most of South and Southeast Asia and into the southern parts of East Asia.

Temperate rainforests are rainforests with coniferous or broadleaf forests that occur in the temperate zone and receive heavy rain.

Dalbergia melanoxylon in french Granadille d'Afrique is a flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to seasonally dry regions of Africa from Senegal east to Eritrea, to southern regions of Tanzania to Mozambique and south to the north-eastern parts of South Africa. The tree is an important timber species in its native areas; it is used in the manufacture of musical instruments, sculptures vinyago in Swahili language and fine furnitures. Populations and genomic resources for genetic biodiversity maintenance in parts of its native range are threatened by overharvesting due to poor or absent conservation planning and by the species' low germination rates.

Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elongated leaves, known as "laurophyll" or "lauroid". Plants from the laurel family (Lauraceae) may or may not be present, depending on the location.
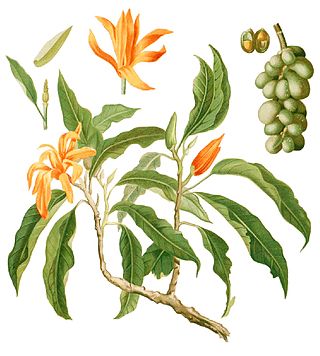
Magnolia champaca, known in English as champak, is a large evergreen tree in the family Magnoliaceae. It was previously classified as Michelia champaca. It is known for its fragrant flowers, and its timber used in woodworking.
Dalbergia baronii is a species of flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is endemic to Madagascar. It is named after the English missionary and botanist Rev. Richard Baron.

Dalbergia cochinchinensis, the Thailand rosewood, Siamese rosewood, or tracwood, is a species of legume in the family Fabaceae.

Dalbergia oliveri is a species of legume in the family Fabaceae which grows in tree form to 15 – 30 meters in height. The fruit is a green pod containing one to two seeds which turn brown to black when ripe. It is threatened by habitat loss and over-harvesting for its valuable red "rosewood" timber.
Kon Ka Kinh National Park is a national park of Vietnam, established by the decision (167/2002/QĐ-TTg) on November 25, 2002 of the then Prime Minister, Phan Văn Khải.

Camphora parthenoxylon is an evergreen tree in the genus Camphora, 10–20 m (33–66 ft) tall. It is native to South and East Asia.

The environment of Argentina is highly biodiverse.

The flora of China consists of a diverse range of plant species including over 39,000 vascular plants, 27,000 species of fungi and 3000 species of bryophytes. More than 30,000 plant species are native to China, representing nearly one-eighth of the world's total plant species, including thousands found nowhere else on Earth. China's land, extending over 9.6 million km, contains a variety of ecosystems and climates for plants to grow in. Some of the main climates include shores, tropical and subtropical forests, deserts, elevated plateaus and mountains. The events of the continental drift and early Paleozoic Caledonian movement also play a part in creating climatic and geographical diversity resulting in high levels of endemic vascular flora. These landscapes provide different ecosystems and climates for plants to grow in, creating a wide variety of different flora spanning over not just China, but different parts of the world.

Dalbergia lanceolaria is a species of tree in the subfamily Faboideae and tribe Dalbergieae. It is a medium-sized tree growing to 20m tall and is native to: India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Burma and Indo-China.
Ormosia henryi is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to southern China, Vietnam, and Thailand.

Magnolia lotungensis, the eastern joy lotus tree, is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae, native to southern China, including Hainan. An androdioecious, hexaploid evergreen tree reaching 30 m (98 ft), it is typically found in forests from 700 to 1,400 m above sea level. It is used as a street tree in a number of southern Chinese cities. Due to its strength, easy maintenance, narrow growth habit with a rounded crown, and cold hardiness, it is showing promise as an ornamental tree in North America and Europe.

Dalbergia miscolobium is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to seasonally dry tropical areas of Bolivia and Brazil. A slow-growing evergreen tree reaching 16 m (52 ft), it is considered "very ornamental" due to its light, bluish-green leaves. It is used as a street tree in a number of Brazilian cities.

Castanopsis eyrei is a species of flowering plant in the family Fagaceae, native to southern China, and Taiwan. An evergreen tree typically 8 to 20 m tall, it is usually found in late successional forests from 300 to 1,700 m above sea level, where it is often the dominant species. It is used as a street tree in a number of southern Chinese cities.

Magnolia insignis, the red lotus tree, is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae, native to Nepal, Assam, Tibet, southern China, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam. It is used as a street tree in a number of southern Chinese cities.

Schima superba is a species of flowering plant in the tea family Theaceae, native to subtropical areas of Vietnam, southern China, Hainan, Taiwan, and the Ryukyu Islands. With Pinus massoniana it often dominates forests from 100 to 800 m in elevation. It is used as a street tree in a number of southern Chinese cities.
Cinnamomum bodinieri is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae, native to southern China. A tree reaching 16 m (52 ft), it is typically found in situations with more light, such as alongside roads and streams or in open forests and thickets. Its essential oil is high in citral. It is used as a street tree in a number of southern Chinese cities.

















