
Madhya Pradesh is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and its largest city is Indore. Other major cities of the state are Jabalpur and Gwalior. Madhya Pradesh is the second largest Indian state by area and the fifth largest state by population with over 72 million residents. It borders the states of Uttar Pradesh to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the east, Maharashtra to the south, Gujarat to the west, and Rajasthan to the northwest.

Nagpur is the third-largest city of the Indian state of Maharashtra after Mumbai and Pune. It is called the heart of India because of its central geographical location. It is the largest and most populated city in central India. Also known as the "Orange City", Nagpur is the 13th largest city in India by population. According to an Oxford's Economics report, Nagpur is projected to be the fifth fastest growing city in the world from 2019 to 2035 with an average growth of 8.41%. It has been proposed as one of the Smart Cities in Maharashtra and is one of the top ten cities in India in Smart City Project execution.

Vidarbha is a geographical region in Maharashtra, which is next to the west Indian state of Gujarat. It forms the eastern part of the state, next to the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, it comprises of the Amravati and Nagpur divisions. As per the 2011 Census, the region had a population of 23,003,179. The region occupies 31.6% of the total area and is home to 21.3% of the total population of Maharashtra. Situated in central India, it borders the state of Madhya Pradesh to the north, Chhattisgarh to the east, Telangana to the south and Marathwada and Uttar Maharashtra regions of Maharashtra to the west.

The Satpura Range is a range of hills in central India. The range rises in eastern Gujarat running east through the border of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh and ends in Chhattisgarh. The range parallels the Vindhya Range to the north, and these two east–west ranges divide Indian Subcontinent into the Indo-Gangetic plain of northern India and the Deccan Plateau of the south. The Narmada River originates from north-eastern end of Satpura in Amarkantak, and runs in the depression between the Satpura and Vindhya ranges, draining the northern slope of the Satpura range, running west towards the Arabian Sea. The Tapti River originates in the eastern-central part of Satpura, crossing the range in the center and running west at the range's southern slopes before meeting the Arabian Sea at Surat, draining the central and southern slopes of the range. Multai, the place of Tapti river origin is located about 465 kilometer far, south-westerly to Amarkantak, separated across by the hill range. The Godavari River and its tributaries drain the Deccan plateau, which lies south of the range, and the Mahanadi River drains the easternmost portion of the range. The Godavari and Mahanadi rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal. At its eastern end, the Satpura range meets the hills of the Chotanagpur Plateau. The Satpura Range is a horst mountain and is flanked by Narmada Graben in the north and much smaller but parallel Tapi Graben in the south.

Bhandara District is an administrative district in the state of Maharashtra in India. The name Bhandara is a corruption of Bhanara. Reference to Bhanara is found in an inscription of 1100 A.D. traced at Ratanpur. The district headquarters are located at Bhandara. The district occupies an area of 3717 km2 and has a population of 1,200,334, of which 19.48% are urban as of 2011. The growth rate of Bhandara is 5.56% Bhandara has a mixed economy with agriculture, industries and forest resources. Bhandara is known for its large production of rice. Tumsar, a tahsil town, is a noted rice market. Bhandara town is also known as "Brass City" owing to the presence of a large brass products industry. Bhandara has several tourist destinations, like Ambagad Fort, Brahmi, Chinchgad, and Dighori.

Chhindwara is a major city in India and a Municipal Corporation in the Chhindwara district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. The city is the administrative headquarters of Chhindwara District. Chhindwara is reachable by rail or road from adjacent cities Betul, Jabalpur and Nagpur. The nearest airports are in Nagpur, Mumbai, New Delhi and Srinagar (130 km); however there is a small airport located in the district
- which is not serviceable for passenger planes.

Chhindwara district is one of the major districts of Madhya Pradesh state of India, and Chhindwara town is the district headquarters. Chhindwara was the largest district in Madhya Pradesh with an area of 10,293 square km before the bifurcation of Pandhurna district. The district is part of Jabalpur division.

Seoni District is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. The town of Seoni is the district's headquarters.

Seoni is a city and a municipality in Seoni district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. This tribal household dominated district was formed in the year 1956.
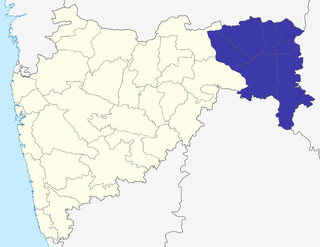
The Nagpur Division is one of six administrative divisions of the state of Maharashtra in India. Nagpur is the easternmost division in the state, with an administrative headquarters in the city of Nagpur. It covers 51,336 km² (19,821 mi²). The Amravati and Nagpur divisions make up the Vidarbha region.

Nagpur district is a district in the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra state in central India. The city of Nagpur is the district administrative centre. The district is part of Nagpur Division.
Bhainsdehi is a city and a Nagar Parishad in Betul district in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. According to mythological beliefs, Bhainsdehi was known as Mahishmati, the capital of Raghuvanshi King Gaya. Which later changed from Mahishmati to Mahishvati and then to Mahishadehi and then to Bhainsdehi. Kukru is the second highest point of Mahadeo hills. Bhainsdehi is the originating place of the river Purna. It is predominantly a tribal tehsil. Bhainsdehi is surrounded by the mountain ranges of Satpura. Prachin Shiv mandir one of the most beautiful place in Bhainsdehi city

Sausar (Saunsar) is a Municipal Council in the central India in the state of Madhya Pradesh. Sausar lies in Vidharbha region, Nagpur is the center for all the economic activities in this region which is just 72 km from Sausar. More than 90 per cent of farmers produce oranges. Cotton is grown in large quantities in the local area.
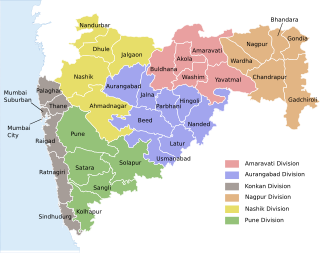
The word Maharashtra, the land of the mainly Marathi-speaking people, appears to be derived from Maharashtri, an old form of Prakrit. Some believe that the word indicates that it was the land of the Mahars and the Rattas, while others consider it to be a corruption of the term 'Maha Kantara', a synonym for 'Dandakaranya'. Maharashtra is the third largest state in India after Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh. It covers an area of 307,713 km2 and is bordered by the states of Madhya Pradesh to the north, Chhattisgarh to the east, Telangana to the southeast, Karnataka to the south and Goa to the southwest. The state of Gujarat lies to the northwest, with the Union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli sandwiched between the borders. Maharashtra has coastline of 720 km.The Arabian Sea makes up Maharashtra's west coast. Maharashtra consists of two major relief divisions. The plateau is a part of the Deccan tableland and the Konkan coastal strip abutting on the Arabian Sea.

Maharashtra attracts tourists from other Indian states and foreign countries. It was the second most visited Indian state by foreigners and fifth most visited state by domestic tourists in the country in 2021. Aurangabad is the tourism capital of Maharashtra.

Gowari is an Indian caste of cattleman or herdsmen, predominantly residing in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh.
Waman Thakre is an Indian photographer and a former deputy director at the Directorate of Panchayat and Social Service of the Government of Madhya Pradesh. He is a Fellow of the Royal Photographic Society and the Photographic Society of America and is a recipient of the Shikhar Award of the MP State government. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2007, for his contributions to Arts.

Kunji Lal Dubey was an Indian independence activist, lawyer, educationist and politician from Madhya Pradesh. He was the first vice chancellor of Rani Durgavati University and the chancellor of Nagpur University. He served as the first speaker of Madhya Pradesh Legislative Assembly in 1956, as the Finance Minister of the State in 1967 and was the president of the Inter University Board of India, Burma and Ceylon. The Government of India awarded him the third highest civilian honour, the Padma Bhushan, in 1964, for his contributions to the society. India Post issued a commemorative stamp on Dubey in 1996.

The Indian state governments have responded to the COVID-19 pandemic in India with various declarations of emergency, closure of institutions and public meeting places, and other restrictions intended to contain the spread of the virus.



















