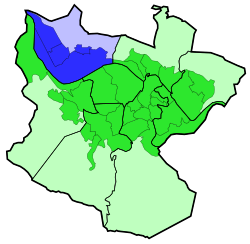
Bilbao is a city in northern Spain, the largest city in the province of Biscay and in the Basque Country as a whole. It is also the largest city proper in northern Spain. Bilbao is the tenth largest city in Spain, with a population of more than 347,000 as of 2023. The Bilbao metropolitan area has 1,037,847 inhabitants, making it the most populous metropolitan area in northern Spain; with a population of 875,552, the comarca of Greater Bilbao is the fifth-largest urban area in Spain. Bilbao is also the main urban area in what is defined as the Greater Basque region.

The Bilbao metro is a rapid transit system serving the city of Bilbao and the region of Greater Bilbao. Lines 1 and 2 have a "Y" shape, as they transit both banks of the river Ibaizabal and then combine to form one line that ends in the south of Bilbao. Line 3 has a "V" shape connecting the municipality of Etxebarri with the Bilbao neighbourhood of Matiko; the apex of the "V" is Zazpikaleak/Casco Viejo station, where all three current lines meet. The metro is connected with the Bilbao tram, Bilboko Aldiriak, Euskotren Trena, Feve, Renfe long-distance trains, and Bilbao's bus station. All three lines use metre gauge.

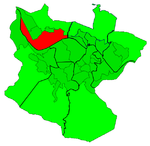
Abando, formerly known as San Vicente de Abando, is one of the eight districts of Bilbao, Basque Country (Spain). It covers most of the city's centre, located on the left bank of the estuary of Bilbao. It is the only district of Bilbao with all of its land completely urbanised. Abando was originally an elizate and also a municipality until 1876, when part of it was annexed to Bilbao, the rest of the elizate's municipal land was integrated into Bilbao in 1890. In 2016 the population was 50,903. Abando is the wealthiest district in Bilbao, with personal and family incomes being well above the citywide average.

Bilbobus is the name for metropolitan bus services in Bilbao.

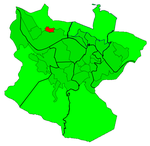
Zorrotzaurre is an artificial island located within the Deusto district of Bilbao, Spain.

Indautxu is a quarter of central Bilbao, Basque Country (Spain), located in the district of Abando. It is a relatively affluent neighbourhood and is most famous for the large number of private hospitals and clinics, the large Society of Jesus school and the Doña Casilda Iturrizar park, all located in the area.

The Abando Indalecio Prieto railway station, usually known simply as Bilbao-Abando and previously known as Estación del Norte is a terminal railway station in Bilbao, Basque Country (Spain). The name comes from Abando, the district in which the station is located, and Indalecio Prieto, who was Minister of Public Works during the Second Spanish Republic. The station serves as the terminus station for several long and medium distance services operated by Renfe as well as commuter rail services within the Bilbao metropolitan area operated by Cercanías. The station has direct access to Metro Bilbao and to the tram, as well as many local and regional bus lines. The railway station Bilbao-Concordia, operated by Renfe Feve is located in close proximity. After the construction of the high-speed line Basque Y is finished, Bilbao-Abando will serve as the western terminus, which will involve the creation of a completely new station replacing the current one.

Bolueta is a station on lines 1 and 2 of the Bilbao metro. The station is located in the neighborhood of the same name, in the district of Begoña. It opened on 5 July 1997.

Zazpikaleak/Casco Viejo – Zazpikaleak and Casco Viejo – is a railway station in Bilbao, Basque Country, Spain. It is located in the historical neighborhood of Casco Viejo, in the district of Ibaiondo. It links the Bilbao metro rapid transit services with the Euskotren Trena commuter rail network. It is the main railway hub for trips between the metropolitan underground network and the railway services to Eibar, Gernika, Bermeo and San Sebastián as well as the Txorierri valley. The original metro station opened on 11 November 1995, and on 8 April 2017 in its current form.

Deustu is a station on lines 1 and 2 of the Bilbao metro. The station is located in the neighbourhood and district of the same name. It is located close to the Bidarte mall and Bilbao's Escuela Oficial de Idiomas. It opened on 11 November 1995.

Sarriko is a station on lines 1 and 2 of the Bilbao metro. The station is located in the neighbourhood of Ibarrekolanda, part of the Deusto district. It is named after the Sarriko park located nearby. The station is in close proximity to the Faculty of Business and Economic Sciences of the University of the Basque Country as well as the conservatory of music. It was opened on 11 November 1995.

San Ignazio is a station on lines 1 and 2 of the Bilbao metro. It is located in the San Ignazio-Elorrieta neighbourhood, part of the Deusto district. The station is in close proximity to the San Ignazio Sports Center and the Elorrieta football field. It was opened on 11 November 1995.

The Bilbao tram is a tram system in Bilbao, Basque Country, Spain. Operated by Euskotren under the brand Euskotren Tranbia, it comprises a single 7.8 km (4.8 mi) line, inaugurated on 18 December 2002 and last extended on 25 March 2022.

The Frank Gehry Bridge is a bridge in Bilbao that connects Deusto and Zorrotzaurre. Its name is a tribute to Canadian-born American architect Frank Gehry, author of the Guggenheim Museum Bilbao.

Matiko is the northern terminus of line 3 of the Bilbao metro. The station is also served by Euskotren Trena commuter and regional rail services. The station is located in the neighbourhood of Matiko-Ciudad Jardín, part of the Uribarri district of Bilbao. In its current form, the station opened on 8 April 2017.

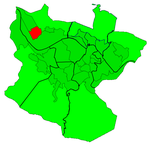
Abandoibarra is an area of the city of Bilbao, Spain, located next to the estuary in the neighborhood of Abando. After the process of deindustrialization experienced by the town since the mid-1990s, Abandoibarra became the central axis of urban regeneration in the city, continuing today in Zorrotzaurre.

The City Hall Bridge, formerly known as the Begoña Bridge, is a bascule bridge on the estuary of Bilbao, connecting the districts of Gazteleku on the right and Abando on the left.

The Deusto Bridge is a bascule bridge over the estuary of Bilbao. This bridge connects the districts of Abando and Deusto.

The Txorierri line, also known as the Bilbao–Lezama railway is a narrow-gauge railway in Biscay, Basque Country, Spain. Owned by Euskal Trenbide Sarea, it runs from Lezama to Matiko, from where it continues as line 3 of the Bilbao metro.