In computing, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabling operating systems and other computer programs to access hardware functions without needing to know precise details about the hardware being used.

Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (ALSA) is a software framework and part of the Linux kernel that provides an application programming interface (API) for sound card device drivers.
OpenSSI is an open-source single-system image clustering system. It allows a collection of computers to be treated as one large system, allowing applications running on any one machine access to the resources of all the machines in the cluster.
udev is a device manager for the Linux kernel. As the successor of devfsd and hotplug, udev primarily manages device nodes in the /dev directory. At the same time, udev also handles all user space events raised when hardware devices are added into the system or removed from it, including firmware loading as required by certain devices.
The Direct Rendering Manager (DRM) is a subsystem of the Linux kernel responsible for interfacing with GPUs of modern video cards. DRM exposes an API that user-space programs can use to send commands and data to the GPU and perform operations such as configuring the mode setting of the display. DRM was first developed as the kernel-space component of the X Server Direct Rendering Infrastructure, but since then it has been used by other graphic stack alternatives such as Wayland.
sysfs is a pseudo file system provided by the Linux kernel that exports information about various kernel subsystems, hardware devices, and associated device drivers from the kernel's device model to user space through virtual files. In addition to providing information about various devices and kernel subsystems, exported virtual files are also used for their configuration.
In Linux, Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is a device mapper framework that provides logical volume management for the Linux kernel. Most modern Linux distributions are LVM-aware to the point of being able to have their root file systems on a logical volume.
The device mapper is a framework provided by the Linux kernel for mapping physical block devices onto higher-level virtual block devices. It forms the foundation of the logical volume manager (LVM), software RAIDs and dm-crypt disk encryption, and offers additional features such as file system snapshots.
In computing, initrd is a scheme for loading a temporary root file system into memory, which may be used as part of the Linux startup process. initrd and initramfs refer to two different methods of achieving this. Both are commonly used to make preparations before the real root file system can be mounted.
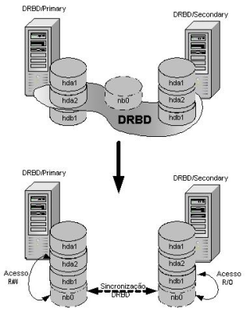
DRBD is a distributed replicated storage system for the Linux platform. It is implemented as a kernel driver, several userspace management applications, and some shell scripts. DRBD is traditionally used in high availability (HA) computer clusters, but beginning with DRBD version 9, it can also be used to create larger software defined storage pools with a focus on cloud integration.

Greg Kroah-Hartman (GKH) is a major Linux kernel developer. As of April 2013 he is the Linux kernel maintainer for the -stable branch, the staging subsystem, USB, driver core, debugfs, kref, kobject, and the sysfs kernel subsystems, Userspace I/O, and TTY layer. He also created linux-hotplug, the udev project, and the Linux Driver Project. He worked for Novell in the SUSE Labs division and, as of 1 February 2012, works at the Linux Foundation.
HAL is a software subsystem for UNIX-like operating systems providing hardware abstraction.
Btrfs is a computer storage format that combines a file system based on the copy-on-write (COW) principle with a logical volume manager, developed together. It was initially designed at Oracle Corporation in 2007 for use in Linux, and since November 2013, the file system's on-disk format has been declared stable in the Linux kernel. According to Oracle, Btrfs "is not a true acronym".
Ceph is an open-source software storage platform, implements object storage on a single distributed computer cluster, and provides 3-in-1 interfaces for object-, block- and file-level storage. Ceph aims primarily for completely distributed operation without a single point of failure, scalable to the exabyte level, and freely available.
GVfs is GNOME's userspace virtual filesystem designed to work with the I/O abstraction of GIO, a library available in GLib since version 2.15.1. It installs several modules that are automatically used by applications using the APIs of libgio. There is also FUSE support that allows applications not using GIO to access the GVfs filesystems.
In Unix-like operating systems, a device file or special file is an interface to a device driver that appears in a file system as if it were an ordinary file. There are also special files in DOS, OS/2, and Windows. These special files allow an application program to interact with a device by using its device driver via standard input/output system calls. Using standard system calls simplifies many programming tasks, and leads to consistent user-space I/O mechanisms regardless of device features and functions.

systemd is a software suite that provides an array of system components for Linux operating systems.
Device Mapper Multipath Input Output often shortened to DM-Multipathing and abbreviated as DM-MPIO provides input-output (I/O) fail-over and load-balancing by using multipath I/O within Linux for block devices. By utilizing device-mapper, the multipathd daemon provides the host-side logic to use multiple paths of a redundant network to provide continuous availability and higher-bandwidth connectivity between the host server and the block-level device. DM-MPIO handles the rerouting of block I/O to an alternate path in the event of a path failure. DM-MPIO can also balance the I/O load across all of the available paths that are typically utilized in Fibre Channel (FC) and iSCSI SAN environments. DM-MPIO is based on the device mapper, which provides the basic framework that maps one block device onto another.
Dracut is a set of tools that provide enhanced functionality for automating the Linux boot process. The tool named dracut is used to create a Linux boot image (initramfs) by copying tools and files from an installed system and combining it with the Dracut framework, which is usually found in /usr/lib/dracut/modules.d.
In computing, a device tree is a data structure describing the hardware components of a particular computer so that the operating system's kernel can use and manage those components, including the CPU or CPUs, the memory, the buses and the peripherals.



