
Centipedes are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda of the subphylum Myriapoda, an arthropod group which includes millipedes and other multi-legged animals. Centipedes are elongated segmented (metameric) creatures with one pair of legs per body segment. All centipedes are venomous and can inflict painful stings, injecting their venom through pincer-like appendages known as forcipules or toxicognaths, which are actually modified legs instead of fangs. Despite the name, no species of centipede has exactly 100 legs; the number of pairs of legs is an odd number that ranges from 15 pairs to 191 pairs.

Myriapods are the members of subphylum Myriapoda, containing arthropods such as millipedes and centipedes. The group contains about 13,000 species, all of them terrestrial.

Pterygotus is a genus of giant predatory eurypterid, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Pterygotus have been discovered in deposits ranging in age from Middle Silurian to Late Devonian, and have been referred to several different species. Fossils have been recovered from four continents; Australia, Europe, North America and South America, which indicates that Pterygotus might have had a nearly cosmopolitan (worldwide) distribution. The type species, P. anglicus, was described by Swiss naturalist Louis Agassiz in 1839, who gave it the name Pterygotus, meaning "winged one". Agassiz mistakenly believed the remains were of a giant fish; he would only realize the mistake five years later in 1844.

Arthropleuridea is an extinct subclass of myriapod arthropods that flourished during the Carboniferous period, having first arisen during the Silurian, and perishing in the Early Permian. Members are characterized by possessing diplosegement paranotal tergal lobes separated from the body axis by a suture, and by sclerotized plates buttressing the leg insertions. Despite their unique features, recent phylogenetic research suggests Arthropleuridea be included among millipedes in the class Diplopoda. The subclass contains three or two recognized orders, each with a single genus.

Arthropleura is a genus of massive myriapod that lived in what is now Europe and North America around 345 to 290 million years ago, from the Viséan stage of the lower Carboniferous Period to the Sakmarian stage of the lower Permian Period. It is related to millipedes, and was capable of reaching at least 2 metres in length, possibly up to over 2.5 metres, making it the largest known land arthropod of all time. Arthropleura is known from body fossils as well as trace fossils, particularly giant trackways up to 50 centimetres (20 in) wide, and potentially also large burrows. It lived in open, sparsely wooded environments near water, and was possibly amphibious.
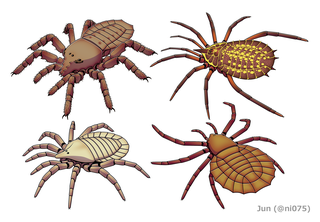
The order Trigonotarbida is a group of extinct arachnids whose fossil record extends from the late Silurian to the early Permian. These animals are known from several localities in Europe and North America, as well as a single record from Argentina. Trigonotarbids can be envisaged as spider-like arachnids, but without silk-producing spinnerets. They ranged in size from a few millimetres to a few centimetres in body length and had segmented abdomens (opisthosoma), with the dorsal exoskeleton (tergites) across the backs of the animals' abdomens, which were characteristically divided into three or five separate plates. Probably living as predators on other arthropods, some later trigonotarbid species were quite heavily armoured and protected themselves with spines and tubercles. About seventy species are currently known, with most fossils originating from the Carboniferous coal measures.
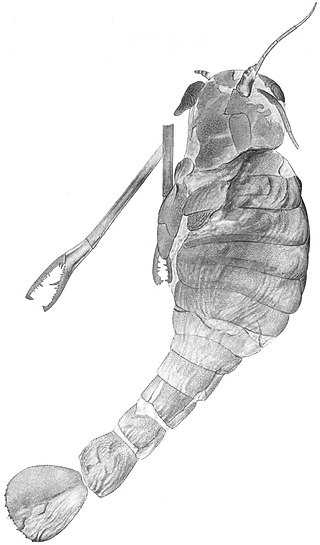
Acutiramus is a genus of giant predatory eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Acutiramus have been discovered in deposits of Late Silurian to Early Devonian age. Eight species have been described, five from North America and two from the Czech Republic. The generic name derives from Latin acuto and Latin ramus ("branch"), referring to the acute angle of the final tooth of the claws relative to the rest of the claw.

Jaekelopterus is a genus of predatory eurypterid, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Jaekelopterus have been discovered in deposits of Early Devonian age, from the Pragian and Emsian stages. There are two known species: the type species J. rhenaniae from brackish to fresh water strata in the Rhineland, and J. howelli from estuarine strata in Wyoming. The generic name combines the name of German paleontologist Otto Jaekel, who described the type species, and the Greek word πτερόν (pteron) meaning "wing".

Erettopterus is a genus of large predatory eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Erettopterus have been discovered in deposits ranging from Early Silurian to the Early Devonian, and have been referred to several different species. Fossils have been recovered from two continents; Europe and North America. The genus name is composed by the Ancient Greek words ἐρέττω (eréttō), which means "rower", and πτερόν (pterón), which means "wing", and therefore, "rower wing".

Adelophthalmus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Adelophthalmus have been discovered in deposits ranging in age from the Early Devonian to the Early Permian, which makes it the longest lived of all known eurypterid genera, with a total temporal range of over 120 million years. Adelopththalmus was the final genus of the Eurypterina suborder of eurypterids and consisted the only known genus of swimming eurypterids from the Middle Devonian until its extinction during the Permian, after which the few surviving eurypterids were all walking forms of the suborder Stylonurina.
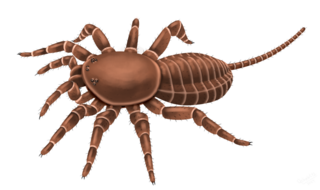
Attercopus is an extinct genus of arachnids, containing one species Attercopus fimbriunguis, known from flattened cuticle fossils from the Panther Mountain Formation in Upstate New York. It is placed in the extinct order Uraraneida, spider-like animals able to produce silk, but which lacked true spinnerets and retained a segmented abdomen bearing a flagellum-like tail resembling that of a whip scorpion. They are thought to be close to the origins of spiders.

Angustidontus is a genus of predatory pelagic crustaceans from the Late Devonian and Early Carboniferous periods, classified as part of the subclass Eumalacostraca. Fossils of the genus have been recovered in relative abundance from Canada, Germany, the Czech Republic, Poland, Belarus, Ukraine and large parts of the United States, including Oklahoma, Ohio, Indiana, Kentucky, Montana, Utah, Nevada.
Antlerpeton is an extinct genus of early tetrapod from the Early Carboniferous of Nevada. It is known from a single poorly preserved skeleton from the Diamond Peak Formation of Eureka County. A mix of features in its compound vertebrae suggest that Antlerpeton is a primitive stem tetrapod that has affinities with later, more advanced forms. Its robust pelvis and hind limbs allowed for effective locomotion on land, but the animal was likely still tied to a semiaquatic lifestyle near the coast.

Callipodida is an order of millipedes containing around 130 species, many characterized by crests or ridges.
The Panther Mountain Formation is a geologic formation in New York. It preserves fossils dating back to the Devonian period. It is located in the counties of Albany, Madison, Oneida, Otsego, and Schoharie. It is well known for its fossil arthropods preserved as flattened cuticles, including Attercopus and Dracochela.

Uraraneida is an extinct order of Paleozoic arachnids related to modern spiders. Two genera of fossils have been definitively placed in this order: Attercopus from the Devonian of United States and Permarachne from the Permian of Russia. Like spiders, they are known to have produced silk, but lack the characteristic spinnerets of modern spiders, and retain elongate telsons.

Necrogammarus salweyi is the binomial name applied to an arthropod fossil discovered in Herefordshire, England. The fossil represents a fragmentary section of the underside and an appendage of a pterygotid eurypterid, a group of large and predatory aquatic arthropods that lived from the late Silurian to the late Devonian. The Necrogammarus fossil is Late Silurian in age and its generic name means "dead lobster", deriving from Ancient Greek νεκρός and Latin gammarus ("lobster").

Borchgrevinkium is an extinct genus of chelicerate arthropod. A fossil of the single and type species, B. taimyrensis, has been discovered in deposits of the Early Devonian period in the Krasnoyarsk Krai, Siberia, Russia. The name of the genus honors Carsten Borchgrevink, an Anglo-Norwegian explorer who participated in many expeditions to Antarctica. Borchgrevinkium represents a poorly known genus whose affinities are uncertain.

Flagellopantopus is an extinct genus of pycnogonid arthropod known from the lower Devonian aged Hunsrück Slate. A single species is currently known, Flagellopantopus blocki, which was described from the Emsian aged Kaub Formation in Germany.

Crussolum is a genus of Silurian and Devonian centipedes from the US and Britain. It is the oldest known centipede.



















