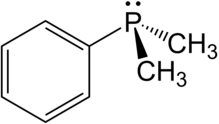
In chemistry, the phosphonium cation describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula PR+
4. These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions.
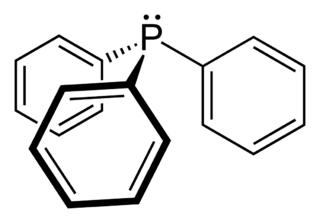
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.
Diphosphene is a type of organophosphorus compound that has a phosphorus–phosphorus double bond, denoted by R-P=P-R'. These compounds are not common but are of theoretical interest. Normally, compounds with the empirical formula RP exist as rings. However, like other multiple bonds between heavy main-group elements, P=P double bonds can be stabilized by a large steric hindrance from the substitutions. The first isolated diphosphene bis(2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenyl)diphosphene was exemplified by Masaaki Yoshifuji and his coworkers in 1981, in which diphosphene is stabilized by two bulky phenyl group.
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.

1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (Ph2PCH2)2 (Ph = phenyl). It is a commonly used bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
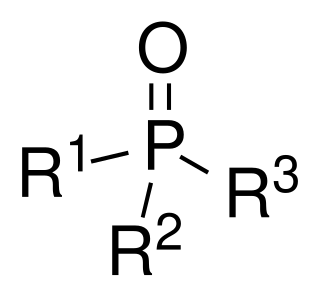
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3).

Trimethylphosphine is a neutral organophosphorus compound with the formula P(CH3)3, commonly abbreviated as PMe3. This colorless liquid has a strongly unpleasant odor, characteristic of alkylphosphines. The compound is a common ligand in coordination chemistry.
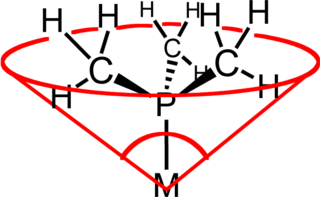
In coordination chemistry, the ligand cone angle is a measure of the steric bulk of a ligand in a transition metal coordination complex. It is defined as the solid angle formed with the metal at the vertex and the outermost edge of the van der Waals spheres of the ligand atoms at the perimeter of the cone. Tertiary phosphine ligands are commonly classified using this parameter, but the method can be applied to any ligand. The term cone angle was first introduced by Chadwick A. Tolman, a research chemist at DuPont. Tolman originally developed the method for phosphine ligands in nickel complexes, determining them from measurements of accurate physical models.
Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PRnH3−n, where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of n: primary phosphines (n = 1), secondary phosphines (n = 2), tertiary phosphines (n = 3). All adopt pyramidal structures. Organophosphines are generally colorless, lipophilic liquids or solids. The parent of the organophosphines is phosphine (PH3).
Martin Arthur Bennett FRS is an Australian inorganic chemist. He gained recognition for studies on the co-ordination chemistry of tertiary phosphines, olefins, and acetylenes, and the relationship of their behaviour to homogeneous catalysis.

Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts.

Tributylphosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C
4H
9)
3. Abbreviated or PBu
3, it is a tertiary phosphine. It is an oily liquid at room temperature, with a nauseating odor. It reacts slowly with atmospheric oxygen, and rapidly with other oxidizing agents, to give the corresponding phosphine oxide. It is usually handled using air-free techniques.

Diphosphane, or diphosphine, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula P2H4. This colourless liquid is one of several binary phosphorus hydrides. It is the impurity that typically causes samples of phosphine to ignite in air.

Diphenylphosphine, also known as diphenylphosphane, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PH. This foul-smelling, colorless liquid is easily oxidized in air. It is a precursor to organophosphorus ligands for use as catalysts.

1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane (dppm), is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH2(PPh2)2. Dppm, a white, crystalline powder, is used in inorganic and organometallic chemistry as a ligand. It is more specifically a chelating ligand because it is a ligand that can bond to metals with two phosphorus donor atoms. The natural bite angle is 73°.

Dichlorotris(triphenylphosphine)ruthenium(II) is a coordination complex of ruthenium. It is a chocolate brown solid that is soluble in organic solvents such as benzene. The compound is used as a precursor to other complexes including those used in homogeneous catalysis.

A metal-phosphine complex is a In coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0).

Carbonyl hydrido tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) [Carbonyl(hydrido)tris(triphenylphosphane)rhodium(I)] is an organorhodium compound with the formula [RhH(CO)(PPh3)3] (Ph = C6H5). It is a yellow, benzene-soluble solid, which is used industrially for hydroformylation.

Bis(diphenylphosphinoethyl)phenylphosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula [Ph2PCH2CH2]2PPh (Ph = C6H5). It is an air-sensitive white solid that function as tridentate ligands in coordination and organometallic chemistry.
A transition metal phosphido complex is a coordination complex containing a phosphido ligand (R2P, where R = H, organic substituent). With two lone pairs on phosphorus, the phosphido anion (R2P−) is comparable to an amido anion (R2N−), except that the M-P distances are longer and the phosphorus atom is more sterically accessible. For these reasons, phosphido is often a bridging ligand. The -PH2 ion or ligand is also called phosphanide or phosphido ligand.