This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2009) |
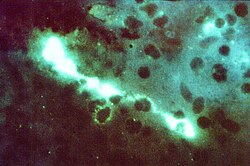
A direct fluorescent antibody (DFA or dFA), also known as "direct immunofluorescence", [1] is an antibody that has been tagged in a direct fluorescent antibody test. Its name derives from the fact that it directly tests the presence of an antigen with the tagged antibody, unlike western blotting, which uses an indirect method of detection, where the primary antibody binds the target antigen, with a secondary antibody directed against the primary, and a tag attached to the secondary antibody.
Contents
Commercial DFA testing kits are available, which contain fluorescently labelled antibodies, designed to specifically target unique antigens present in the bacteria or virus, but not present in mammals (Eukaryotes). This technique can be used to quickly determine if a subject has a specific viral or bacterial infection.
In the case of respiratory viruses, many of which have similar broad symptoms, detection can be carried out using nasal wash samples from the subject with the suspected infection. Although shedding cells in the respiratory tract can be obtained, it is often in low numbers, and so an alternative method can be adopted where compatible cell culture can be exposed to infected nasal wash samples, so if the virus is present it can be grown up to a larger quantity, which can then give a clearer positive or negative reading.
As with all types of fluorescence microscopy, the correct absorption wavelength needs to be determined in order to excite the fluorophore tag attached to the antibody, and detect the fluorescence given off, which indicates which cells are positive for the presence of the virus or bacteria being detected.
Direct immunofluorescence can be used to detect deposits of immunoglobulins and complement proteins in biopsies of skin, kidney and other organs. Their presence is indicative of an autoimmune disease. When skin not exposed to the sun is tested, a positive direct IF (the so-called Lupus band test) is an evidence of systemic lupus erythematosus. [2] Direct fluorescent antibody can also be used to detect parasitic infections, as was pioneered by Sadun, et al. (1960).