
Phytosaurs are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the family Phytosauridae and the order Phytosauria. Phytosauria and Phytosauridae are often considered to be equivalent groupings containing the same species, but some studies have identified non-phytosaurid phytosaurians. Phytosaurs were long-snouted and heavily armoured, bearing a remarkable resemblance to modern crocodilians in size, appearance, and lifestyle, as an example of convergence or parallel evolution. The name "phytosaur" means "plant reptile", as the first fossils of phytosaurs were mistakenly thought to belong to plant eaters. The name is misleading because the sharp teeth in phytosaur jaws clearly show that they were predators.

Thecodontosaurus is a genus of herbivorous basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the late Triassic period.

Procompsognathus is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 210 million years ago during the later part of the Triassic Period, in what is now Germany. Procompsognathus was a small-sized, lightly built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, that could grow up to 1 m (3.3 ft) long.

Liliensternus is an extinct genus of basal neotheropod dinosaur that lived approximately 210 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period in what is now Germany. Liliensternus was a moderate-sized, bipedal, ground-dwelling carnivore, that could grow up to 5.15 m (16.9 ft) long. It is the best represented Triassic theropod from Europe and one of the largest known.
Halticosaurus (pron.:"HAL-tick-oh-SORE-us") is a dubious genus of theropod dinosaur from the late Triassic period. It is known from a single fragmentary fossil specimen of the species H. longotarsus, found in the Middle Stubensandstein formation of what is present-day Germany and possibly also the Moon-Airel Formation of France. The only known specimen was poorly preserved and may have been put together from bones of unrelated animals. Further research would be required to determine which of the bones belonged together, and what kind of theropod Halticosaurus was. However, most of the bones have been lost. For these reasons, Halticosaurus is considered to be a nomen dubium.

Teratosaurus is a genus of rauisuchians known from the Triassic Stubensandstein of Germany. It is estimated to be 6.2 meters (20.3 ft) long.

Efraasia is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur. It was a herbivore which lived during the middle Norian stage of the Late Triassic, around 210 million years ago, in what is now Germany. It was named in 1973 after Eberhard Fraas, who during the early twentieth century collected what were the original type specimens.
Elachistosuchus is an extinct genus of neodiapsid reptile, most likely basal archosauromorph, known from the Late Triassic Arnstadt Formation of Saxony-Anhalt, central Germany. It contains a single species, Elachistosuchus huenei, known from a single individual. E. huenei, originally considered a pseudosuchian archosaur and then a rhynchocephalian lepidosaur, was largely ignored in the scientific literature, as its small size and fragility did not permit further mechanical preparation and examination. More recently however a non-invasive μCT scanning was performed to resolve its placement within Reptilia, and found it to represent a more basal reptile, potentially closely related to several early archosauromorph clades.
Spinosuchus is an extinct genus of trilophosaurid allokotosaur from the Late Triassic of Texas, southern United States. It has been assigned to a variety of groups over its history, from coelophysid dinosaur to pseudosuchian to uncertain theropod dinosaur and to Proterosuchidae. This uncertainty is not unusual, given that it was only known from a poorly preserved, wall-mounted, partial vertebral column of an animal that lived in a time of diverse, poorly known reptile groups. However, newly collected material and recent phylogenetic studies of early archosauromorphs suggest that is represents an advance trilophosaurid very closely related to Trilophosaurus.
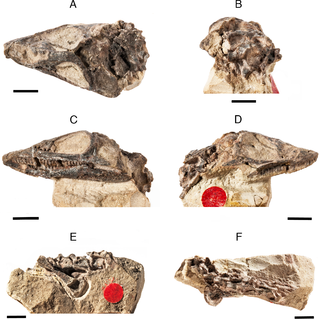
Paleorhinus is an extinct genus of basal phytosaur known from the Late Triassic of Texas and Wyoming, United States, Bavaria, Germany and possibly Poland. It contains two valid species, the type species: Paleorhinus bransoni and Paleorhinus angustifrons. Paleorhinus had a length of about 2.5 meters.

Parasuchus is an extinct genus of phytosaur known from the Late Triassic of Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, India. It contains a single species, Parasuchus hislopi.

Garjainia is an extinct genus of erythrosuchid archosauriform reptile from the Olenekian of Russia and South Africa. It was approximately 1.50–2 m long. It contained two species, Garjainia prima from the Yarengian/Yarkenskian Supergorizont of Russia, and Garjainia madiba from the Burgersdorp Formation of South Africa. "Vjuskovia triplicostata", a name assigned to some erythrosuchid fossils from Russia, has been synonymized with Garjainia prima.
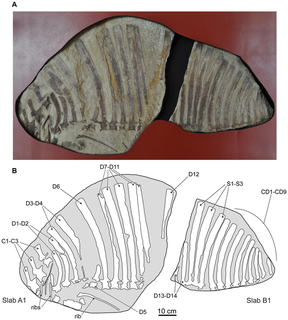
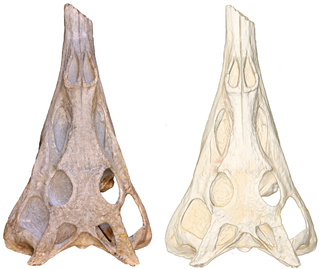
Ctenosauriscus is an extinct genus of sail-backed poposauroid archosaur from Early Triassic deposits of Lower Saxony in northern Germany. It gives its name to the family Ctenosauriscidae, which includes other sail-backed poposauroids such as Arizonasaurus. Fossils have been found in latest Olenekian deposits around 247.5-247.2 million years old, making it one of the first known archosaurs.
Ebrachosuchus is an extinct genus of basal phytosaur known from the Late Triassic of Bavaria, southern Germany. It is known only from the holotype BSPG 1931 X 501, a complete skull missing both mandibles. It was collected at Ebrach Quarry, bed number 9 from the late Carnian-aged Blasensandstein Member of the Hassberge Formation. It was first named by Oskar Kuhn in 1936 and the type species is Ebrachosuchus neukami.
Heterodontosuchus is a dubious genus of extinct phytosaur. The genus was first described from a fragmentary anterior section of the mandible found from the Henry Mountains in southeastern Utah, USA. More fossils were later found from Arizona. The name Heterodontosuchus refers to the difference in size between anterior and posterior teeth on this mandible. The teeth were compressed antero-posteriorly spaced closely together. The genus is now thought to be synonymous with Nicrosaurus, and the type and only species, H. ganei, is regarded as a nomen dubium due to the fragmentary nature of the remains associated with it.
Stagonosuchus is an extinct genus of loricatan, or possibly a species of Prestosuchus. Fossils have been found from the Late Triassic Manda Formation in Tanzania that are Anisian in age.
Francosuchus is a dubious genus of probably basal phytosaur known from the Late Triassic of Bavaria, southern Germany. It was named by Oskar Kuhn in 1933 and the type species is Francosuchus broilii. In the same article Kuhn also named a second species Francosuchus latus. Both species were known solely from their holotypes, two partial skulls that were housed at the Bavarian State Collection for Palaeontogy and Geology. Both specimens were collected at Ebrach Quarry, bed number 13 from the late Carnian-aged Blasensandstein Member of the Hassberge Formation. As the holotypes were destroyed during World War II and poorly documented, Francosuchus and its species are usually considered to be nomina dubia.
Mesorhinosuchus is an extinct genus of basal phytosaur possibly known from the Early Triassic of Saxony-Anhalt, central-eastern Germany. It was first named by Otto Jaekel in 1910 and the type species is Mesorhinus fraasi. The generic name Mesorhinus was preoccupied by Mesorhinus piramydatus Ameghino, 1885, a macraucheniid meridiungulatan mammal. Thus, an alternative generic name, Mesorhinosuchus, was proposed by Oskar Kuhn in 1961. The genus is occasionally misspelled as Mesorhinosaurus, while Stocker and Butler (2013) recently misspelled its original generic name as Mesosuchus.
Wannia is an extinct genus of basal phytosaur reptile known from the Late Triassic of Texas, southern United States. It contains a single species, Wannia scurriensis, which is known from a single specimen. This species was originally named as a species referred to Paleorhinus and later was considered as a possible junior synonym of Paleorhinus bransoni. However its re-description revealed five autapomorphies, and a phylogenetic position as the most basal known phytosaur, justifying the erection of a new generic name for the species.
Saurosphargis is an extinct genus of a basal marine reptile, saurosphargid, known from the Middle Triassic of southwestern Poland and eastern Netherlands. It contains a single species, Saurosphargis volzi.










