The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, 419.2 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, 358.9 Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied.

Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species. The earliest ammonites appear during the Devonian, and the last species vanished in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.
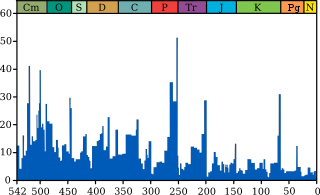
The Late Devonian extinction was one of five major extinction events in the history of life on Earth. A major extinction, the Kellwasser event, occurred at the boundary that marks the beginning of the last phase of the Devonian period, the Famennian faunal stage, about 376–360 million years ago. Overall, 19% of all families and 50% of all genera became extinct. A second, distinct mass extinction, the Hangenberg event, closed the Devonian period.
The Givetian is one of two faunal stages in the Middle Devonian period. It lasted from 387.7 million years ago to 382.7 million years ago. It was preceded by the Eifelian stage and followed by the Frasnian stage. It is named after the town of Givet in France. The oldest forests occurred during the late Givetian. The lower GSSP is located at Jebel Mech Irdane, Tafilalt, Morocco.

Dunkleosteus is an extinct genus of large armored, jawed fishes that existed during the Late Devonian period, about 358–382 million years ago. It consists of ten species, some of which are among the largest placoderms to have ever lived: D. terrelli, D. belgicus, D. denisoni, D. marsaisi, D. magnificus, D. missouriensis, D. newberryi, D. amblyodoratus, and D. raveri. The largest and most well known species is D. terrelli, which grew up to 8.79 m (28.8 ft) long and 4 t in weight. Dunkleosteus could quickly open and close its jaw, like modern-day suction feeders, and had a bite force of 6,000 N at the tip and 7,400 N at the blade edge. Numerous fossils of the various species have been found in North America, Poland, Belgium, and Morocco.

The Frasnian is one of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian period. It lasted from 382.7 million years ago to 372.2 million years ago. It was preceded by the Givetian stage and followed by the Famennian stage.
The Famennian is the latter of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian epoch. It lasted from 372.2 million years ago to 358.9 million years ago. It was preceded by the Frasnian stage and followed by the Tournaisian stage.

Stromatoporoidea is an extinct clade of sea sponges common in the fossil record from the Ordovician through the Devonian. They were especially abundant in the Silurian and Devonian. These invertebrates were important reef-formers throughout the Paleozoic and the Late Mesozoic. The group was previously thought to be related to the corals and placed in the Phylum Cnidaria. They are now classified in the phylum Porifera, specifically the sclerosponges. There are numerous fossil forms with spherical, branching or encrusting skeletons of laminated calcite with vertical pillars between the laminae. Specimen of its oldest genus, Priscastroma, have been found within the Middle Ordovician Sediments. This same genus has been referred to as the species P. gemina Khrom., and is known to have been known to branch off into two forms, A and B. Form A gave rise to the genus Cystostroma while form B gave rise to the genus Labechia and its descendants.

Cheirolepis is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived in the Devonian period of Europe and North America. It is the only genus yet known within the family Cheirolepidae and the order Cheirolepiformes. It was among the most basal of the Devonian actinopterygians and is considered the first to possess the "standard" dermal cranial bones seen in later actinopterygians.

The Emsian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian epoch. It lasted from 407.6 ± 2.6 million years ago to 393.3 ± 1.2 million years ago. It was preceded by the Pragian stage and followed by the Eifelian stage. It is named after the Ems river in Germany. The GSSP is located in the Zinzil'ban Gorge in the Kitab State Geological Reserve of Uzbekistan, 35 centimetres (14 in) above the contact with the Madmon Formation.
The Pragian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian epoch. It lasted from 410.8 ± 2.8 million years ago to 407.6 ± 2.8 million years ago. It was preceded by the Lochkovian stage and followed by the Emsian stage. The most important Lagerstätte of the Pragian is Rhynie chert in Scotland. It is named after the city of Prague. The GSSP is located within the Praha Formation at Velká Chuchle, Prague.

Dunkleosteidae is an extinct family of arthrodire placoderms. The gigantic apex predator Dunkleosteus terrelli is the best known member of this group. While they were previously thought to be close relatives of the genus Dinichthys and grouped together in the family Dinichthyidae, more recent studies have shown that the two taxa represent two very distinct clades within Arthrodira. The reappraisal of Kiangyousteus lead to a restructuring of the family, with the inclusions of the benthic, aberrant Heterosteus as the sister taxon of Dunkleosteus, and the Late Emsian Xiangshuiosteus as the sister taxon of Eastmanosteus calliaspis, and the removal of Westralichthys from the family
Tornoceratidae is a family of goniatitid ammonoids from the middle and upper Devonian. The family is included in the suborder Tornoceratina and the superfamily Tornoceratoidea.
Aulatornoceratinae is one of three subfamilies of the gonititid family Tornoceratidae, an extinct order of Paleozoic ammonoid cephalopods. Aulotornoceratinae was established as a subfamily by R.T.Becker, 1993, initially for Aulatornoceras, named by Schindewolf, 1922. Subsequently four other genera have been added.

Glyptolepis is an extinct genus of porolepiform lobe-finned fish which lived during Devonian Period, from the early Eifelian to Frasnian Age.

Eastmanosteus is a fossil genus of dunkleosteid placoderms. It was closely related to the giant Dunkleosteus, but differed from that genus in size, in possessing a distinctive tuberculated bone ornament, a differently shaped nuchal plate and a more zig-zagging course of the sutures of the skull roof.
Palmatolepis is an extinct conodont genus in the family Palmatolepidae. It was the most abundant genus of conodonts of the Late Devonian, disappearing during the Devonian/Carboniferous crisis.
Acanthoclymenia is genus of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the Acanthoclymeniidae family. Species belonging to this genus lived in middle and late Devonian. Its fossils were found in Europe, Asia, north Africa, North America and Australia. Species of this genus had discoidal shells with flattened venter.
Cryptotaxis is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Cryptotaxidae from the Famennian.
Crassotornoceras is genus of ammonoids that lived during Upper Devonian period, from the base of Frasnian age until the base of Maenecoceras subvaricatum zone. Animals belonging to this genus had small subglobular conches with thin umbilicus. These were maybe ornamented by ribs and had biconvex growth lines. Suture had small, tongue-like adventitious lobe. Their fossils were found in United Kingdom, Germany, France, Belgium and Morocco.









