Related Research Articles

Trachyte is an extrusive igneous rock composed mostly of alkali feldspar. It is usually light-colored and aphanitic (fine-grained), with minor amounts of mafic minerals, and is formed by the rapid cooling of lava enriched with silica and alkali metals. It is the volcanic equivalent of syenite.

Amphibolite is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flaky) structure. The small flakes of black and white in the rock often give it a salt-and-pepper appearance.

The St. Francois Mountains in southeast Missouri are a mountain range of Precambrian igneous mountains rising over the Ozark Plateau. This range is one of the oldest exposures of igneous rock in North America. The name of the range is spelled out as Saint Francois Mountains in official GNIS sources, but it is sometimes misspelled in use as St. Francis Mountains to match the anglicized pronunciation of both the range and St. Francois County.

Mount Hampton is a shield volcano with a circular ice-filled caldera. It is a twin volcano with Whitney Peak to the northwest and has erupted phonolite rocks. It is the northernmost of the volcanoes which comprise the Executive Committee Range in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica and was active during the Miocene.

Mount Murphy is a massive, snow-covered mountain with steep, rocky slopes rising to 2,505 metres (8,219 ft) in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. It is directly south of Bear Peninsula and is bounded by Smith Glacier, Pope Glacier and Haynes Glacier. Volcanic activity began in the Miocene with the eruption of basaltic and trachytic lava. Volcanism on the slopes of the volcano resumed much later during the Pleistocene, with a parasitic cone having been K–Ar dated to 0.9 million years old.

Mount Takahe is a 3,460-metre-high (11,350 ft) snow-covered shield volcano in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica, 200 kilometres (120 mi) from the Amundsen Sea. It is a c. 30-kilometre-wide (19 mi) mountain with parasitic vents and a caldera up to 8 kilometres (5 mi) wide. Most of the volcano is formed by trachytic lava flows, but hyaloclastite is also found. Snow, ice, and glaciers cover most of Mount Takahe. With a volume of 780 km3 (200 cu mi), it is a massive volcano; the parts of the edifice that are buried underneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet are probably even larger. It is part of the West Antarctic Rift System along with 18 other known volcanoes.

Toney Mountain is an elongated snow-covered shield volcano, 38 nautical miles long and rising to 3,595 metres (11,795 ft) at Richmond Peak, located 35 nautical miles southwest of Kohler Range in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica.
The Pleiades are a volcanic group in northern Victoria Land of Antarctica. It consists of youthful cones and domes with Mount Atlas/Mount Pleiones, a small stratovolcano formed by three overlapping cones, being the dominant volcano and rising 500 m (1,600 ft) above the Evans Névé plateau. Two other named cones are Alcyone Cone and Taygete Cone, the latter of which has been radiometrically dated to have erupted during the Holocene. A number of tephra layers across Antarctica have been attributed to eruptions of this volcanic group, including several that may have occurred within the last few hundred years.

Crary Mountains are a group of ice-covered volcanoes in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. They consist of two or three shield volcanoes, named Mount Rees, Mount Steere and Mount Frakes, which developed during the course of the Miocene and Pliocene and last erupted about 30,000-40,000 years ago. The first two volcanoes are both heavily incised by cirques, while Mount Frakes is better preserved and has a 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) wide caldera at its summit. Boyd Ridge is another part of the mountain range and lies southeast of Mount Frakes; it might be the emergent part of a platform that underlies the mountain range.
The Gabbro Hills are a group of rugged ridges and coastal hills which border the Antarctic Ross Ice Shelf between Barrett Glacier and Gough Glacier and extend south to Ropebrake Pass. They were so named by the Southern Party of the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) (1963–64) because of the prevalence of gabbro, a dark, plutonic rock, in the area.
Mount Giles is a mainly snow-covered mountain, 820 metres (2,690 ft) high, located 5 nautical miles south-southeast of Lynch Point on the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. The mountain is the highest elevation on the divide between the seaward ends of Frostman Glacier and Hull Glacier.
Coulter Heights are snow-covered heights that rise between Strauss Glacier and Frostman Glacier near the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. The rock outcrops of Kuberry Rocks, Matikonis Peak and Lambert Nunatak protrude above the snow surface of the heights.

Pope Glacier is a glacier about 20 nautical miles (37 km) long, flowing north along the west side of Mount Murphy to Crosson Ice Shelf on Walgreen Coast, in Marie Byrd Land. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1959–66. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) after Maj. Donald R. Pope, (CE) USA, civil engineer on the staff of the Commander, Naval Support Force, Antarctica, 1965–67. It is a tributary of Smith Glacier.
The Phillips Mountains are a range of mountains on the north side of Balchen Glacier and Block Bay in the Ford Ranges, Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica.
Land Bay is an ice-filled bay, about 40 nautical miles wide, indenting the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica, just eastward of Groves Island. It was discovered by the United States Antarctic Service, and takes its name from Land Glacier which descends into the bay.

The Siilinjärvi carbonatite complex is located in central Finland close to the city of Kuopio. It is named after the nearby town of Siilinjärvi, located approximately 5 km west of the southern extension of the complex. Siilinjärvi is the second largest carbonatite complex in Finland after the Sokli formation, and one of the oldest carbonatites on Earth at 2610±4 Ma. The carbonatite complex consists of a roughly 16 km long steeply dipping lenticular body surrounded by granite gneiss. The maximum width of the body is 1.5 km and the surface area is 14.7 km2. The complex was discovered in 1950 by the Geological Survey of Finland with help of local mineral collectors. The exploration drilling began in 1958 by Lohjan Kalkkitehdas Oy. Typpi Oy continued drilling between years 1964 and 1967, and Apatiitti Oy drilled from 1967 to 1968. After the drillings, the laboratory and pilot plant work were made. The mine was opened by Kemira Oyj in 1979 as an open pit. The operation was sold to Yara in 2007.

Mount Berlin is a glacier-covered volcano in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica, 100 kilometres (62 mi) from the Amundsen Sea. It is a roughly 20-kilometre-wide (12 mi) mountain with parasitic vents that consists of two coalesced volcanoes: Berlin proper with the 2-kilometre-wide (1.2 mi) Berlin Crater and Merrem Peak with a 2.5-by-1-kilometre-wide crater, 3.5 kilometres (2.2 mi) away from Berlin. The summit of the volcano is 3,478 metres (11,411 ft) above sea level. It has a volume of 200 cubic kilometres (48 cu mi) and rises from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. It is part of the Marie Byrd Land Volcanic Province. Trachyte is the dominant volcanic rock and occurs in the form of lava flows and pyroclastic rocks.

The Concord Gabbro-Syenite Complex is a paleozoic pluton located in North Carolina.
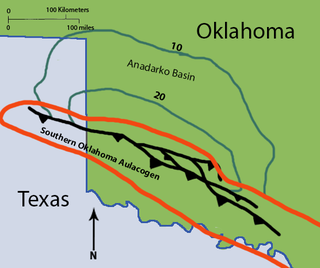
The Roosevelt Gabbros are an intrusive igneous geological formation in southwestern Oklahoma. They are one of two formations recognized in the Raggedy Mountain Gabbro Group, the other being the Glen Mountain Layered Complex. The Roosevelt Gabbros are generally characterized as biotite gabbros, which form many dikes and sills through the older Glen Mountain Layered Complex. They are named after the town of Roosevelt in Kiowa County, Oklahoma.
References
- ↑ "Dorrel Rock". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 2023-08-19.
- ↑ Stewart, J., 2011. Antarctica: An Encyclopedia, 2nd ed. Jefferson, North Carolina and London, McFarland & Company, Inc. 1771 pp. ISBN 978-0-7864-3590-6
- ↑ Woolley, A.R., 2019. Dorrel Rock In Woolley, A.R., ed., pp. 5. Alkaline rocks and carbonatites of the world. Part 4, Antarctica, Asia and Europe (excluding the former USSR), Australasia and Oceanic Islands. London, The Geological Society of London. 562 pp. ISBN 978- 1-78620-44 5-5
- ↑ Rocchi, S., LeMasurier, W.E., and Di Vincenzo, G., 2006. Oligocene to Holocene erosion and glacial history in Marie Byrd Land, West Antarctica, inferred from exhumation of the Dorrel Rock intrusive complex and from volcano morphologies.Geological Society of America Bulletin, 118(7-8), pp.991-1005.