
The orca or killer whale is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is recognizable by its black-and-white patterned body. A cosmopolitan species, orcas can be found in all of the world's oceans in a variety of marine environments, from Arctic and Antarctic regions to tropical seas.

Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine environments for feeding and survival.

Angling is a fishing technique that uses a fish hook or "angle" attached to a fishing line to tether individual fish in the mouth. The fishing line is usually manipulated via a fishing rod, although rodless techniques such as handlining and longlining also exist. Modern angling rods are usually fitted with a reel that functions as a cranking device for storing, retrieving and releasing out the line, although Tenkara fishing and cane pole fishing are two rod-angling methods that do not use any reel. The hook itself can be additionally weighted with a dense tackle called a sinker, and is typically dressed with an appetizing bait to attract the fish and enticing it into swallowing the hook, but sometimes an inedible fake bait with multiple attached hooks is used instead of a single hook with edible bait. A bite indicator, such as a float or a quiver tip, is often used to relay underwater status of the hook to the surface.

Longline fishing, or longlining, is a commercial fishing angling technique that uses a long main line with baited hooks attached at intervals via short branch lines called snoods or gangions. A snood is attached to the main line using a clip or swivel, with the hook at the other end. Longlines are classified mainly by where they are placed in the water column. This can be at the surface or at the bottom. Lines can also be set by means of an anchor, or left to drift. Hundreds or even thousands of baited hooks can hang from a single line.This can lead to many deaths of different marine species Longliners – fishing vessels rigged for longlining – commonly target swordfish, tuna, halibut, sablefish and many other species.

Bycatch, in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juveniles of the target species. The term "bycatch" is also sometimes used for untargeted catch in other forms of animal harvesting or collecting. Non-marine species that are caught but regarded as generally "undesirable" are referred to as "rough fish" and "coarse fish".

The Antarctic toothfish is a large, black or brown fish found in very cold (subzero) waters of the Southern Ocean near Antarctica. It is the largest fish in the Southern Ocean, feeding on shrimp and smaller fish, and preyed on by whales, orcas, and seals. It is caught for food and marketed as Chilean sea bass together with its sister species, the more northerly Patagonian toothfish. Often mistakenly called "Antarctic cod," the Antarctic toothfish belongs to the notothen family (Nototheniidae), a group of fish species abundant near Antarctica.

The Patagonian toothfish is a species of notothen found in cold waters between depths of 45 and 3,850 m in the southern Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans and Southern Ocean on seamounts and continental shelves around most Subantarctic islands.
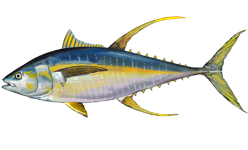
The yellowfin tuna is a species of tuna found in pelagic waters of tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide.

Gillnetting is a fishing method that uses gillnets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is generally referred to as a "cork line." The line along the bottom of the panels is generally weighted. Traditionally this line has been weighted with lead and may be referred to as "lead line." A gillnet is normally set in a straight line. Gillnets can be characterized by mesh size, as well as colour and type of filament from which they are made. Fish may be caught by gillnets in three ways:
- Wedged – held by the mesh around the body.
- Gilled – held by mesh slipping behind the opercula.
- Tangled – held by teeth, spines, maxillaries, or other protrusions without the body penetrating the mesh.

Arripis is a genus of marine fishes from Australia and New Zealand, known as Australian salmon, kahawai and Australian herring. They are the only members of the family Arripidae. Despite the common name, Australian salmon are not related to the salmon family Salmonidae of the Northern Hemisphere, just as Australian herring are not related to herring of the Northern Hemisphere, but belong to the order Perciformes of perch-like fishes. Australian salmon were named so by early European settlers after their superficial resemblance to the salmoniform fishes.

The National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), informally known as NOAA Fisheries, is a United States federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce's National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) that is responsible for the stewardship of U.S. national marine resources. It conserves and manages fisheries to promote sustainability and prevent lost economic potential associated with overfishing, declining species, and degraded habitats.

A trotline is a heavy fishing line with shorter, baited branch lines commonly referred to as snoods suspending down at intervals using clips or swivels, with a hook at the free end of each snood.

Carousel feeding is a cooperative hunting method used by Norwegian orcas to capture wintering Norwegian spring-spawning herring. The term carousel feeding was first used to describe a similar hunting behaviour in bottlenose dolphins in the Black Sea. There are two main phases of carousel feeding in orcas, the herding phase and the feeding phase. In the herding phase the orcas surround a school of herring and herd them into a tight ball. They tighten the ball by blowing bubbles, flashing their white underside and slapping their tails on the surface. They move the ball of herring toward the surface of the water before initiating the feeding phase. During the feeding phase several orcas begin to eat while the others continue herding the fish to maintain the ball. The feeding orcas whip their tails into the ball to stun and kill several herring at a time. The dead and stunned herring are then consumed and their heads and spines discarded.

Fishing techniques are methods for catching fish. The term may also be applied to methods for catching other aquatic animals such as molluscs and edible marine invertebrates.
A mammals and birds excluder device or MBED is a device added to fishing gear that avoids the killing of marine mammals and seabirds during commercial fishing. This device was designed mainly for the interactions with toothed whales: sperm and killer whales.
This page is a list of fishing topics.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to fishing:
This is a glossary of terms used in fisheries, fisheries management and fisheries science.

The southern resident orcas, also known as the southern resident killer whales (SRKW), are the smallest of four separate, non-interbreeding communities of the exclusively fish-eating ecotype of orca in the northeast portion of the North Pacific Ocean. The fish-eating ecotype was historically given the name 'resident,' but other ecotypes are also resident in the area. The National Marine Fisheries Service listed this distinct population segment of orcas as endangered, effective from 2005, under the Endangered Species Act. In Canada the SRKW are listed as endangered on Species at Risk Act Schedule 1. They are commonly referred to as the "orcas of the Salish Sea", "fish-eating orcas", "southern residents", or the "SRKW population". Unlike some other resident communities, the SRKW is only one clan (J) that consists of 3 pods with several matrilines within each pod. As of July 2021 there are only 74 individuals. The world's oldest known orca, Granny or J2, had belonged to and led the J pod of the SRKW population. As of October 2016, she is missing and presumed deceased. J2 was estimated to have been born around 1911, which means she would have been 105 years old at the time of her death, and the oldest known orca to date. On July 24, 2018, the first calf born in three years died after being alive for only half an hour.

Orcas or killer whales have a cosmopolitan distribution and several distinct populations or types have been documented or suggested. Three to five types of orcas may be distinct enough to be considered different races, subspecies, or possibly even species. The IUCN reported in 2008, "The taxonomy of this genus is clearly in need of review, and it is likely that O. orca will be split into a number of different species or at least subspecies over the next few years." Although large variation in the ecological distinctiveness of different orca groups complicate simple differentiation into types. Mammal-eating orcas in different regions were long thought likely to be closely related, but genetic testing has refuted this hypothesis.


















