
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques include hand-gathering, spearing, netting, angling, shooting and trapping, as well as more destructive and often illegal techniques such as electrocution, blasting and poisoning.

A fisherman or fisher is someone who captures fish and other animals from a body of water, or gathers shellfish.

Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place. Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies and the oceans. About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem, causing declines in some populations.

The fishing industry includes any industry or activity that takes, cultures, processes, preserves, stores, transports, markets or sells fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including recreational, subsistence and commercial fishing, as well as the related harvesting, processing, and marketing sectors. The commercial activity is aimed at the delivery of fish and other seafood products for human consumption or as input factors in other industrial processes. The livelihood of over 500 million people in developing countries depends directly or indirectly on fisheries and aquaculture.

The goal of fisheries management is to produce sustainable biological, environmental and socioeconomic benefits from renewable aquatic resources. Wild fisheries are classified as renewable when the organisms of interest produce an annual biological surplus that with judicious management can be harvested without reducing future productivity. Fishery management employs activities that protect fishery resources so sustainable exploitation is possible, drawing on fisheries science and possibly including the precautionary principle.

Gillnetting is a fishing method that uses gillnets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is generally referred to as a "cork line." The line along the bottom of the panels is generally weighted. Traditionally this line has been weighted with lead and may be referred to as "lead line." A gillnet is normally set in a straight line. Gillnets can be characterized by mesh size, as well as colour and type of filament from which they are made. Fish may be caught by gillnets in three ways:
- Wedged – held by the mesh around the body.
- Gilled – held by mesh slipping behind the opercula.
- Tangled – held by teeth, spines, maxillaries, or other protrusions without the body penetrating the mesh.

Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often pursue fish far into the ocean under adverse conditions. Large-scale commercial fishing is called industrial fishing.

A fishing net is a net used for fishing. Some fishing nets are also called fish traps, for example fyke nets. Fishing nets are usually meshes formed by knotting a relatively thin thread. Early nets were woven from grasses, flaxes and other fibrous plant material. Later cotton was used. Modern nets are usually made of artificial polyamides like nylon, although nets of organic polyamides such as wool or silk thread were common until recently and are still used.
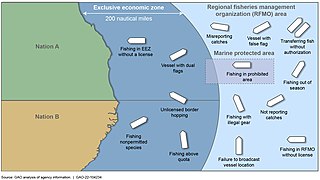
Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU) is an issue around the world. Fishing industry observers believe IUU occurs in most fisheries, and accounts for up to 30% of total catches in some important fisheries.

A fishing vessel is a boat or ship used to catch fish and other valuable nektonic aquatic animals in the sea, lake or river. Humans have used different kinds of surface vessels in commercial, artisanal and recreational fishing.

A fishing village is a village, usually located near a fishing ground, with an economy based on catching fish and harvesting seafood. The continents and islands around the world have coastlines totalling around 356,000 kilometres (221,000 mi). From Neolithic times, these coastlines, as well as the shorelines of inland lakes and the banks of rivers, have been punctuated with fishing villages. Most surviving fishing villages are traditional.

Fishing techniques are methods for catching fish. The term may also be applied to methods for catching other aquatic animals such as molluscs and edible marine invertebrates.

Fishing in Ghana is made up of both ocean caught fish, as well as freshwater fishing in lakes and rivers. The fishing industry has been expanding due to increased interest by the government and substantial cage farming in the Volta Basin.

There are two major sources of fish in Uganda; one is from aquaculture, the other from fishing in rivers and lakes. The latter has made up the largest and most significant share of all fishing. Open water covers 15.3 percent of Uganda's surface and comprises five major lakes which are the main sources of fish in the country. Lake Victoria continues to be the most important water body in Uganda both in size and contribution to the total fish catch, followed by Lake Albert and Lake Kyoga.
This is a glossary of terms used in fisheries, fisheries management and fisheries science.

The coastline of the Russian Federation is the fourth longest in the world after the coastlines of Canada, Greenland, and Indonesia. The Russian fishing industry has an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of 7.6 million km2 including access to twelve seas in three oceans, together with the landlocked Caspian Sea and more than two million rivers.
A community-supported fishery (CSF) is an alternative business model for selling fresh, locally sourced seafood. CSF programs, modeled after increasingly popular community-supported agriculture programs, offer members weekly shares of fresh seafood for a pre-paid membership fee. The first CSF program was started in Port Clyde, Maine, in 2007, and similar CSF programs have since been started across the United States and in Europe. Community supported fisheries aim to promote a positive relationship between fishermen, consumers, and the ocean by providing high-quality, locally caught seafood to members. CSF programs began as a method to help marine ecosystems recover from the effects of overfishing while maintaining a thriving fishing community.

Lift nets, also called lever nets, are a method of fishing using nets that are submerged to a certain depth and then lifted out of the water vertically. The nets can be flat or shaped like a bag, a rectangle, a pyramid, or a cone. Lift nets can be hand-operated, boat-operated, or shore-operated. They typically use bait or a light-source as a fish-attractor. Lift nets are also sometimes called "dip nets", though that term applies more accurately to hand nets.

Fishing in Egypt includes every form of fishing as a hobby or professional nowadays. In Egypt, the fishing industry is well developed and the country is considered one of the best fishing destinations in the world.

The municipal fisheries in the Philippines are the Philippine fisheries that fall under the jurisdiction of local governments, namely cities and municipalities. This includes all fisheries on inland waters, and in waters within 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) of the coast. While the term may technically include aquaculture activities, it is usually used to discuss capture fisheries. Municipal fisheries are restricted to boats of 3 gross tonnes or smaller, and commercial fishing vessels are generally prohibited from fishing in these waters.

































