
Aquaculture, also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Aquaculture is also a practice used for restoring and rehabilitating marine and freshwater ecosystems. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, is aquaculture in seawater habitats and lagoons, as opposed to freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain fish products as food.
Agriculture and aquaculture in Hong Kong are considered sunset industries. Most agricultural produce is directly imported from the neighbouring mainland China. In 2006 the industry accounts for less than 0.3% of the labour sector. Geographically Hong Kong consists largely of steep, unproductive hillside. The local aquaculture industry is also facing challenges from competition with imported aquatic food products and concern of fish and seafood safety.

San Quintín is a city in San Quintín Municipality, Baja California, located on the Pacific Coast of Mexico. The city had a population of 4777 in 2011. San Quintín is an important agricultural center for Baja California. The city is also an emerging tourist destination, known for its sand dunes and beaches.

Integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA) is a type of aquaculture where the byproducts, including waste, from one aquatic species are used as inputs for another. Farmers combine fed aquaculture with inorganic extractive and organic extractive aquaculture to create balanced systems for environment remediation (biomitigation), economic stability and social acceptability.

Fishing in India is a major sector within the economy of India contributing 1.07% of its total GDP. The fishing sector in India supports the livelihood of over 28 million people in the country, especially within the marginalized and vulnerable communities. India is the third largest fish producing country in the world accounting for 7.96% of the global production and second largest producer of fish through aquaculture, after China. The total fish production during the FY 2020-21 is estimated at 14.73 million metric tonnes. According to the National Fisheries Development Board the Fisheries Industry generates an export earnings of Rs 334.41 billion. Centrally sponsored schemes will increase exports by Rs 1 lakh crore in FY25. 65,000 fishermen have been trained under these schemes from 2017 to 2020. Freshwater fishing consists of 55% of total fish production.

Fishing in Ghana is made up of both ocean caught fish, as well as freshwater fishing in lakes and rivers.

A raceway, also known as a flow-through system, is an artificial channel used in aquaculture to culture aquatic organisms. Raceway systems are among the earliest methods used for inland aquaculture. A raceway usually consists of rectangular basins or canals constructed of concrete and equipped with an inlet and outlet. A continuous water flow-through is maintained to provide the required level of water quality, which allows animals to be cultured at higher densities within the raceway.
This page is a list of fishing topics.

The fishing industry in the land-locked country of Laos is a major source of sustenance and food security to its people dwelling near rivers, reservoirs and ponds. Apart from wild capture fisheries, which is a major component of fish production, aquaculture and stocking are significant developments in the country. Historically, fishing activity was recorded in writings on the gate and walls of the Wat Xieng Thong in Luang Prabang dated 1560. For many Laotians, freshwater fish are the principal source of protein. The percentage of people involved in regular fishing activity is very small, only near major rivers or reservoirs, as for most of the fishers it is a part-time activity.

Aquaculture started to take off in New Zealand in the 1980s. It is dominated by mussels, oysters and salmon. In 2007, aquaculture generated about NZ$360 million in sales on an area of 7,700 hectares. $240 million was earned in exports.
Aquaculture in Vanuatu exists on a small scale, both commercially and privately. Several aquacultural efforts have been made in the country, including attempts to raise Pacific oyster, rabbitfish, Malaysian prawn, and tilapia. Experiments with Kappaphycus alvarezii and three species of giant clam were carried out by the Fisheries Department in 1999. The official Fisheries Department records state that $1165 US of cultured coral was exported from the country in 2000, with 275 pieces in total. The cultivation of Macrobrachium lar in taro terraces is practiced for subsistence purposes, and Macrobrachium rosenbergii has been identified by the Vanuatu government as a high-priority species.

Aquaculture in Australia is the country's fastest-growing primary industry, accounting for 34% of the total gross value of production of seafood. 10 species of fish are farmed in Australia, and production is dominated by southern bluefin tuna, Atlantic salmon and barramundi. Mud crabs have also been cultivated in Australia for many years, sometimes leading to over-exploitation. Traditionally, this aquaculture was limited to table oysters and pearls, but since the early 1970s, there has been significant research and commercial development of other forms of aquaculture, including finfish, crustaceans, and molluscs.

China, with one-fifth of the world's population, accounts for two-thirds of the world's reported aquaculture production.
Seafood in Australia comes from local and international commercial fisheries, aquaculture and recreational anglers. It is an economically important sector, and along with agriculture and forestry contributed $24,744 million to Australia's GDP in year 2007–2008, out of a total GDP of $1,084,146 million. Commercial fisheries in Commonwealth waters are managed by the Australian Fisheries Management Authority, while commercial and recreational fishing in state waters is managed by various state-level agencies.
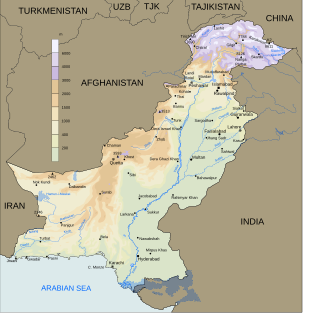
The fishing industry plays a significant part in the national economy of Pakistan. With a coastline of about 1,120 km, Pakistan has enough fishery resources that remain to be developed. Most of the population of the coastal areas of Sindh and Balochistan depends on fisheries for livelihood. It is also a major source of export earning.

South Korea is a major center of aquaculture production, and the world's third largest producer of farmed algae as of 2020.

The fishing industry in Denmark operates around the coastline, from western Jutland to Bornholm. While the overall contribution of the fisheries sector to the country's economy is only about 0.5 percent, Denmark is ranked fifth in the world in exports of fish and fish products. Approximately 20,000 Danish people are employed in fishing, aquaculture, and related industries.
The Benguela Current Commission, or BCC, is a multi-sectoral inter-governmental, initiative of Angola, Namibia and South Africa. It promotes the sustainable management and protection of the Benguela Current Large Marine Ecosystem, or BCLME. The BCC was established in January 2007 through the signing of an Interim Agreement between the governments of Angola, Namibia and South Africa. Then, on 18 March 2013, the three governments signed the Benguela Current Convention, an environmental treaty that entrenches the Benguela Current Commission as a permanent inter-governmental organization.
The Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) is an independent non-profit organisation and labelling organization that establishes protocol on farmed seafood while ensuring sustainable aquaculture. The ASC provides producers with a certification of environmental sustainability and social responsibility.

Aquaculture in the United Kingdom is dominated by salmon farming, then by mussel production with trout being the third most important enterprise. Aquaculture in the United Kingdom represents a significant business for the UK, producing over 200,000 tonnes of fish whilst earning over £700 million in 2012 (€793 million).
















