
Trawling is an industrial method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net, which is heavily weighted to keep it on the seafloor, through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch different species of fishes or sometimes targeted species. Trawls are often called towed gear or dragged gear.

Longline fishing, or longlining, is a commercial fishing angling technique that uses a long main line with baited hooks attached at intervals via short branch lines called snoods or gangions. A snood is attached to the main line using a clip or swivel, with the hook at the other end. Longlines are classified mainly by where they are placed in the water column. This can be at the surface or at the bottom. Lines can also be set by means of an anchor, or left to drift. Hundreds or even thousands of baited hooks can hang from a single line. This can lead to many deaths of different marine species. Longliners – fishing vessels rigged for longlining – commonly target swordfish, tuna, halibut, sablefish and many other species.
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word pelagic is derived from Ancient Greek πέλαγος (pélagos) 'open sea'. The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients all change. In a manner analogous to stratification in the Earth's atmosphere, the water column can be divided vertically into up to five different layers, with the number of layers depending on the depth of the water.

Gillnetting is a fishing method that uses gillnets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is generally referred to as a "cork line." The line along the bottom of the panels is generally weighted. Traditionally this line has been weighted with lead and may be referred to as "lead line." A gillnet is normally set in a straight line. Gillnets can be characterized by mesh size, as well as colour and type of filament from which they are made. Fish may be caught by gillnets in three ways:
- Wedged – held by the mesh around the body.
- Gilled – held by mesh slipping behind the opercula.
- Tangled – held by teeth, spines, maxillaries, or other protrusions without the body penetrating the mesh.

Bottom trawling is trawling along the seafloor. It is also referred to as "dragging". The scientific community divides bottom trawling into benthic trawling and demersal trawling. Benthic trawling is towing a net at the very bottom of the ocean and demersal trawling is towing a net just above the benthic zone. Bottom trawling can be contrasted with midwater trawling, where a net is towed higher in the water column. Midwater trawling catches pelagic fish such as anchovies and mackerel, whereas bottom trawling targets both bottom-living fish (groundfish) and semi-pelagic species such as cod, squid, shrimp, and rockfish.
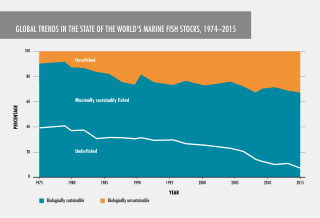
Fish stocks are subpopulations of a particular species of fish, for which intrinsic parameters are traditionally regarded as the significant factors determining the stock's population dynamics, while extrinsic factors are traditionally ignored.

Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with demersal fish that live on or near the bottom, and reef fish that are associated with coral reefs.

Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes. They occupy the sea floors and lake beds, which usually consist of mud, sand, gravel or rocks. In coastal waters, they are found on or near the continental shelf, and in deep waters, they are found on or near the continental slope or along the continental rise. They are not generally found in the deepest waters, such as abyssal depths or on the abyssal plain, but they can be found around seamounts and islands. The word demersal comes from the Latin demergere, which means to sink.

Unsustainable fishing methods refers to the use of various fishing methods used to capture or harvest fish at a rate which is unsustainable for fish populations. These methods facilitate destructive fishing practices that damage ecosystems within the ocean, and result in overfishing.

The fishing industry in Scotland comprises a significant proportion of the United Kingdom fishing industry. A recent inquiry by the Royal Society of Edinburgh found fishing to be of much greater social, economic and cultural importance to Scotland than it is relative to the rest of the UK. Scotland has just 8.4 per cent of the UK population but lands at its ports over 60 per cent of the total catch in the UK.

A factory ship, also known as a fish processing vessel, is a large ocean-going vessel with extensive on-board facilities for processing and freezing caught fish or whales. Modern factory ships are automated and enlarged versions of the earlier whalers, and their use for fishing has grown dramatically. Some factory ships are equipped to serve as a mother ship.

The End of the Line: How Overfishing Is Changing the World and What We Eat is a book by journalist Charles Clover about overfishing. It was made into a movie released in 2009 and was re-released with updates in 2017.

Fishing techniques are methods for catching fish. The term may also be applied to methods for catching other aquatic animals such as molluscs and edible marine invertebrates.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to fishing:
Destructive fishing practices are fishing practices which easily result in irreversible damage to habitats and the sustainability of the fishery ecosystems. Such damages can be caused by direct physical destruction of the underwater landform and vegetation, overfishing, indiscriminate killing/maiming of aquatic life, disruption of vital reproductive cycles, and lingering water pollution.

Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish that feed on plankton and other tiny organisms. They are preyed on by larger predators, including larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals. Typical ocean forage fish feed near the base of the food chain on plankton, often by filter feeding. They include particularly fishes of the order Clupeiformes, but also other small fish, including halfbeaks, silversides, smelt such as capelin and goldband fusiliers.

As with other countries, the 200 nautical miles (370 km) exclusive economic zone (EEZ) off the coast of the United States gives its fishing industry special fishing rights. It covers 11.4 million square kilometres, which is the second largest zone in the world, exceeding the land area of the United States.

A marine habitat is a habitat that supports marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea. A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species. The marine environment supports many kinds of these habitats.

The Cape horse mackerel is a mackerel-like species in the family Carangidae. It is a pelagic species of the south eastern Atlantic Ocean which is a target of fisheries, mainly as bycatch.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to fisheries:
















