| Drosera petiolaris | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Droseraceae |
| Genus: | Drosera |
| Subgenus: | Drosera subg. Lasiocephala |
| Species: | D. petiolaris |
| Binomial name | |
| Drosera petiolaris | |
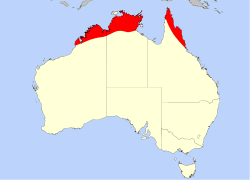 | |
| Distribution of D. petiolaris in Australia | |
Drosera petiolaris is a carnivorous plant in the genus Drosera and is the eponymous species of the petiolaris species complex, which mostly refers to the entire subgenus Lasiocephala . It is native to Northern Australia, including the northern regions of Western Australia, the Northern Territory, and Queensland, and New Guinea; this distribution is the largest in the subgenus and the only that extends beyond Australia. Its leaves are arranged in a compact basal rosette with long, narrow petioles emerging from the center of the rosette. Carnivorous leaves are held at the end of the petiole with long retentive glands. [1] [2]