Makrukpronounced [màːk rúk]), or Thai chess, is a board game that descended from the 6th-century Indian game of chaturanga or a close relative thereof, and therefore related to chess. It is regarded as the most similar living game to this common ancestor of all chess variants.

Sittuyin, also known as Burmese chess, is a variant of chess that is a direct offspring of the Indian game of chaturanga which arrived in 8th century AD. Sit is the modern Burmese word for army or war ; the word sittuyin can be translated as representation of the four characteristics of army—chariot, elephant, cavalry and infantry.
Chaturaji is a four-player chess-like game. It was first described in detail c. 1030 by Al-Biruni in his book India. Originally, this was a game of chance: the pieces to be moved were decided by rolling two dice. A diceless variant of the game was still played in India at the close of the 19th century.
Knight Relay chess is a chess variant invented by Mannis Charosh in 1972. In this game knights "relay" their power to friendly pieces.
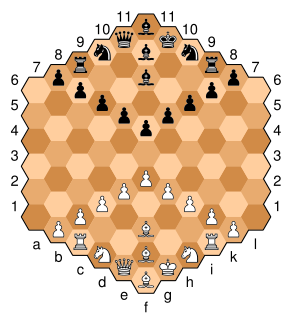
Hexagonal chess refers to a group of chess variants played on boards composed of hexagon cells. The best known is Gliński's variant, played on a symmetric 91-cell hexagonal board.

Wildebeest Chess is a chess variant created by R. Wayne Schmittberger in 1987. The Wildebeest board is 11×10 squares. Besides the standard chess pieces, each side has two camels and one wildebeest. The inventor's intent is "to balance the number of 'riders'—pieces that move along open lines—with the number of 'leapers'—pieces that jump".

Dragonfly is a chess variant invented by Christian Freeling in 1983. There are no queens, and a captured bishop, knight, or rook becomes the property of the capturer, who may play it as his own on a turn to any open square. The board is 7×7 squares, or alternatively a 61-cell hexagon with two additional pawns per side.

Rhombic Chess is a chess variant for two players created by Tony Paletta in 1980. The gameboard has an overall hexagonal shape and comprises 72 rhombi in three alternating colors. Each player commands a full set of standard chess pieces.

Wolf Chess is a chess variant invented by Dr. Arno von Wilpert in 1943. It is played on a 10×8 chessboard and employs several fairy pieces including wolf and fox – compound pieces popular in chess variants and known by different names.

Triangular Chess is a chess variant for two players invented by George R. Dekle, Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a hexagon-shaped gameboard comprising 96 triangular cells. Each player commands a full set of chess pieces in addition to three extra pawns and a unicorn.

Masonic Chess is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle, Sr. in 1983. The game is played on a modified chessboard whereby even-numbered ranks are indented to the right—resembling masonry brickwork. The moves of the pieces are adapted to the new geometry; in other respects the game is the same as chess.

Tri-Chess is the name of a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle, Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board comprising 150 triangular cells. The standard chess pieces are present, minus the queens, and plus the chancellor and cardinal compound fairy pieces per side.
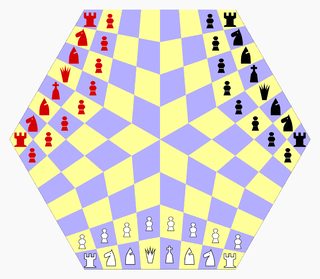
Three-Man Chess is a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle, Sr. in 1984. The game is played on a hexagonal board comprising 96 quadrilateral cells. Each player controls a standard army of chess pieces.
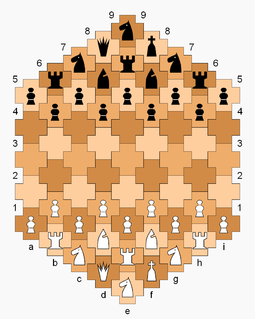
Cross Chess is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle, Sr. in 1982. The game is played on a board comprising 61 cross-shaped cells, with players each having an extra rook, knight, and pawn in addition to the standard number of chess pieces. Pieces move in the context of a gameboard with hexagonal cells, but Cross Chess has its own definition of ranks and diagonals.

Quatrochess is a chess variant for four players invented by George R. Dekle, Sr. in 1986. The board comprises 14×14 squares minus the four central squares. Each player controls a standard set of sixteen chess pieces, and additionally nine fairy pieces. The game can be played in partnership or all-versus-all.
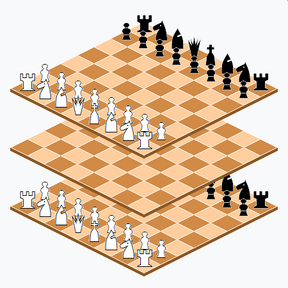
Parallel Worlds Chess is a three-dimensional chess variant invented by R. Wayne Schmittberger in the 1980s. The gamespace comprises three 8×8 chessboards at different levels. Each side commands two full chess armies on levels 1 and 3. Level 2 begins empty and obeys its own move rules.

Falcon-Hunter Chess is a chess variant invented by Karl Schultz in 1943 employing the two fairy chess pieces falcon and hunter. The game takes several forms, including variations Hunter Chess and Decimal Falcon-Hunter Chess added in the 1950s.

Hostage Chess is a chess variant invented by John Leslie in 1997. Captured pieces are not eliminated from the game but can reenter active play through drops, similar to shogi. Unlike shogi, the piece a player may drop is one of his own pieces previously captured by the opponent. In exchange, the player returns a previously captured enemy piece which the opponent may drop on a future turn. This is the characteristic feature of the game.

A chess variant is a game "related to, derived from, or inspired by chess". Such variants can differ from chess in many different ways, ranging from minor modifications to the rules, to games which have only a slight resemblance.






















