Baroque chess is a chess variant invented in 1962 by Robert Abbott. In 1963, at the suggestion of his publisher, he changed the name to Ultima, by which name it is also known. Abbott later considered his invention flawed and suggested amendments to the rules, but these suggestions have been substantially ignored by the gaming community, which continues to play by the 1962 rules. Since the rules for Baroque were first laid down in 1962, some regional variation has arisen, causing the game to diverge from Ultima.
Circe chess is a chess variant in which captured pieces are reborn on their starting positions as soon as they are captured. The game was invented by French composer Pierre Monréal in 1967 and the rules of Circe chess were first detailed by Monréal and Jean-Pierre Boyer in an article in Problème, 1968.
Monster chess—or Super King chess—is a chess variant in which the White side has only a king and four pawns to fight against all the pieces of the Black side. All the rules of chess apply, except that White makes two successive moves per turn. The white king can move into check on the first move of the turn and move out of check during the second move. The goal for both sides is to checkmate the opponent's king.
Capablanca chess is a chess variant invented in the 1920s by World Chess Champion José Raúl Capablanca. It incorporates two new pieces and is played on a 10×8 board. Capablanca believed that chess would be played out in a few decades. This threat of "draw death" for chess was his main motivation for creating a more complex version of the game.
A fairy chess piece, variant chess piece, unorthodox chess piece, or heterodox chess piece is a chess piece not used in conventional chess but incorporated into certain chess variants and some chess problems. Compared to conventional pieces, fairy pieces vary mostly in the way they move, but they may also follow special rules for capturing, promotions, etc. Because of the distributed and uncoordinated nature of unorthodox chess development, the same piece can have different names, and different pieces can have the same name in various contexts as it can be noted in the list of fairy chess pieces.
Progressive chess is a chess variant in which players, rather than just making one move per turn, play progressively longer series of moves. The game starts with White making one move, then Black makes two consecutive moves, White replies with three, Black makes four and so on. Progressive chess can be combined with other variants; for example, when Circe chess is played as a game, it is usually progressively. Progressive chess is considered particularly apt for playing correspondence chess using mail or some other slow medium, because of the relatively small number of moves in a typical game.
Madrasi chess is a chess variant invented in 1979 by Abdul Jabbar Karwatkar. The game uses the conventional rules of chess with the addition that when a piece is attacked by a piece of the same type but opposite colour it is paralysed and becomes unable to move, capture or give check.

Vernon Rylands Parton was an English chess enthusiast and prolific chess variant inventor, his most renowned variants being Alice chess and Racing Kings. Many of Parton's variants were inspired by the fictional characters and stories in the works of Lewis Carroll. Parton's formal education background, like Lewis Carroll's, was in mathematics. Parton's interests were wide and he was a great believer in Esperanto.
Extinction chess is a chess variant invented by R. Wayne Schmittberger, editor of Games magazine, in 1985. Instead of checkmate as the winning condition, the object of the game is the elimination of all of a particular type of piece of the opponent. In other words, the objective is any of the following:
Kriegspiel is a chess variant invented by Henry Michael Temple in 1899 and based upon the original Kriegsspiel developed by Georg von Reiswitz in 1812. In this game, each player can see their own pieces but not those of their opponent. For this reason, it is necessary to have a third person act as an umpire, with full information about the progress of the game. Players attempt to move on their turns, and the umpire declares their attempts 'legal' or 'illegal'. If the move is illegal, the player tries again; if it is legal, that move stands. Each player is given information about checks and captures. They may also ask the umpire if there are any legal captures with a pawn. Since the position of the opponent's pieces is unknown, Kriegspiel is a game of imperfect information.

Hexagonal chess is a group of chess variants played on boards composed of hexagon cells. The best known is Gliński's variant, played on a symmetric 91-cell hexagonal board.
Dunsany's chess, also known as Dunsany's game, is an asymmetric chess variant in which Black has the standard chess army and White has 32 pawns. This game was invented by Lord Dunsany in 1942. It was published the same year in Fairy Chess Review and in Joseph Boyer's Nouveaux Jeux d'Echecs Non-orthodoxes.
Monochromatic chess is a chess variant with unknown origin. The initial board position and all rules are the same as in regular chess, except that pieces that begin on a black square must always stay on a black square and pieces that begin on a white square must always stay on a white square. This would mean that knights can never move, but The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants says that knights make a double jump. It has been suggested that a knight be replaced with a (3,1)-leaper (camel).

2000 A.D. is a chess variant created by V. R. Parton which employs fairy chess pieces on a 10×10 board. Parton published the variant in his 1972 monograph My Game for 2000 A.D. and After.
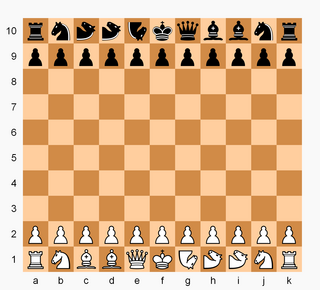
Wildebeest chess is a chess variant created by R. Wayne Schmittberger in 1987. The Wildebeest board is 11×10 squares. Besides the standard chess pieces, each side has two camels and one "wildebeest" - a piece which may move as either a camel or a knight.

The amazon, also known as the queen+knight compound or the dragon, is a fairy chess piece that can move like a queen or a knight. It may thus be considered the sum of all orthodox chess pieces other than the king and the pawn. The amazon can force checkmate on an enemy king without the help of any other friendly piece.

Chesquerque is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board composed of four Alquerque boards combined into a square. Like Alquerque, pieces are positioned on points of intersection and make their moves along marked lines ; as such, the board comprises a 9×9 grid with 81 positions (points) that pieces can move to.

Hostage chess is a chess variant invented by John A. Leslie in 1997. Captured pieces are not eliminated from the game but can reenter active play through drops, similar to shogi. Unlike shogi, the piece a player may drop is one of their own pieces previously captured by the opponent. In exchange, the player returns a previously captured enemy piece which the opponent may drop on a future turn. This is the characteristic feature of the game.
Dynamo chess is a chess variant invented by chess problemists Hans Klüver and Peter Kahl in 1968. The invention was inspired by the closely related variant push chess, invented by Fred Galvin in 1967. The pieces, board, and starting position of Dynamo chess are the same as in orthodox chess, but captures are eliminated and enemy pieces are instead "pushed" or "pulled" off the board. On any given move, a player can make a standard move as in orthodox chess, or execute a "push move" or a "pull move". A move that is either a push move or a pull move is called a "dynamo move".







