Three-dimensional chess is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other.
A fairy chess piece, variant chess piece, unorthodox chess piece, or heterodox chess piece is a chess piece not used in conventional chess but incorporated into certain chess variants and some chess problems. Compared to conventional pieces, fairy pieces vary mostly in the way they move, but they may also follow special rules for capturing, promotions, etc. Because of the distributed and uncoordinated nature of unorthodox chess development, the same piece can have different names, and different pieces can have the same name in various contexts. Most are symbolised as inverted or rotated icons of the standard pieces in diagrams, and the meanings of these "wildcards" must be defined in each context separately. Pieces invented for use in chess variants rather than problems sometimes instead have special icons designed for them, but with some exceptions, many of these are not used beyond the individual games for which they were invented.

Hexagonal chess is a group of chess variants played on boards composed of hexagon cells. The best known is Gliński's variant, played on a symmetric 91-cell hexagonal board.
Wildebeest chess is a chess variant created by R. Wayne Schmittberger in 1987. The Wildebeest board is 11×10 squares. Besides the standard chess pieces, each side has two camels and one "wildebeest" - a piece which may move as either a camel or a knight.

Dragonfly is a chess variant invented by Christian Freeling in 1983. There are no queens, and a captured bishop, knight, or rook becomes the property of the capturer, who may play it as their own on a turn to any open square. The board is 7×7 squares, or alternatively a 61-cell hexagon with two additional pawns per side.

Rhombic chess is a chess variant for two players created by Tony Paletta in 1980. The gameboard has an overall hexagonal shape and comprises 72 rhombi in three alternating colors. Each player commands a full set of standard chess pieces.

Wolf chess is a chess variant invented by Dr. Arno von Wilpert in 1943. It is played on an 8×10 chessboard and employs several fairy pieces including wolf and fox – compound pieces popular in chess variants and known by different names.

Trishogi is a shogi variant for two players created by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1987. The gameboard comprises 9×10 interlocking triangular cells. The game is in all respects the same as shogi, except that piece moves have been transfigured for the triangular board-cell geometry.
Hexshogi is a shogi variant for two players created by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The gameboard comprises 85 hexagonal cells. The game is in all respects the same as shogi, except that piece moves have been transfigured for the hexagonal board-cell geometry.

Masonic chess is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1983. The game is played on a modified chessboard whereby even-numbered ranks are indented to the right—resembling masonry brickwork. The moves of the pieces are adapted to the new geometry; in other respects the game is the same as chess.

Masonic shogi is a shogi variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1987. The game is played on a modified shogi board whereby alternating ranks are indented to the right—resembling masonry brickwork. The moves of pieces are adapted to the new geometry; in other respects the game is the same as shogi.

Chesquerque is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board composed of four Alquerque boards combined into a square. Like Alquerque, pieces are positioned on points of intersection and make their moves along marked lines ; as such, the board comprises a 9×9 grid with 81 positions (points) that pieces can move to.

Tri-chess is the name of a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board comprising 150 triangular cells. The standard chess pieces are present, minus the queens, and plus the chancellor and cardinal compound fairy pieces per side.
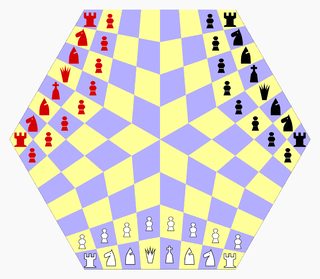
Three-man chess is a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1984. The game is played on a hexagonal board comprising 96 quadrilateral cells. Each player controls a standard army of chess pieces.
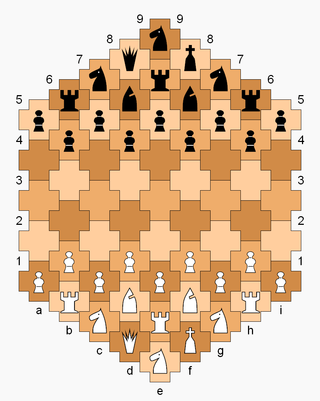
Cross chess is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1982. The game is played on a board comprising 61 cross-shaped cells, with players each having an extra rook, knight, and pawn in addition to the standard number of chess pieces. Pieces move in the context of a gameboard with hexagonal cells, but Cross chess has its own definition of ranks and diagonals.

Quatrochess is a chess variant for four players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. It is played on a square 14×14 board that excludes the four central squares. Each player controls a standard set of sixteen chess pieces, and additionally nine fairy pieces. The game can be played in partnership or all-versus-all.

Rollerball is a chess variant invented by Jean-Louis Cazaux in 1998. The game was inspired by the 1975 science-fiction movie Rollerball, specifically the futuristic and violent sport portrayed in the film.

Falcon–hunter chess is a chess variant invented by Karl Schultz in 1943, employing the two fairy chess pieces falcon and hunter. The game takes several forms, including variations hunter chess and decimal falcon–hunter chess added in the 1950s.

Congo is a chess variant invented by Demian Freeling in 1982 when he was nearly 8 years old. His father encouraged him to design a variant using a 7×7 gameboard. Demian was already familiar with chess and xiangqi, and the result blends some features from both. Congo became the second-most popular chess variant at the Fanaat games club in Enschede, the Netherlands.