Checkless chess, also known as prohibition chess, is a chess variant where neither player may give check unless it is checkmate. All other rules are as in regular chess. The origin of the game is unknown, dating from the mid-19th century. The variant is a popular problem theme, usually requiring a fairy mate.

Hexagonal chess is a group of chess variants played on boards composed of hexagon cells. The best known is Gliński's variant, played on a symmetric 91-cell hexagonal board.
Three-player chess is a family of chess variants specially designed for three players. Many variations of three-player chess have been devised. They usually use a non-standard board, for example, a hexagonal or three-sided board that connects the center cells in a special way. The three armies are differentiated usually by color.

Dragonfly is a chess variant invented by Christian Freeling in 1983. There are no queens, and a captured bishop, knight, or rook becomes the property of the capturer, who may play it as their own on a turn to any open square. The board is 7×7 squares, or alternatively a 61-cell hexagon with two additional pawns per side.

Rhombic chess is a chess variant for two players created by Tony Paletta in 1980. The gameboard has an overall hexagonal shape and comprises 72 rhombi in three alternating colors. Each player commands a full set of standard chess pieces.

Triangular chess is a chess variant for two players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a hexagon-shaped gameboard comprising 96 triangular cells. Each player commands a full set of chess pieces in addition to three extra pawns and a unicorn.

Trishogi is a shogi variant for two players created by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1987. The gameboard comprises 9×10 interlocking triangular cells. The game is in all respects the same as shogi, except that piece moves have been transfigured for the triangular board-cell geometry.
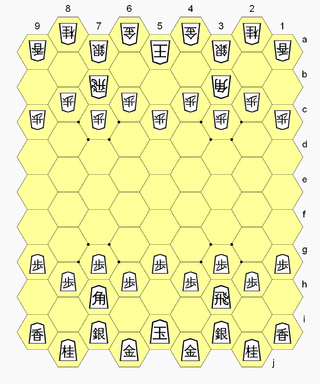
Hexshogi is a shogi variant for two players created by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The gameboard comprises 85 hexagonal cells. The game is in all respects the same as shogi, except that piece moves have been transfigured for the hexagonal board-cell geometry.

Masonic chess is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1983. The game is played on a modified chessboard whereby even-numbered ranks are indented to the right—resembling masonry brickwork. The moves of the pieces are adapted to the new geometry; in other respects the game is the same as chess.

Masonic shogi is a shogi variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1987. The game is played on a modified shogi board whereby alternating ranks are indented to the right—resembling masonry brickwork. The moves of pieces are adapted to the new geometry; in other respects the game is the same as shogi.

Chesquerque is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board composed of four Alquerque boards combined into a square. Like Alquerque, pieces are positioned on points of intersection and make their moves along marked lines ; as such, the board comprises a 9×9 grid with 81 positions (points) that pieces can move to.

Tri-chess is the name of a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board comprising 150 triangular cells. The standard chess pieces are present, minus the queens, and plus the chancellor and cardinal compound fairy pieces per side.
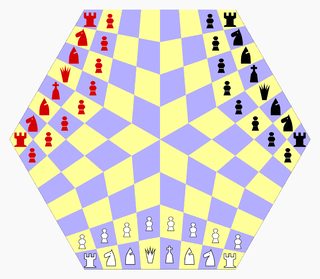
Three-man chess is a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1984. The game is played on a hexagonal board comprising 96 quadrilateral cells. Each player controls a standard army of chess pieces.
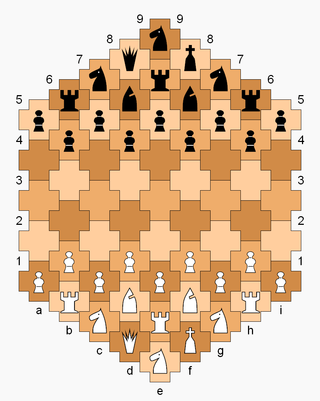
Cross chess is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1982. The game is played on a board comprising 61 cross-shaped cells, with players each having an extra rook, knight, and pawn in addition to the standard number of chess pieces. Pieces move in the context of a gameboard with hexagonal cells, but Cross chess has its own definition of ranks and diagonals.

Quatrochess is a chess variant for four players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. It is played on a square 14×14 board that excludes the four central squares. Each player controls a standard set of sixteen chess pieces, and additionally nine fairy pieces. The game can be played in partnership or all-versus-all.

Space shogi is a three-dimensional shogi variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1987. The gamespace comprises nine 9×9 shogi boards stacked vertically. Each player controls a standard set of shogi pieces.

George Robert "Bob" Dekle Sr. is an American lawyer who was an Assistant State Attorney in Florida's Third Judicial Circuit from 1975 through 2005. During this time, he served as lead prosecuting attorney in the 1980 Orlando murder trial of serial killer Ted Bundy, which ultimately delivered the death penalty that was carried out in 1989. Dekle's book on the case, The Last Murder: The Investigation, Prosecution, and Execution of Ted Bundy, was published in 2011.
Chancellor chess is a chess variant invented by Benjamin R. Foster in 1887. It features all the regular chess pieces plus one chancellor and extra pawn per side, on a 9×9 board.

A chess variant is a game related to, derived from, or inspired by chess. Such variants can differ from chess in many different ways.

















