
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 22 January 2003.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 14 June 1901. The Liberal Democratic League remained the largest party, winning 26 of the 100 seats in the House of Representatives.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 16 June 1905. The Liberal Democratic League remained the largest party, winning 34 of the 100 seats in the House of Representatives.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 11 June 1909. The Anti-Revolutionary Party and the General League of Roman Catholic Caucuses emerged as the largest parties, each winning 25 of the 100 seats in the House of Representatives.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 1 July 1925. The General League of Roman Catholic Caucuses remained the largest party in the House of Representatives, winning 30 of the 100 seats.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 3 July 1929. The Roman Catholic State Party remained the largest party in the House of Representatives, winning 30 of the 100 seats.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 26 April 1933. The Roman Catholic State Party remained the largest party in the House of Representatives, winning 28 of the 100 seats.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 26 May 1937. The Roman Catholic State Party remained the largest party in the House of Representatives, winning 31 of the 100 seats.
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 17 May 1946, the first after World War II. The Catholic People's Party, a continuation of the pre-war Roman Catholic State Party, remained the largest party in the House of Representatives, winning 32 of the 100 seats.
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 7 July 1948. The Catholic People's Party remained the largest party in the House of Representatives, winning 32 of the 100 seats.
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 25 June 1952. The Catholic People's Party and the Labour Party both won 30 of the 100 seats in the House of Representatives. It was the first time since 1913 that the Catholic People's Party and its predecessors had not received a plurality of the vote.
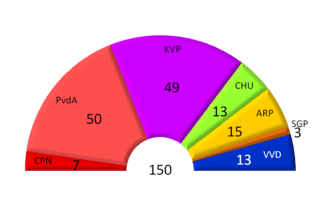
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 13 June 1956. For the first time, the Labour Party (PvdA) emerged as the largest party, winning 50 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives.
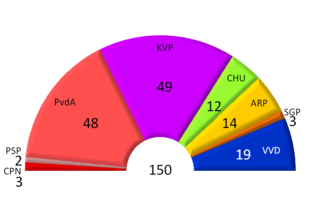
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 12 March 1959. The Catholic People's Party emerged as the largest party, winning 49 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 15 February 1967. The Catholic People's Party (KVP) remained the largest party, winning 42 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives.

Early general elections were held in the Netherlands on 29 November 1972. The Labour Party (PvdA) remained the largest party, winning 43 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 25 May 1977. The Labour Party remained the largest party, winning 53 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives. Following the election, it took 208 days of negotiations to form a new government. This was a European record for longest government formation that stood until after the 2010 Belgian general election. The Christian Democratic Appeal was formed by the Anti-Revolutionary Party (ARP), Christian Historical Union (CHU) and the Catholic People's Party (KVP) in 1976. The first joint party leader was a member of the KVP, Dries van Agt.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 26 May 1981. The Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA) emerged as the largest party, winning 48 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives.

Early general elections were held in the Netherlands on 8 September 1982. The Labour Party emerged as the largest party, winning 47 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives.
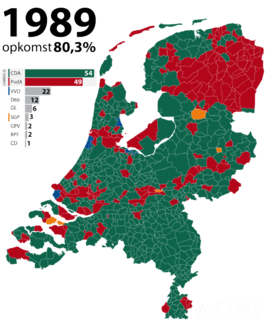
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 6 September 1989. The Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA) remained the largest party, winning 54 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives. This chamber served for 4 years and 7 months, the longest tenure of any modern Dutch parliament.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 3 May 1994. The Labour Party emerged as the largest party, winning 37 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives. The election resulted in significant losses for both the Labour Party and the Christian Democratic Appeal. The two liberal parties, People's Party for Freedom and Democracy and Democrats 66 made large gains, whilst two pro-elderly parties and the Socialist Party all passed the electoral threshold to win seats.
















