
Acropomatidae is a family of ray-finned fish in the order Acropomatiformes, commonly known as lanternbellies. Acropoma species are notable for having light-emitting organs along their undersides. They are found in all temperate and tropical oceans, usually at depths of several hundred meters. There are about 32 species in as many as 9 genera, although some authorities recognise fewer genera than Fishbase does.

Ophichthidae is a family of fish in the order Anguilliformes, commonly known as the snake eels. The term "Ophichthidae" comes from Greek ophis ("serpent") and ichthys ("fish"). Snake eels are also burrowing eels. They are named for their physical appearance, as they have long, cylindrical, snake-like bodies. This family is found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate waters. They inhabit a wide range of habitats, from coastal shallows and even rivers, to depths below 800 m (2,600 ft). Most species are bottom dwellers, hiding in mud or sand to capture their prey of crustaceans and small fish, but some are pelagic.

Cutthroat eels are a family, Synaphobranchidae, of eels, the only members of the suborder Synaphobranchoidei. They are found worldwide in temperate and tropical seas.

Ilyophis is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. These eels are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Plectranthias is a genus of ray-finned fish in the subfamily Anthiinae, part of the family Serranidae, the groupers and sea basses. They are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean.

Malthopsis, the gnome batfishes or triangular batfishes, is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes. The triangular batfishes are distributed throughout the warmer waters of the world, although they are absent from the Eastern Atlantic Ocean. The genus was originally proposed in 1891 by the British naturalist Alfred W. Alcock.
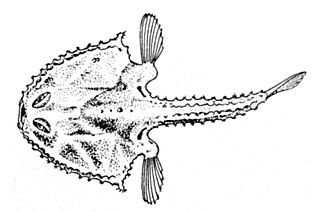
Halieutaea is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ogcocephalidae, the deep sea batfishes. These fishes are found in the Indian and Western Pacific Oceans.
Atractodenchelys is a genus of eels in the cutthroat eel family, Synaphobranchidae.

Dysommina is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. These eels are known from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Meadia is a genus of eels in the cutthroat eel family Synaphobranchidae. It currently contains the following species:

Dysomma anguillare, the shortbelly eel, stout moray, mustard eel or arrowtooth eel, is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Keppel Harcourt Barnard in 1923. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean and Indo-Western Pacific, including the United States, Venezuela, South Africa, Zanzibar, and Japan. It lives at a depth range of 30 to 270 metres, and inhabits muddy sediments in coastal waters and large rivermouths. Males can reach a maximum total length of 52 centimetres (20 in).
Dysomma dolichosomatum is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Christine Karrer in 1983. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific. It dwells at a depth range of 550–555 metres.
Dysomma fuscoventralis is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Christine Karrer and Wolfgang Klausewitz in 1982. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is endemic to the Red Sea. It dwells at a depth range of 750–1425 metres.
Dysomma goslinei is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins and Charles Richard Robins in 1976. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific. Males can reach a maximum total length of 19.7 centimetres.
Dysomma longirostrum is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Chen Yu-Yun and Michael Hin-Kiu Mok in 2001. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling eel which is known from Taiwan, in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 100–150 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 19.6 centimetres.
Dysomma melanurum is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Johnson T. F. Chen and Herman Ting-Chen Weng in 1967. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western Pacific Ocean. Males can reach a maximum total length of 23.7 centimetres.
Dysomma opisthoproctus is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Chen Yu-Yun and Michael Hin-Kiu Mok in 1995. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known only from northeastern Taiwan, in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 200 metres. Males are known to reach a total length of 42.1 centimetres.
Dysomma polycatodon is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Christine Karrer in 1983. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 170–175 metres.

Chelidoperca, commonly known as perchlet, is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes which is a member of the subfamily Serraninae of the family Serranidae, which includes the groupers and anthias. They are found in the Indo-Pacific region.

Ilyophinae, the arrowtooth ells or mustard eels, is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes belongiing to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. Within its family this subfamily shows greatest number of species and the greatest morphological diversity.









