
The Nymphalidae are the largest family of butterflies, with more than 6,000 species distributed throughout most of the world. Belonging to the superfamily Papilionoidea, they are usually medium-sized to large butterflies. Most species have a reduced pair of forelegs and many hold their colourful wings flat when resting. They are also called brush-footed butterflies or four-footed butterflies, because they are known to stand on only four legs while the other two are curled up; in some species, these forelegs have a brush-like set of hairs, which gives this family its other common name. Many species are brightly coloured and include popular species such as the emperors, monarch butterfly, admirals, tortoiseshells, and fritillaries. However, the under wings are, in contrast, often dull and in some species look remarkably like dead leaves, or are much paler, producing a cryptic effect that helps the butterflies blend into their surroundings.

Apocynaceae is a family of flowering plants that includes trees, shrubs, herbs, stem succulents, and vines, commonly known as the dogbane family, because some taxa were used as dog poison. Members of the family are native to the European, Asian, African, Australian, and American tropics or subtropics, with some temperate members. The former family Asclepiadaceae is considered a subfamily of Apocynaceae and contains 348 genera. A list of Apocynaceae genera may be found here.

Pachypodium is a genus of succulent spine-bearing trees and shrubs, native to Madagascar and Africa. It belongs to the family Apocynaceae.

The Asclepiadoideae are a subfamily of plants in the family Apocynaceae. Formerly, it was treated as a separate family under the name Asclepiadaceae, e.g. by APG II, and known as the milkweed family.

Ceropegia is a genus of plants within the family Apocynaceae, native to Africa, southern Asia, and Australia. It was named by Carl Linnaeus, who first described this genus in his Genera plantarum, which appeared in 1737. Linnaeus referred to the description and picture of a plant in the Horti Malabarici as the plant for which the genus was created. In 1753 he named this species as Ceropegia candelabrum. Linnaeus did not explain the etymology but later explanations stated that the name Ceropegia was from the Greek word keropegion κηροπηγɩον. This means candelabrum in Latin, which has a broader range than the modern word - "a candlestick, a branched candlestick, a chandelier, candelabrum, or also lamp-stand, light-stand, sometimes of exquisite workmanship".

Dogbane, dog-bane, dog's bane, and other variations, some of them regional and some transient, are names for certain plants that are reputed to kill or repel dogs; "bane" originally meant "slayer", and was later applied to plants to indicate that they were poisonous to particular creatures.

Apocynoideae is a subfamily of the flowering plant family Apocynaceae, also called the 'dogbane' or milkweed family, containing about 860 species across 78 genera. Several are of pharmacological interest; Strophanthus has furnished highly effective arrow poisons, due to their cardiac glycoside content. Apocynoideae also includes many popular landscaping and ornamental species, one of the best-known, and most infamous, being the oleander ; the subfamily also contains remarkable pachycaul genera like Adenium and Pachypodium.

Hancornia is a genus of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1812. It is native to South America. It contains only one known species, Hancornia speciosa, commonly called mangabeira, which produces fruits known as mangabas.

Thevetia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described for modern science as a genus in 1758. It is native to Mexico, Central America, South America, and Cuba. The taxonomy of the genus is controversial, with some authors including Cascabela within Thevetia, while others accept the two genera as separate.

John Miers, FRS FLS, knight grand cross of the Order of the Rose, was a British botanist and engineer, best known for his work on the flora of Chile and Argentina.

Dyera is a genus of tropical trees up to 80 m in height. They are in family Apocynaceae, native to southeast Asia. It was first described as a genus in 1882, by Joseph Dalton Hooker.

Ichnocarpus frutescens is a species of flowering plant in the dogbane family Apocynaceae, known by the English common name black creeper. It is native to much of China, India, Southeast Asia, and northern Australia.
Haplophyton is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described in 1844. It is native to the southwestern United States, Mexico, Cuba, and Guatemala. It is a suffrutescent herb with alternative leaves and showy colorful flowers.

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.
Farquharia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1912. It contains only one recognized species, Farquharia elliptica, native to tropical western and central Africa.
Mortoniella is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1939. It contains only one known species, Mortoniella pittieri, native to Central America.
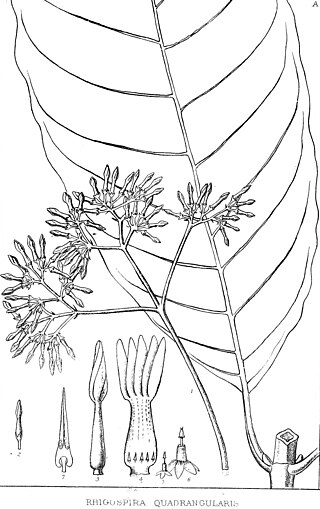
Rhigospira is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1878 by John Miers. The species, Rhigospira quadrangularis was first described as Ambelania quadrangularis by Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1860 but was transferred to the genus, Rhigospira, in 1878 by John Miers. The genus contains only one known species, Rhigospira quadrangularis, native to northwestern South America.
Artia is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described in 1941. The genus is endemic to New Caledonia and the nearby Loyalty Islandsin the SW Pacific. Artia is closely related to Parsonsia and Prestonia.

Periplocoideae is a subfamily of the dogbane plant family, Apocynaceae. It was not divided into tribes as of 2014.
The European Conference on Underwater Acoustics (ECUA) was a conference on underwater acoustics that took place in Europe every two years, until 2012, when it was held in Edinburgh (Scotland), and organized by the Institute of Acoustics. Previous editions took place in Delft, Algarve, and Paris and Istanbul.














