Gwynedd is a county in the north-west of Wales. It borders Anglesey across the Menai Strait to the north, Conwy, Denbighshire, and Powys to the east, Ceredigion over the Dyfi estuary to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. The city of Bangor is the largest settlement, and the administrative centre is Caernarfon. The preserved county of Gwynedd, which is used for ceremonial purposes, includes the Isle of Anglesey.

Powys is a county and preserved county in Wales. It borders Gwynedd, Denbighshire, and Wrexham to the north; the English ceremonial counties of Shropshire and Herefordshire to the east; Monmouthshire, Blaenau Gwent, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Rhondda Cynon Taf, and Neath Port Talbot to the south; and Carmarthenshire and Ceredigion to the west. The largest settlement is Newtown, and the administrative centre is Llandrindod Wells.

Caernarfonshire, sometimes spelled Caernarvonshire or Carnarvonshire, was one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales, in the north-west of Wales.

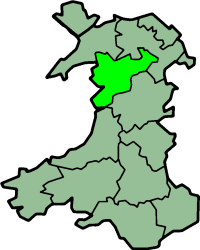
Merionethshire, or Merioneth, was one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales, in the north-west of Wales.

Montgomeryshire was one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales. It was named after its county town, Montgomery, which in turn was named after one of William the Conqueror's main counsellors, Roger de Montgomerie, who was the 1st Earl of Shrewsbury.

Denbighshire is a county in the north-east of Wales. It borders the Irish Sea to the north, Flintshire to the east, Wrexham to the southeast, Powys to the south, and Gwynedd and Conwy to the west. Rhyl is the largest town, and Ruthin is the administrative centre. Its borders differ from the historic county of the same name.

Denbighshire, or the County of Denbigh, was one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales, in the north of Wales. It was a maritime county, that was bounded to the north by the Irish Sea, to the east by Flintshire, Cheshire and Shropshire, to the south by Montgomeryshire and Merionethshire, and to the west by Caernarfonshire.

The Statute of Rhuddlan, also known as the Statutes of Wales or as the Statute of Wales, was a royal ordinance by Edward I of England, which gave the constitutional basis for the government of the Principality of Wales from 1284 until 1536.
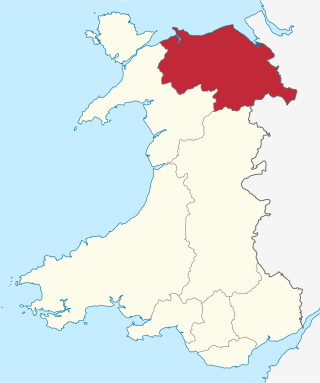
Clwyd is a preserved county of Wales, situated in the north-east corner of the country; it is named after the River Clwyd, which runs through the area. To the north lies the Irish Sea, with the English ceremonial counties of Cheshire to the east and Shropshire to the south-east. Powys and Gwynedd lie to the south and west respectively. Clwyd also shares a maritime boundary with Merseyside along the River Dee. Between 1974 and 1996, a slightly different area had a county council, with local government functions shared with six district councils. In 1996, Clwyd was abolished, and the new principal areas of Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Flintshire and Wrexham County Borough were created; under this reorganisation, "Clwyd" became a preserved county, with the name being retained for certain ceremonial functions.

Corwen is a town and community in the county of Denbighshire in Wales. Historically, Corwen was part of the county of Merionethshire. Corwen stands on the banks of the River Dee beneath the Berwyn mountains. The town is situated 10 miles (16 km) west of Llangollen and 13 miles (21 km) south of Ruthin. At the 2011 Census, Corwen had a population of 2,325, decreasing slightly from the 2001 population of 2,398, The community, with an area of 69.51 km2 (26.84 sq mi), includes Corwen and the surrounding villages of Carrog, Clawdd Poncen and Glyndyfrdwy. The Office for National Statistics identifies Corwen Built-up area with a 2011 population of 477 and an area of 0.25 km2 (0.097 sq mi).

The Principality of Wales was originally the territory of the native Welsh princes of the House of Aberffraw from 1216 to 1283, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales during its height of 1267–1277. Following the conquest of Wales by Edward I of England of 1277 to 1283, those parts of Wales retained under the direct control of the English crown, principally in the north and west of the country, were re-constituted as a new Principality of Wales and ruled either by the monarch or the monarch's heir though not formally incorporated into the Kingdom of England. This was ultimately accomplished with the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542 when the Principality ceased to exist as a separate entity.

Powys Fadog was the northern portion of the former princely realm of Powys. The princes of Powys Fadog would build their royal seat at Castell Dinas Brân, and their religious center at Valle Crucis Abbey. Some of its lordships included those of Maelor, Mochnant, Glyndyfrdwy, Yale, and Bromfield and Yale. Following the division of Powys, their cousin branch, the princes of Powys Wenwynwyn, would build Powis Castle.

The Llŷn Peninsula is a peninsula in Gwynedd, Wales, with an area of about 400 km2 (150 sq mi), and a population of at least 20,000. It extends 30 miles (50 km) into the Irish Sea, and its southern coast is the northern boundary of the Tremadog Bay inlet of Cardigan Bay. The peninsula was a cantref within the medieval kingdom of Gwynedd, and became part of Caernarfonshire from 1284 until that county was abolished for administrative purposes in 1974. It borders Arfon and Eifionydd to the east, but the boundary is vague.

Gruffudd Fychan I, was a Prince of Powys Fadog from 1277 to 1284. He paid homage to Edward Longshanks for the Lordship of Yale, and fought the War of 1282–1283.

Hughes of Gwerclas were a native Welsh royal family descended from prince Owain Brogyntyn the illegitimate but acknowledged son of prince Madog ap Maredudd by a daughter of the "Maer du" or "black mayor" of Rûg in Edernion. His father granted to him and his successors the Cantref of Edeyrnion and the Lordship of Dinmael. These areas were both remote frontier lands situated between Powys and the neighbouring ascendant Kingdom of Gwynedd. From the earlier part of the 12th Century both lordships usually paid homage to Gwynedd.

Rhug is a township in the parish of Corwen, Denbighshire, Wales, formerly in the old cantref of Edeirnion and later a part of Merionethshire, two miles from Corwen and ten miles north east of Bala. It includes the hamlet of Bonwen. It is situated near the River Dee, under Berwyn range. About 1150, it was ruled by the Maer Du or "Black Mayor of Rhug" and later became part of the lands of the barons of Edeirnion who ruled from Gwerclas Castle.

Llansanffraid Glyndyfrdwy is a former civil parish in the Edeirnion area of Denbighshire in Wales. Until 1974 it was part of Merionethshire, and was transferred to Glyndŵr District in Clwyd by the Local Government Act 1972. It became part of Denbighshire in 1996, and now forms part of the community of Corwen. It includes the village of Carrog.

Betws Gwerfil Goch is a village and community in Denbighshire, Wales. It had a population of 351 at the 2011 census. Until 1974 it was part of Edeirnion Rural District in Meirionnydd, and was transferred to Glyndŵr District in Clwyd by the Local Government Act 1972. It became part of Denbighshire in 1996. The community includes Melin-y-Wig village.

The conquest of Wales by Edward I took place between 1277 and 1283. It is sometimes referred to as the Edwardian conquest of Wales, to distinguish it from the earlier Norman conquest of Wales. In two campaigns, in 1277 and 1282–83, respectively, Edward I of England first greatly reduced the territory of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, and then completely overran it, as well as the other remaining Welsh principalities.