Related Research Articles
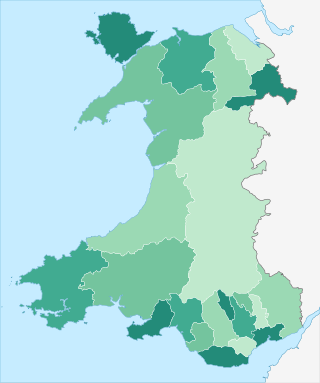
Since 1 April 1996, Wales has been divided into 22 single-tier principal areas, styled as counties or county boroughs for local government purposes. The elected councils of these areas are responsible for the provision of all local government services, including education, social work, environmental protection, and most highways. Below these there are also elected community councils to which responsibility for specific aspects of the application of local policy may be devolved. The last set of local elections in Wales took place in 2022, with the next due to take place in 2027.

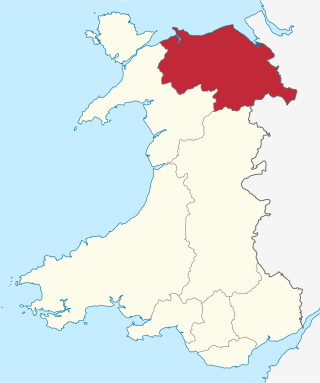
Flintshire is a county in the north-east of Wales. It has a maritime border with Merseyside along the Dee Estuary to the north, and land borders with Cheshire to the east, Wrexham County Borough to the south, and Denbighshire to the west. Connah's Quay is the largest town, while Flintshire County Council is based in Mold.
Flintshire, also known as the County of Flint, is one of Wales' thirteen historic counties, and a former administrative county. It mostly lies on the north-east coast of Wales.
Clwyd is a preserved county of Wales, situated in the north-east corner of the country; it is named after the River Clwyd, which runs through the area. To the north lies the Irish Sea, with the English ceremonial counties of Cheshire to the east and Shropshire to the south-east. Powys and Gwynedd lie to the south and west respectively. Clwyd also shares a maritime boundary with Merseyside along the River Dee. Between 1974 and 1996, a slightly different area had a county council, with local government functions shared with six district councils. In 1996, Clwyd was abolished, and the new principal areas of Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Flintshire and Wrexham County Borough were created; under this reorganisation, "Clwyd" became a preserved county, with the name being retained for certain ceremonial functions.

North Wales is a region of Wales, encompassing its northernmost areas. It borders mid Wales to the south, England to the east, and the Irish Sea to the north and west. The area is highly mountainous and rural, with Snowdonia National Park and the Clwydian Range and Dee Valley, known for its mountains, waterfalls and trails, wholly within the region. Its population is concentrated in the north-east and northern coastal areas, with significant Welsh-speaking populations in its western and rural areas. North Wales is imprecisely defined, lacking any exact definition or administrative structure. It is commonly defined administratively as its six most northern principal areas, but other definitions exist, with Montgomeryshire historically considered to be part of the region.

The Borderlands line, also known as the Bidston–Wrexham or Wrexham–Bidston line, is a railway line between Bidston on the Wirral Peninsula in England and Wrexham Central in the north-east of Wales. Passenger train services are part of the Wales & Borders franchise and are operated by Transport for Wales Rail. The line connects to the Merseyrail network at Bidston, the North Wales Coast Line at Shotton and the Shrewsbury–Chester line at Wrexham General. Parts of the line in Wales are used by freight trains, serving Deeside Industrial Park and the Hanson Cement works to the south of Buckley.

North Wales Police is the territorial police force responsible for policing North Wales. Its headquarters are in Colwyn Bay. As of March 2020, the force has 1,510 police officers, 170 special constables, 182 police community support officers (PCSO), 71 police support volunteers (PSV), and 984 staff.
The South West Wales Integrated Transport Consortium is an alliance of four unitary authorities in south west Wales: Pembrokeshire, Swansea, Neath Port Talbot and Carmarthenshire. It is one of four transport consortia supported by the Welsh Government.

Foryd railway station was a railway station built to serve Kinmel Bay, then in Flintshire but now in Conwy County Borough, Wales.

The South Wales Metro is an integrated heavy rail, light rail and bus-based public transport services and systems network currently being developed in South East Wales around the hub of Cardiff Central. The first phase was approved for development in October 2013. Works are currently under way, with a brand new depot under construction at Taff's Well and new trains being built by Stadler Rail in Switzerland. The development will also include the electrification of the core Valley Lines and new stations.

North East Wales is an area or region of Wales, commonly defined as a grouping of the principal areas of Denbighshire, Flintshire, and Wrexham County Borough in the north-east of the country. These principal areas comprise most of the former administrative county of Clwyd. It is bordered by Conwy, and Gwynedd, in North West Wales to the west, Powys, in Mid Wales to the south, the English counties of Cheshire, and Shropshire to the east, and the Irish Sea, and Dee estuary to the north. It is the more urban, densely populated, and industrial part of the north Wales geographic region, centred on the city of Wrexham and the towns of Rhyl and Prestatyn, and the conurbation of Deeside. The region's close links with North West England in general and Merseyside in particular are crucial to the region's economy. The Clwydian Range and Dee Valley Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty is located in the region. Other attractions include historical buildings such as Chirk Castle, and Erddig in Wrexham, valley towns such as Corwen and Llangollen, and the Pontcysyllte Aqueduct and Canal World Heritage Site.
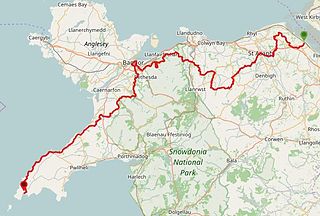
The North Wales Pilgrim's Way is a long-distance walking route in North Wales, running from near Holywell in the east to Bardsey Island in the west. The first half of the trail takes an inland route, with the second half following the north coast of the Llŷn Peninsula. It measures 133.9 miles (215 km) in length, and was officially launched at Porth y Swnt, Aberdaron on 10 July 2014.
The North Wales Metro is a rail and bus transport improvement programme in north Wales. Styled as a "Metro", it is conceptually a multi-modal system with a combination of bus, heavy rail, and light rail services. It was initially focused on linking major settlements and employment areas of the north-east of Wales with the North West of England, with its hubs located in Wrexham, Chester and Deeside, although the programme has since expanded, with proposals extending to Anglesey in the north-west of Wales. The existing Borderlands line forms a core rail component of the network, where projects to increase connections, integrated access, and service frequency between Wrexham, Deeside and Liverpool are centred upon. The proposals were put forward in 2016 as is part of Welsh Labour's plan for north Wales. Labour has pledged to open the system by 2035. The proposals were included in the 2018 Wales & Borders franchise contest. It is the second of the three regional metros proposed by the Welsh Government to go ahead, after the South Wales Metro, and before the Swansea Bay and West Wales Metro. The project is described to be in its initial phases.

The North and Mid Wales Trunk Road Agent is one of the two trunk road agents in Wales. It is responsible for managing trunk roads in North and Mid Wales on behalf of the Welsh Government. A merger of two trunk road agencies, established separately on 1 April 2006, the North Wales Trunk Road Agency and Mid Wales Trunk Road Agency, the two bodies were merged and renamed to its current name on 1 April 2012. The agent manages trunk roads in eight principal areas of the north and mid regions of Wales: the respective principal councils of Anglesey, Ceredigion, Conwy, Denbighshire, Flintshire, Gwynedd, Powys, and Wrexham. The remainder of Wales is managed by the South Wales Trunk Road Agent.
Deeside Parkway is a proposed railway station situated between Neston and Hawarden Bridge on the Borderlands Line. The station is intended to serve the Deeside area of Flintshire, North Wales, particularly the Deeside Industrial Park.

Fflecsi is a trial demand-responsive bus service administered by Transport for Wales (TfW) and local authorities, operated by local bus operators across Wales. Pilot trials of the service are conducted across Wales, which included a city-wide trial in Newport until September 2022. The effectiveness of the service is being monitored as full bus services resume in Wales during the COVID-19 pandemic. During the pilots, fflecsi will replace some pre-existing scheduled bus routes in the service areas where it operates. The technology behind the service is made by ViaVan, and the pilot is funded by the Welsh Government, to invest in new approaches to public transport in Wales as part of their Llwybr Newydd strategy. The pilot was included in Welsh Labour's manifesto for the 2021 Senedd election, as part of their plan to increase investment in bus services, and reducing Wales' carbon emissions.

Wales has traditionally been divided into a number of ambiguous and ill-defined areas described as "regions", reflecting historical, geographical, administrative, cultural and electoral boundaries within the country. Presently, the most common form of division of Wales into "regions" has been using cardinal and intercardinal references: north or south-west for example. None of the variously described "regions" have official status or defined boundaries; neither is there a fixed number of regions. Various organisations use different regions and combinations of regions for their individual purposes. This includes devolved institutions, such as Visit Wales, Natural Resources Wales, and the Welsh Government itself, using different sets of Wales' regions. Wales is most commonly sub-divided into between two and four regions, with a North–South divide, and North, Mid, South East and South West division being common. This article lists the various terms applied to be the "regions of Wales" and the regions used by various organisations.
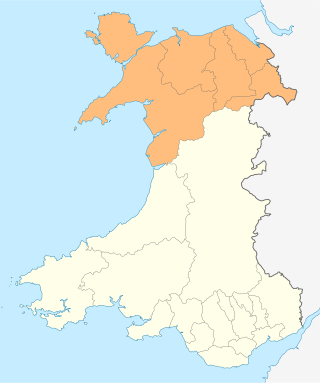
Ambition North Wales, is a joint committee and decision-making body overseeing the North Wales Growth Deal, a regional economic growth deal covering the North Wales region. It is a partnership between the six local authorities of Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Flintshire, Gwynedd, Isle of Anglesey, and Wrexham County Borough, and other local partners in the region, including Bangor University, Wrexham Glyndŵr University, Grŵp Llandrillo Menai, Coleg Cambria, and various private sector representatives.

Regional economy in Wales is centred on four regional economic boards in Wales. Each board oversees a city or growth deal, signed between 2016 and 2022, lasting 10–15 years. Two of the deals are city deals signed and proposed by their respective economic boards, and their areas are described as "city regions"; the Cardiff Capital Region and Swansea Bay City Region. Whereas in North Wales, the North Wales Economic Ambition Board negotiated a North Wales growth deal signed in 2020, and in Mid Wales, the Growing Mid Wales Partnership, led negotiations for a Mid Wales growth deal signed in 2022. The programmes are based on the City deal and Growth deal initiatives set up by the Coalition UK Government in 2012, to promote the decentralisation of the UK economy, by stimulating local economic growth.

Broughton railway station is a proposed railway station on the North Wales Coast line, situated north of Broughton, Flintshire, Wales. Recent proposals for the station use a site north of Airbus UK's West factory site and Hawarden Airport, where the B5129 crosses the North Wales Coast line. Older proposals for the station include using the old sites of the former Sandycroft and Saltney Ferry railway stations.
References
- ↑ "Homepage". Archived from the original on 20 May 2014.
- ↑ Welsh Statutory Instrument 2006 No. 2993 (W.280)
- ↑ "North Wales News - Latest news, pictures, video - North Wales Live". Daily Post. 8 August 2008.
- ↑ "Ministerial Advisory Group – Phase 2 Report on Transport" (PDF). 15 July 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 August 2009.