
Gwynedd is a county in the north-west of Wales. It borders Anglesey across the Menai Strait to the north, Conwy, Denbighshire, and Powys to the east, Ceredigion over the Dyfi estuary to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. The city of Bangor is the largest settlement, and the administrative centre is Caernarfon. The preserved county of Gwynedd, which is used for ceremonial purposes, includes the Isle of Anglesey.
Local government in Wales is primarily undertaken by the twenty-two principal councils. The councils are unitary authorities, meaning they are responsible for providing local government services within their principal area, including education, social work, environmental protection, and most highway maintenance. The principal areas are divided into communities, most of which have an elected community council. The services provided by community councils vary, but they will typically maintain public spaces and facilities. Local councils in Wales are elected; the most recent local elections in Wales took place in 2022, and the next are due to take place in 2027.
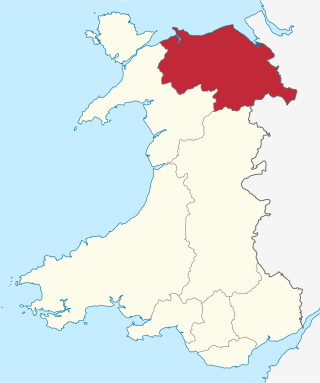
Clwyd is a preserved county of Wales, situated in the north-east corner of the country; it is named after the River Clwyd, which runs through the area. To the north lies the Irish Sea, with the English ceremonial counties of Cheshire to the east and Shropshire to the south-east. Powys and Gwynedd lie to the south and west respectively. Clwyd also shares a maritime boundary with Merseyside along the River Dee. Between 1974 and 1996, a slightly different area had a county council, with local government functions shared with six district councils. In 1996, Clwyd was abolished, and the new principal areas of Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Flintshire and Wrexham County Borough were created; under this reorganisation, "Clwyd" became a preserved county, with the name being retained for certain ceremonial functions.

Llanfairfechan is a town and community in the Conwy County Borough, Wales. It is known as a seaside resort and had a population at the 2001 Census of 3,755, reducing to 3,637 at the 2011 Census. The history of the area dates back to at least Roman times, as demonstrated by the discovery of a large second century milestone, which is now preserved in the British Museum.

North Wales is a region of Wales, encompassing its northernmost areas. It borders mid Wales to the south, England to the east, and the Irish Sea to the north and west. The area is highly mountainous and rural, with Snowdonia National Park and the Clwydian Range and Dee Valley, known for its mountains, waterfalls and trails, wholly within the region. Its population is concentrated in the north-east and northern coastal areas, with significant Welsh-speaking populations in its western and rural areas. North Wales is imprecisely defined, lacking any exact definition or administrative structure. It is commonly defined administratively as its six most northern principal areas, but other definitions exist, with Montgomeryshire historically considered to be part of the region.

South West Wales is one of the regions of Wales comprising the unitary authorities of Swansea, Neath Port Talbot, Carmarthenshire and Pembrokeshire.

Tourism in Wales makes up a significant portion of the Welsh economy and attracting millions of visitors each year. The tourism industry in Wales was worth around £5bn in 2017. The tourism industry also makes a significant contribution to the Welsh economy, supporting over 100,000 jobs and more than 8% of the Welsh workforce. Wales attracts visitors from overseas, particularly from the United States, Australia, Germany and the Republic of Ireland.
A Welsh Government sponsored body (WGSB) is a non-departmental public body directly funded by the Welsh Government. Under the Government of Wales Act 1998 the bodies were sponsored by the National Assembly for Wales and were known as an Assembly sponsored public body, and this was changed by the Schedule 3 of the Wales Act 2017 which amended the Government of Wales Act 2006.

The Welsh Local Government Association represents the interests of local authorities in Wales. It is affiliated with the Local Government Association for England and Wales and acts as Wales’ regional employers organisation.

The Campaign for the Protection of Rural Wales (CPRW) (Welsh: Ymgyrch Diogelu Cymru Wledig (YDCW)), originally named the Council for the Preservation of Rural Wales, is a charity in Wales that aims to secure the protection and enhancement of the country's landscapes and environment.

Monmouthpedia is a collaborative project linking the online encyclopaedia Wikipedia and the town of Monmouth in Wales.
'THIS WEEK' was the free national tourism newspaper for Wales published between 1988 and 2005, established by Steven Potter and Terry Jackson to provide Local Knowledge Nationwide to visitors. It laid claim to being the first colour tabloid newspaper published in the United Kingdom using new, digital pre-press technology on an Apple Macintosh 512K desktop computer, a claim that remains undisputed. It laid further claim in 1995 to being the first newspaper published online, to extend local knowledge Worldwide using the original Netscape Navigator v1.0 web browser within months of its 14 December 1994 launch.

North East Wales is an area or region of Wales, commonly defined as a grouping of the principal areas of Denbighshire, Flintshire, and Wrexham County Borough in the north-east of the country. These principal areas comprise most of the former administrative county of Clwyd. It is bordered by Conwy, and Gwynedd, in North West Wales to the west, Powys, in Mid Wales to the south, the English counties of Cheshire, and Shropshire to the east, and the Irish Sea, and Dee estuary to the north. It is the more urban, densely populated, and industrial part of the north Wales geographic region, centred on the city of Wrexham and the towns of Rhyl and Prestatyn, and the conurbation of Deeside. The region's close links with North West England in general and Merseyside in particular are crucial to the region's economy. The Clwydian Range and Dee Valley Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty is located in the region. Other attractions include historical buildings such as Chirk Castle, and Erddig in Wrexham, valley towns such as Corwen and Llangollen, and the Pontcysyllte Aqueduct and Canal World Heritage Site.
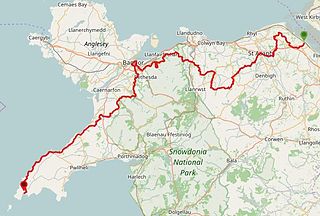
The North Wales Pilgrim's Way is a long-distance walking route in North Wales, running from near Holywell in the east to Bardsey Island in the west. The first half of the trail takes an inland route, with the second half following the north coast of the Llŷn Peninsula. It measures 133.9 miles (215 km) in length, and was officially launched at Porth y Swnt, Aberdaron on 10 July 2014.
The North Wales Metro is a rail and bus transport improvement programme in north Wales. Styled as a "Metro", it is conceptually a multi-modal system with a combination of bus, heavy rail, and light rail services. It was initially focused on linking major settlements and employment areas of the north-east of Wales with the North West of England, with its hubs located in Wrexham, Chester and Deeside, although the programme has since expanded, with proposals extending to Anglesey in the north-west of Wales. The existing Borderlands line forms a core rail component of the network, where projects to increase connections, integrated access, and service frequency between Wrexham, Deeside and Liverpool are centred upon. The proposals were put forward in 2016 as is part of Welsh Labour's plan for north Wales. Labour has pledged to open the system by 2035. The proposals were included in the 2018 Wales & Borders franchise contest. It is the second of the three regional metros proposed by the Welsh Government to go ahead, after the South Wales Metro, and before the Swansea Bay and West Wales Metro. The project is described to be in its initial phases.

Fflecsi is a trial demand-responsive bus service administered by Transport for Wales (TfW) and local authorities, operated by local bus operators across Wales. Pilot trials of the service are conducted across Wales, which included a city-wide trial in Newport until September 2022. The effectiveness of the service is being monitored as full bus services resume in Wales during the COVID-19 pandemic. During the pilots, fflecsi will replace some pre-existing scheduled bus routes in the service areas where it operates. The technology behind the service is made by ViaVan, and the pilot is funded by the Welsh Government, to invest in new approaches to public transport in Wales as part of their Llwybr Newydd strategy. The pilot was included in Welsh Labour's manifesto for the 2021 Senedd election, as part of their plan to increase investment in bus services, and reducing Wales' carbon emissions.

Wales has traditionally been divided into a number of ambiguous and ill-defined areas described as regions, reflecting historical, geographical, administrative, cultural and electoral boundaries within the country. Presently, the most common form of division of Wales into "regions" has been using cardinal and intercardinal references: north or south-west for example. None of the variously described "regions" have official status or defined boundaries; neither is there a fixed number of regions. Various organisations use different regions and combinations of regions for their individual purposes. This includes devolved institutions, such as Visit Wales, Natural Resources Wales, and the Welsh Government itself, using different sets of Wales' regions. Wales is most commonly sub-divided into between two and four regions, with a North–South divide, and North, Mid, South East and South West division being common. This article lists the various terms applied to be the "regions of Wales" and the regions used by various organisations.
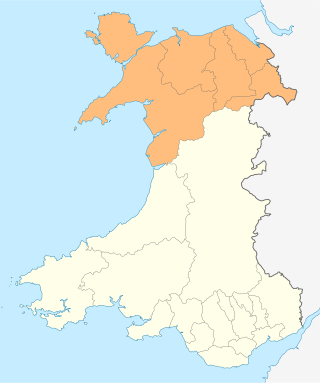
Ambition North Wales is a joint committee and decision-making body overseeing the North Wales Growth Deal, a regional economic growth deal covering the North Wales region. It is a partnership between the six local authorities of Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Flintshire, Gwynedd, Isle of Anglesey, and Wrexham County Borough, and other local partners in the region, including Bangor University, Wrexham University, Grŵp Llandrillo Menai, Coleg Cambria, and various private sector representatives.

Regional economy in Wales is centred on four regional economic boards in Wales. Each board oversees a city or growth deal, signed between 2016 and 2022, lasting 10–15 years. Two of the deals are city deals signed and proposed by their respective economic boards, and their areas are described as "city regions"; the Cardiff Capital Region and Swansea Bay City Region. Whereas in North Wales, the North Wales Economic Ambition Board negotiated a North Wales growth deal signed in 2020, and in Mid Wales, the Growing Mid Wales Partnership, led negotiations for a Mid Wales growth deal signed in 2022. The programmes are based on the City deal and Growth deal initiatives set up by the Coalition UK Government in 2012, to promote the decentralisation of the UK economy, by stimulating local economic growth.

Menter Môn is a social enterprise organisation, based in Anglesey, Wales. It mainly operates in Anglesey and Gwynedd, although some of its programmes and funds extent to other parts of north and west Wales. Menter Môn focuses on delivering local projects, including those specialising in local regeneration, the environment and culture.
















