
Prumnopitys taxifolia, the mataī or black pine, is an endemic New Zealand coniferous tree that grows on the North Island and South Island. It also occurs on Stewart Island/Rakiura but is uncommon there.

Alstroemeriaceae is a family of flowering plants, with 254 known species in four genera, almost entirely native to the Americas, from Central America to southern South America. One species of Luzuriaga occurs in New Zealand, and the genus Drymophila is endemic to south-eastern Australia.
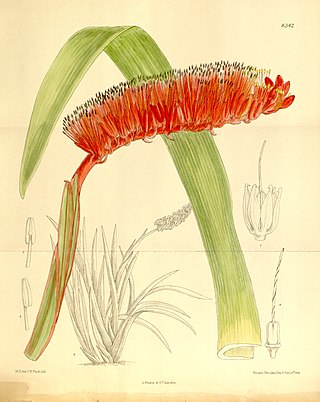
Xeronema is a genus of flowering plants containing two species, Xeronema moorei from New Caledonia, and Xeronema callistemon from the Poor Knights Islands and Taranga Island in New Zealand. The plants are herbaceous monocots, spreading by rhizomes, and have large flowers set on terminal spikes, with stamens towering above the flowers.

Pseudopanax is a small genus of 7 species of evergreen plants which are endemic to New Zealand. Flowers of the genus occur in terminal umbels.

Mystacinidae is a family of unusual bats, the New Zealand short-tailed bats. There is one living genus, Mystacina, with two species, one of which could have possibly become extinct in the 1960s. They are medium-sized bats, about 6 centimetres (2.4 in) in length, with grey, velvety fur.

Myoporum is a genus of flowering plants in the figwort family, Scrophulariaceae. There are 30 species in the genus, eighteen of which are endemic to Australia although others are endemic to Pacific Islands, including New Zealand, and one is endemic to two Indian Ocean islands. They are shrubs or small trees with leaves that are arranged alternately and have white, occasionally pink flowers and a fruit that is a drupe.

Lamponidae is a family of spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1893. It contains about 200 described species in 23 genera, most of which are endemic to Australia, with the genus Centrocalia endemic to New Caledonia, and two Lampona species also occurring in New Zealand where they are commonly known as 'white-tailed spiders'. Lampona papua is endemic to New Guinea, where two otherwise Australian species also occur.

Paphies is a genus of large, edible, saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Mesodesmatidae. The genus is endemic to New Zealand. The species in this genus include the pipi, tuatua and toheroa.

Mnesarchaea is a genus of "New Zealand primitive moths" in the family Mnesarchaeidae. This genus is endemic to New Zealand.

Porrhothele is a genus of mygalomorph spiders endemic to New Zealand. They are the only members of the family Porrhothelidae. They were first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892. Originally placed with the curtain web spiders, it was moved to the Hexathelidae in 1980, they were placed in their own family in 2018.

The New Zealand goose is a bird of the extinct genus Cnemiornis of the family Anatidae, subfamily Anserinae. The genus, endemic to New Zealand, consisted of two species: the North Island goose, C. gracilis and the South Island goose C. calcitrans.

Asaphodes is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae erected by Edward Meyrick in 1885. This genus is endemic to New Zealand and species within this genus are found throughout New Zealand including the North, South and Stewart / Rakiura Islands.

Hadramphus, commonly known as knobbled weevils, is a genus of flightless molytine weevils from the family Curculionidae. It is endemic to New Zealand and consists of four species.

The Chalcodryidae are a family of beetles in the superfamily Tenebrionoidea. It contains at least five species in two genera Chalcodrya and Philpottia, which are endemic to New Zealand. They are generally found associated with moss or lichen covered branches, with the larvae having been found to be associated with dead twigs. They are likely noctural, feeding on lichen and other plant material at night. The genera Sirrhas and Onysius, formerly placed in this family, have subsequently been transferred to Promecheilidae.

Parienia is a genus of moths belonging to the subfamily Olethreutinae of the family Tortricidae. This genus was described by Edward Meyrick in 1881. It consists of only one species, Parienia mochlophorana, which is endemic to New Zealand.

Heterocrossa ignobilis is a species of moth in the family Carposinidae. It was described by Alfred Philpott and is endemic to New Zealand and has been observed in Canterbury, in the South Island. Adults are on the wing in January.

Toronia is a genus of tree in the family Proteaceae that contains a single species, Toronia toru, which is endemic to New Zealand. The genus is closely related to the large genus Persoonia, and in fact this species was long regarded as one until placed in its own new genus by Lawrie Johnson and Barbara G. Briggs in their 1975 monograph "On the Proteaceae: the evolution and classification of a southern family".

Cyclaxyridae are a family of beetles in the superfamily Cucujoidea. The only living genus is Cyclaxyra, with two species endemic to New Zealand. Other species have been named from fossils. They are also known as sooty mould beetles due to the association of Cyclaxyra with sooty mould. The extant species are mycophagous, feeding on spores, conidia, and hyphae.

Edpercivalia harrisoni is a species of caddisfly belonging to the family Hydrobiosidae. The species was first described by Keith Arthur John Wise in 1982, and is endemic to New Zealand.



















