
Sauria is the clade containing the most recent common ancestor of archosaurs and lepidosaurs, and all its descendants. Assuming turtles lie within Sauria, the group can be considered the crown group of diapsids, or reptiles in general. Recent genomic studies and comprehensive studies in the fossil record suggest that turtles are closely related to archosaurs, not to the pre-Saurian parareptiles as previously thought. Sauria includes all modern reptiles as well as various extinct groups. Sauria lies within the larger total group Sauropsida, which also contains various stem-reptiles which are more closely related to reptiles than to mammals. Prior to its modern usage, "Sauria" was used as a name for the suborder occupied by lizards, which before 1800 were considered crocodilians.

Ambystomatidae is a family of salamanders belonging to the order Caudata in the class Amphibia. It contains only one genus, Ambystoma, the mole salamanders. These salamanders are mostly terrestrial and eat invertebrates, although some species are known to eat smaller salamanders. They can be found throughout the US and some areas of Canada in damp forests or plains. This family contains some of the largest terrestrial salamanders in the world, the Tiger salamander and the Pacific giant salamander. Some species are toxic and can secrete poison from their bodies as protection against predators or infraspecific competition. Neoteny has been observed in several species in Ambystomatidae, and some of them like the Axolotl live all of their lives under water in their larval stage.

The sac spiders of the family Clubionidae have a very confusing taxonomic history. Once, this family was a large catch-all taxon for a disparate collection of spiders, similar only in that they had eight eyes arranged in two rows and conical anterior spinnerets that touched, and were wandering predators that built silken retreats, or sacs, usually on plant terminals, between leaves, under bark, or under rocks. These are now recognized to include several families, some of which are more closely related to the three-clawed spiders, like lynx and wolf spiders, than to Clubionidae and related families.

Buprestoidea is a superfamily of beetles.

Tineoidea is the ditrysian superfamily of moths that includes clothes moths, bagworms and relatives. There are six families usually included within it, Eriocottidae, Arrhenophanidae, Lypusidae, Acrolophidae, Tineidae and Psychidae, whose relationships are currently uncertain.

Rhipidistia, also known as Dipnotetrapodomorpha, is a clade of lobe-finned fishes which includes the tetrapods and lungfishes. Rhipidistia formerly referred to a subgroup of Sarcopterygii consisting of the Porolepiformes and Osteolepiformes, a definition that is now obsolete. However as cladistic understanding of the vertebrates has improved over the last few decades, a monophyletic Rhipidistia is now understood to include the whole of Tetrapoda and the lungfishes.

The Diopsoidea are a small but diverse cosmopolitan superfamily of acalyptrate muscoids, especially prevalent in the tropics. Some flux exists in the family constituency of this group, and the final classification is likely to require the use of molecular systematics.

The dreamers are a family, Oneirodidae, of deep-sea anglerfishes in the order Lophiiformes. They are the largest and most diverse group of deep-sea anglerfish, and also the least well known with 16 genera represented by only one, two, or three female specimens. 62 species within the family, and that contains more females than males. They are found in deep, temperate waters around the world. They are small fish, the largest species only growing to about 20 cm (7.9 in) in total length. The largest female size that’s known is about 370-mm and the largest known male is 16.5 mm. Females are dark brown to black all over their entire body, meanwhile males are also dark brown to black, but the nasal area is not pigmented for them. Female dreamers are found in a preservative dark brown to black color externally except for the escal appendages and distal portion of the escal bulb. Males are also the same color, except in their nasal areas.

Eosuchians are an extinct order of diapsid reptiles. Depending on which taxa are included the order may have ranged from the late Carboniferous to the Eocene but the consensus is that eosuchians are confined to the Permian and Triassic.
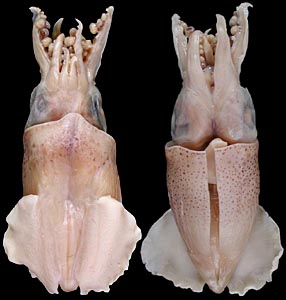
A. aldrichi is a small species of squid found in northern Australian waters. The species was described by Chung Cheng Lu in 2005 based on specimens collected in the inshore waters of Northern Australia. The largest known individual of this species is a mature female measuring 27.6 mm (1.09 in) in mantle length (ML). The holotype is a mature male of 21.3 mm (0.84 in) ML. A live specimen of A. aldrichi has yet to be recorded. A. aldrichi is a member of the class Cephalopoda and part of the subclass Coleodia. Within this class there are two orders, the Myopsida and Oegopsida, which both fall under the superorder Decapodiformes. A. aldrichi falls under the order of Myospida, and is the only member of its genus, Australiteuthis, and family, Australiteuthidae.

Discosauriscus was a small seymouriamorph which lived in what is now Central and Western Europe in the Early Permian Period. Its best fossils have been found in the Broumov and Bacov Formations of Boskovice Furrow, in the Czech Republic.
The Glossosomatidae are a family of the class Insecta and order Trichoptera.The family contains 23 genera in three subfamilies. In the US alone, there are 76 spp. in 6 different genera.

The Gomphales are an order of basidiomycete fungi. Some or all families belonging to Gomphales have been sometimes included in the order Phallales, the now-obsolete Ramariaceae was also previously included in Cantharellales. Recent phylogenetic analyses include in Gomphales the families of the original description of the order by Walter Jülich, with addition of Clavariadelphaceae. According to one 2008 estimate, the Gomphales contain 18 genera and 336 species.

The Nemouridae are a family of stoneflies containing more than 700 described species, occurring primarily in the Holarctic region. Members of this family are commonly known as spring stoneflies or brown stoneflies. Fly fishermen often refer to these insects as tiny winter blacks.

The Neoscopelidae are a small family of deep-sea fish closely related to the lanternfish. They are found in tropical and subtropical marine waters worldwide.

Utegenia is a genus of early tetrapod. It is usually regarded as a basal seymouriamorph, but sometimes included in the Discosauriscidae or as a sister taxon of the latter. Only one species, Utegenia shpinari, found from Kazakhstan, is known. Urumqia, another basal seymouriamorph, from Urumqi, Xinjiang of China is probably a junior synonym of Utegenia.
Meruidae is a recently described family of aquatic beetles in the suborder Adephaga, with only one genus and species, Meru phyllisae. This beetle species was first found in the early 1980s. At 0.8 mm, it is one of the smallest adephagan beetles in the world. A recent survey of aquatic beetles of Venezuela prove that Meru is most common during the wet season, when larger areas of granitic rock surface are covered with water film, which the adult beetles as well as the larvae inhabit.

The neon flying squid, sometimes called the red flying squid, akaika, and red squid is a species of large flying squid in the family Ommastrephidae. They are found in subtropical and temperate oceanic waters globally.

Corvoidea is a superfamily of birds in the order of Passeriformes.

Cirroctopus is a genus of four species of octopuses within the monotypic family Cirroctopodidae. Members of this genus have larger fins than other cirrate octopuses, and tend to be more muscular. They are found in the southern hemisphere, where they live at depths of over 300m.


















