Edward Kutchat | |
|---|---|
| Born | Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India |
| Occupation | Tribal leader |
| Awards | Padma Shri |
Edward Kutchat was an Indian tribal leader [1] and the Chief of the Tribal Council of Car Nicobar island. [2] [3] He was featured in the media for cooperating with the Indian Government by offering his land for the expansion of airfields in Car Nicobar island, in exchange for the jacket worn by Jawaharlal Nehru, on a visit to the island. [4] He was also reported to have assisted Nicobarese people in promoting their business. [5] The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of Padma Shri in 1989. [6]

The Andaman Islands are an archipelago in the northeastern Indian Ocean about 130 km (81 mi) southwest off the coasts of Myanmar's Ayeyarwady Region. Together with the Nicobar Islands to their south, the Andamans serve as a maritime boundary between the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Andaman Sea to the east. Most of the islands are part of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India, while the Coco Islands and Preparis Island are part of the Yangon Region of Myanmar.

The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 571 islands, of which 37 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The territory is about 150 km (93 mi) north of Aceh in Indonesia and separated from Thailand and Myanmar by the Andaman Sea. It comprises two island groups, the Andaman Islands (partly) and the Nicobar Islands, separated by the 150 km wide Ten Degree Channel, with the Andaman islands to the north of this latitude, and the Nicobar islands to the south. The Andaman Sea lies to the east and the Bay of Bengal to the west. The island chains are thought to be a submerged extension of the Arakan Mountains.
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, 150 kilometres (93 mi) northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) southeast of the Indian subcontinent, across the Bay of Bengal, they are part of India, as the Nicobar district within the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.

According to official estimates in India, 10,749 people were killed, 5,640 people were missing and thousands of people became homeless when a tsunami triggered by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake near the Indonesian island of Sumatra struck the southern coast on 26 December 2004. The earthquake registered 9.1–9.3 Mw and was the largest in five decades. It was followed by strong aftershocks on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The death toll of the earthquake was 1,500 people.
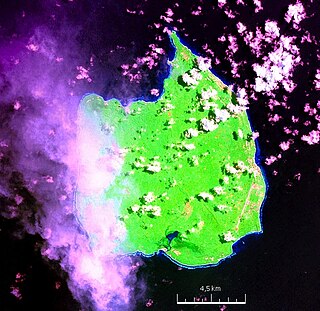
Car Nicobar is the northernmost of the Nicobar Islands. It is also one of three local administrative divisions of the Indian district of Nicobar, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Annual rainfall is 2800 millimetres.
Nancowry is an island in the central part of the Nicobar Islands chain, located in the northeast Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea.
Trinket Island is one of the 24 islands that make up the Nicobar Islands chain, located in the northeast Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. It is located east of Kamorta Island.

The Shompen or Shom Pen are the indigenous people of the interior of Great Nicobar Island, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Nicobar district is one of three districts in the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The district's administrative territory encompasses all of the Nicobar Islands, which are located in the Indian Ocean, between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The headquarters of the district is the village of Malacca, located on the island of Car Nicobar.
Katchal is one of the Nicobar Islands, India.

The Nicobarese people are an Austroasiatic-speaking people of the Nicobar Islands, a chain of islands in the Bay of Bengal north of Sumatra, forming part of the union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Only 12 of the 19 islands are inhabited. The largest and main island is Great Nicobar. The term Nicobarese refers to the dominant tribes of the Nicobar Islands. On each island, the people have specific names, but together they are the Nicobarese. They call themselves Holchu, which means "friend".
Shanti Teresa Lakra is an Indian medical nurse and healthcare professional, known for her services to Onge tribe in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, in the aftermath of the Tsunami of 2004. The Government of India honored Lakra in 2011, with the fourth highest civilian award of Padma Shri.
Tillangchong, also known as Tillanchang, is an island and a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India.
Chuckchucha is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Car Nicobar tehsil. The headquarters of the island's central tribal cooperative society 'Ellon Hinengo Limited'(EHL) was established here in 1945. The society was started by the Jadwet family of Burma (Myanmar).
Hintona is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Nancowry tehsil.
Shompen hut is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Great Nicobar tehsil.

Deborah Herold is an Indian cyclist.

John Richardson was an Indian Anglican bishop and politician.
Vaseem Iqbal is the first tribal person from the Andaman and Nicobar islands to receive a PhD. He is currently employed by the Central Agriculture Research Institute in Port Blair as a researcher.
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is an archipelago of 572 islands of which 37 are inhabited. It is a union territory of India.