| Eiderstedt Frisian | |
|---|---|
| Eidersteder Friesisch / Ejderstedfrisisk | |
| Region | peninsula Eiderstedt |
| Ethnicity | North Frisians |
| Extinct | 18th century |
Indo-European
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | None |
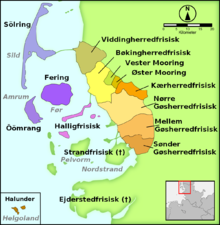
Eiderstedt Frisian (German : Eiderstedter Friesisch, Danish : Ejderstedfrisisk) was a dialect of the North Frisian language which was originally spoken on Eiderstedt, formerly part of the Danish Duchy of Schleswig. The Frisian language became extinct on Eiderstedt in mid-18th century. [1]
In contrast to the northern hundreds, Eiderstedt was economically strong and wealthy and was oriented towards the southern, Low German parts of Holstein. During the 16th century there was moreover a strong Dutch immigration. [2]
Eiderstedt Frisian is attributed to the insular dialects, but there are also characteristics of the mainland dialects. The difference between the insular and the mainland dialects dates back to the Frisian immigrants during several different centuries.