This article includes a list of references, related reading or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
 T-35 seized by the U.S., as DD 935. | |
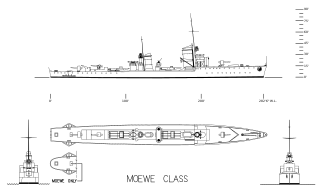
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Flottentorpedoboot 1939 |
| Builders: | Schichau, Elbing |
| Operators: | |
| Preceded by: | Type 37 torpedo boat |
| Succeeded by: | Type 40 torpedo boat |
| In commission: | 1941–58 |
| Completed: | 15 |
| Lost: | 11 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Torpedo boat |
| Displacement: |
|
| Length: | |
| Beam: | 10 m (32 ft 10 in) |
| Draft: | 3.22 m (10 ft 7 in) |
| Installed power: | 32,560 shp (24,280 kW) |
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | 32.5 kn (60.2 km/h; 37.4 mph) |
| Range: | 2,400 nmi (4,400 km; 2,800 mi) at 19 kn (35 km/h; 22 mph) |
| Complement: | 205 |
| Armament: |
|
The Elbing-class (or Type 1939) torpedo boats were a class of 15 small warships that served in the Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. Although classed as Flottentorpedoboot ("fleet torpedo boat") by the Germans, in most respects—displacement, weaponry, usage—they were comparable to contemporary medium-size destroyers. The most notable difference was in the armament of the Elbings being fewer in number and of a smaller caliber — 10.5 cm (4.1 in) SK C/32 compared to the 4.7 in (120 mm) of contemporary British destroyers such as the "J"-, "K"- and "N"-classes.

A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is built and primarily intended for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the armed forces of a state. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are usually faster and more manoeuvrable than merchant ships. Unlike a merchant ship, which carries cargo, a warship typically carries only weapons, ammunition and supplies for its crew. Warships usually belong to a navy, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations.

Nazi Germany is the common English name for Germany between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and his Nazi Party (NSDAP) controlled the country through a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a totalitarian state that controlled nearly all aspects of life via the Gleichschaltung legal process. The official name of the state was Deutsches Reich until 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany is also known as the Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", the first two being the Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and the German Empire (1871–1918). The Nazi regime ended after the Allies defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.

The Kriegsmarine was the navy of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war Reichsmarine (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The Kriegsmarine was one of three official branches, along with the Heer (Army) and the Luftwaffe of the Wehrmacht, the German armed forces from 1933 to 1945.
Contents
Service was either in western France from late 1942-August 1944 or in the Baltic Sea from March 1944 until the end of the war.

The Baltic Sea is a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Sweden, northeast Germany, Poland, Russia and the North and Central European Plain.
The design and weapons mix resulted from experience of earlier, more specialised classes such as the Type 35. The Elbings were a radical change to an all-purpose vessel capable of torpedo attacks, anti-aircraft defence and escort duties. These ships adopted unit machinery with two separate engine rooms and two boiler rooms. Their machinery was however relatively unreliable.

The Type 35 torpedo boat was a class of a dozen torpedo boats built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine in the late 1930s. Although the first boats were completed a few months after the start of World War II in September 1939, none of them were able to participate in the Norwegian Campaign of April–June 1940. They began escorting convoys and minelayers as they laid their minefields in the North Sea and English Channel in July. Most of the boats were transferred to Norway in November where they made an unsuccessful attempt to attack shipping along the Scottish coast that saw one boat sunk.

A modern torpedo is a self-propelled weapon with an explosive warhead, launched above or below the water surface, propelled underwater towards a target, and designed to detonate either on contact with its target or in proximity to it.
They were effective fighting vessels, a notable success being the sinking of the British light cruiser HMS Charybdis and the escort destroyer HMS Limbourne by torpedoes, off Brittany in October 1943. The 4th Torpedo Boat Flotilla—T22, T23, T24, T25, and T26—had been protecting an important blockade runner though despite their success it ran aground and was lost. Two vessels, T25 and T26, were lost in a similar operation three months later. Three ships—T22, T30, and T32—were accidentally lost on 18 August 1943 on a German minefield in the Gulf of Finland. In April 1944 the Canadian destroyer HMCS Athabaskan was torpedoed by T24.
A light cruiser is a type of small- or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck. Prior to this smaller cruisers had been of the protected cruiser model, possessing armored decks only. While lighter and smaller than other contemporary ships they were still true cruisers, retaining the extended radius of action and self-sufficiency to act independently across the world. Through their history they served in a variety of roles, primarily as convoy escorts and destroyer command ships, but also as scouts and fleet support vessels for battle fleets.

HMS Charybdis was a Dido-class cruiser of the Royal Navy. She served during the Second World War and was sunk with heavy loss of life by German torpedo boats in an action in the English Channel in October 1943.

The Battle of Sept-Îles was a naval battle fought on the night of 22/23 October 1943 during World War II as part of the Atlantic campaign. The battle took place off the Sept-Îles near the French coast in the English Channel between a light cruiser and six destroyers of the British Royal Navy, and a minesweeper and torpedo boat flotillas of the German Kriegsmarine hoping to intercept and escort a blockade runner. The battle ended with HMS Charybdis being sunk and the Hunt-class destroyer HMS Limbourne being scuttled after suffering damage; nearly 500 British sailors lost their lives in the battle. The battle was the last surface fleet action of the war where the Royal Navy was defeated, and the last German surface fleet action victory.
Construction of the class took place in the Schichau shipyard in Elbing (now Elbląg), hence the Allied name for the class. The first examples were commissioned in late 1942 and the last in late 1944.

The Schichau-Werke was a German engineering works and shipyard based in Elbing, Germany on the Frisches Haff of then-East Prussia. It also had a subsidiary shipyard in nearby Danzig. Due to the Soviet conquest of eastern Germany, Schichau moved to Bremerhaven in March 1945, and its successors continued in business until 2009.

Elbląg is a city in northern Poland on the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 121,191 inhabitants. It is the capital of Elbląg County and has been assigned to the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. Previously it was the capital of Elbląg Voivodeship (1975–1998) and a county seat within Gdańsk Voivodeship (1945–1975).