
Renewable energy in Germany is mainly based on wind and biomass, plus solar and hydro. Germany had the world's largest photovoltaic installed capacity until 2014, and as of 2021 it has over 58 GW. It is also the world's third country by installed total wind power capacity, 64 GW in 2021 and second for offshore wind, with over 7 GW. Germany has been called "the world's first major renewable energy economy".

Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat. Second-generation technologies are market-ready and are being deployed at the present time; they include solar heating, photovoltaics, wind power, solar thermal power stations, and modern forms of bioenergy. Third-generation technologies require continued R&D efforts in order to make large contributions on a global scale and include advanced biomass gasification, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and ocean energy. As of 2012, renewable energy accounts for about half of new nameplate electrical capacity installed and costs are continuing to fall.

Ensuring adequate energy supply to sustain economic growth has been a core concern of the Chinese government since 1949. The country is the world's largest emitter of greenhouse gases, and coal in China is a major cause of global warming. However, from 2010 to 2015 China reduced energy consumption per unit of GDP by 18%, and CO2 emissions per unit of GDP by 20%. On a per-capita basis, it was the world's 51st largest emitter of greenhouse gases in 2016. China is also the world's largest renewable energy producer. China is the largest producer of hydroelectricity, solar power and wind power in the world. The energy policy of China is connected to its industrial policy. The goals of China's industrial policy dictate its energy needs.

Renewable energy in Finland grew to 38.7% of total final energy consumption by year end 2014, achieving joint second position with Latvia in terms of renewable energy consumption by share amongst the EU-28 countries, behind its neighbour Sweden in first position on a 52.6% share. The 2014 share in Finland breaks down as renewable energy providing 52% of the heating and cooling sector, 31.4% of the electricity sector and 21.6% of the transport sector. By 2014, Finland had already exceeded its 2020 target for renewable energy use under the EU renewable energy directive as shown in the table of country targets.
Mandatory renewable energy targets are part of government legislated schemes which require electricity merchandisers to source-specific amounts of aggregate electricity sales from renewable energy sources according to a fixed time frame. The objective of these schemes is to promote renewable energy and decrease dependency on fossil fuels. If this results in an additional expenditure of electricity, the additional cost is distributed across most customers by increases in other tariffs. The cost of this measure is therefore not funded by the government budgets, except for costs of establishing and monitoring the scheme and any audit and enforcement actions. As the cost of renewable energy has become cheaper than other sources, meeting and exceeding a renewable energy target will also reduce the expenditure of electricity to consumers.

The energy sector in Switzerland is, by its structure and importance, typical of a developed country. Apart from hydroelectric power and firewood, the country has few indigenous energy resources: oil products, natural gas and nuclear fuel are imported, so that in 2013 only 22.6% of primary energy consumption was supplied by local resources.

Energy in Australia is the production in Australia of energy and electricity, for consumption or export. Energy policy of Australia describes the politics of Australia as it relates to energy.

Majority of electricity production in Sweden relies on hydro power and nuclear power. In 2008 the consumption of electricity in Sweden was 16018 kWh per capita, compared to EU average 7409 kWh per capita. Sweden has a national grid, which is part of the Synchronous grid of Northern Europe. A specialty of the Nordic energy market is the existence of so-called electricity price areas, which complicate the wholesale Nordic energy market.
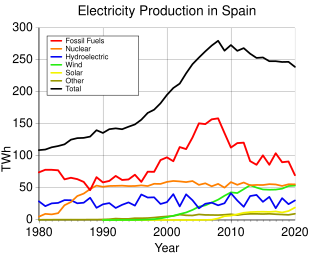
The electricity sector in Spain describes electricity in Spain. In 2008, Spain consumed 88% of the average electricity consumption for a European Union 15 country. In 2009, Spain exported about 3% of the electricity it produced. The volume of renewable electricity produced in 2009 was 5% greater than in 2004, and accounted for about 26% of the electricity consumption. The share of nuclear power declined notably between 2004 and 2005. The volume of nuclear power per person has declined consistently during 2004–2009.

The total electricity consumption of the Netherlands in 2021 was 117 terawatt-hours (TWh). The consumption grew from 7 TWh in 1950 by an average of 4.5% per year. As of 2021, the main resources for electricity in the Netherlands are fossil fuels, such as natural gas and coal. In 2021, fossil fuels accounted for about 62% of the produced electricity. Renewable energy sources, such as biomass, wind power, and solar power, produce 38% of the total electricity. There is one nuclear plant in the Netherlands, in Borssele, which is responsible for about 3% of total generation. The majority of the electricity, more than 75%, is produced centrally by thermal and nuclear units.

The electricity sector in Belgium describes electricity in Belgium. Production by power source in 2009 was 53% nuclear, 40% fossil electricity and 7% renewable electricity. 2% of production was exported in 2009. In 2008 import was 11%. Belgium is highly nuclear dependent country where the share of renewable electricity has been low. The share of renewable electricity was about 2% in 2005. Plan for 2020 is wind 10.5 TWh (9.5%), biomass 11 TWh and PV 1 TWh.

The electricity sector in Switzerland relies mainly on hydroelectricity, since the Alps cover almost two-thirds of the country's land mass, providing many large mountain lakes and artificial reservoirs suited for hydro power. In addition, the water masses drained from the Swiss Alps are intensively used by run-of-the-river hydroelectricity (ROR). With 9,052 kWh per person in 2008, the country's electricity consumption is relatively high and was 22% above the European Union's average.

Electricity sector in Luxembourg describes electricity issues in Luxembourg. Luxembourg is a member of OECD and European Union. Luxembourg imports most of its energy. Luxembourg is the EU country with the second smallest forecast of renewables in 2020. Luxembourg has one of the highest emissions of carbon dioxide per person in Europe.

Energy in Sweden describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Sweden. Electricity sector in Sweden is the main article of electricity in Sweden. The Swedish climate bill of February 2017 aims to make Sweden carbon neutral by 2045. The Swedish target is to decline emission of climate gases 63% from 1990 to 2030 and international transportation excluding foreign flights 70%. By 2014 just over half of the country's total final energy consumption in electricity, heating and cooling and transport combined was provided by renewables, the highest share amongst the then 28 EU member countries. About a third of Sweden's electricity is generated by nuclear power. In generating a year's worth of this energy, Swedes generate about 4 tonnes of CO2 emissions each. Since 2010, sustainability measures have reduced total emissions even as the population has increased.
Energy in the United Arab Emirates describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). UAE has 7% of global proved oil reserves, about 100 billion barrels. Primary energy use in 2009 in UAE was 693 TWh and 151 TWh per million persons.
Electricity in Cyprus is managed by the Electricity Authority of Cyprus. Power is primarily generated at three fuel oil-burning stations but the use of distributed renewable energy is expanding.

Energy in Belarus describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Belarus. Belarus is a net energy importer. According to IEA, the energy import vastly exceeded the energy production in 2015, describing Belarus as one of the world's least energy sufficient countries in the world. Belarus is very dependent on Russia.
Energy in Luxembourg describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Luxembourg. Energy policy of Luxembourg will describe the politics of Luxembourg related to energy in greater detail. Electricity sector in Luxembourg is the main article of electricity in Luxembourg.

Primary energy use in Slovakia was 194 TWh and 36 TWh per million inhabitants in 2009.

World energy supply and consumption is global production and preparation of fuel, generation of electricity, energy transport, and energy consumption. It is a basic part of economic activity. It includes heat, but not energy from food.
















