
Airbreathing catfish comprise the family Clariidae of the order Siluriformes. Sixteen genera and about 117 species of clariid fishes are described; all are freshwater species. Other groups of catfish also breathe air, such as the Callichthyidae and Loricariidae.

The driftwood catfishes are catfishes of the family Auchenipteridae. The two genera of the former family Ageneiosidae have been placed here, resulting in a grouping of about 125 species in about 22 genera.

Auchenipterichthys is a genus of driftwood catfishes found in South America.
Erethistoides is a genus of South Asian river catfishes.
Corumbataia is a genus of armored catfishes native to South America where they are only known from Brazil.

Bagarius is an Asian genus of catfishes of the family Sisoridae. It includes five to six extant species and potentially one extinct fossil species, B. gigas.
Cetopsidium is a genus of catfishes of the family Cetopsidae.

Paracetopsis is a genus of whale catfishes found in tropical South America.
Pseudexostoma is a genus of fish in the family Sisoridae endemic to China. These species are restricted to the upper Salween and one upper branch of the Irrawaddy in China. P. brachysoma is known only from the middle and lower Nujiang River. P. yunnanensis is only known from the upper Dayinjiang. These rivers were once connected, but are now separated. Also, the environment and temperature of the Nujiang River became greatly different between the northern and southern areas, leading to speciation.
Denticetopsis is a genus of catfishes of the family Cetopsidae.

Lasiancistrus is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes. They are native to South America and Panama.
Breitensteinia is a genus of catfishes of the family Akysidae. It includes three species.
Pseudolithoxus is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes with five described species from the basins of the Orinoco, Casiquiare and upper Rio Negro in Venezuela. Additionally, a possibly undescribed species is known from the Trombetas and Nhamundá rivers in Brazil.

Cetopsis is a genus of catfishes of the family Cetopsidae.

Auchenipterus is a genus of driftwood catfishes.
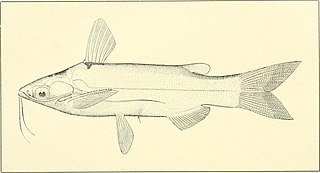
Entomocorus benjamini is a species of driftwood catfish found in the Madeira River system in Bolivia and Brazil. This species grows to a length of 7.0 cm and can be distinguished from it congeners in that the distal half of dorsal caudal fin lobe and the edge of the ventral lobe is pigmented.
Entomocorus gameroi is a species of driftwood catfish native to Venezuela and questionably present in Colombia. It is found in the Apure River basin. It grows to a length of 7.0 cm and can be distinguished from its congeners by an oblique band crossing from the dorsal profile of the caudal peduncle to the middle-upper rays of the caudal fin. E. gameroi is classified as an omnivore with a tendency towards insectivory; it has been found to eat cladocerans, copepods, and water mites, as well as ostracods, insects including coleopterans, dipterans, ephemeropterans, hemipterans, and seeds and other vegetal matter.
Entomocorus melaphareus is a species of driftwood catfish endemic to Brazil where it is found in the Amazon River. It grows to a length of 5.9 cm and can be distinguished from its congeners by an inconspicuous patch exists on the dorsal lobe of the caudal fin. It also has pigmented pectoral and pelvic fins, while these fins in the other three species are unpigmented.

Entomocorus radiosus is a species of driftwood catfish endemic to Brazil where it is found in the Rio Paraguay in the Pantanal region of Mato Grosso. It is the smallest known member of its genus growing to a length of 5.3 cm. It can be distinguished from its congeners because its anal fin base is longer and has more branched anal fin rays. E. radiosus is a zooplanktivore which also eats insects; this species predominantly consumes microcrustaceans, but also fed on insects.

Guyanancistrus nassauensis is a species of catfish belonging to the family Loricariidae, the suckermouth armored catfishes. It is discovered in 2005 and formally described in 2018. G. nassauensis is a rare species, highly endemic to the Nassau Mountains in Suriname, and is threatened with extinction by proposed or ongoing mining activities.










