
Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Skinks are characterized by their smaller legs in comparison to typical lizards and are found in different habitats except arctic and subarctic regions.

Carlia is a genus of skinks, commonly known as four-fingered skinks or rainbow skinks, in the subfamily Eugongylinae. Before being placed in this new subfamily, Carlia was recovered in a clade with the genera Niveoscincus, Lampropholis, and others of the Eugongylus group within Lygosominae.

Eugongylus is a genus of skinks in the subfamily Eugongylinae. It was previously recognised as namesake of the Eugonglyus group of genera within Lygosominae, where it occupied a quite basal position. Members of this genus are commonly called mastiff skinks or short-legged giant skinks.

Lampropholis is a genus of skinks, commonly known as sunskinks, in the lizard subfamily Eugongylinae of the family Scincidae. The genus Lampropholis was previously found to belong to a clade with the genera Niveoscincus, Leiolopisma and others of the Eugongylus group within Lygosominae. All species of Lampropholis are endemic to Australia. For similar skinks see genera Bassiana, Pseudemoia, and Niveoscincus.

Leiolopisma is a genus of skinks. Most species occur in the region of New Caledonia-New Zealand, and they are related to other genera from that general area, such as Emoia; these and others form the Eugongylus group. One living and two extinct taxa represent a clade endemic to the Mascarenes.(Austin & Arnold 2006)

Oligosoma is a genus of small to medium-sized skinks found only in New Zealand, Norfolk Island and Lord Howe Island. Oligosoma had previously been found to belong to the Eugongylus group of genera in the subfamily Lygosominae; the Australian genus Bassiana appears to be fairly closely related.

The Mediterraneanshort-toed lark is a small passerine bird found in and around the Mediterranean Basin. It is a common bird with a very wide range from Canary Islands north to the Iberian Peninsula and east throughout North Africa to parts of the Middle East. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".

The pink-backed pelican is a bird of the pelican family. It is a resident breeder in the swamps and shallow lakes of Africa and southern Arabia; it has also apparently been extirpated from Madagascar.

The Bermuda skink, longnose skink, or (Bermuda) rock lizard is a critically endangered species and the only endemic land-living vertebrate of Bermuda. It is a relatively small skink : adults reach an average snout-to-vent length of about 8 cm (3.1 in).

The Gran Canaria skink is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. It is endemic to Gran Canaria in the Canary Islands.
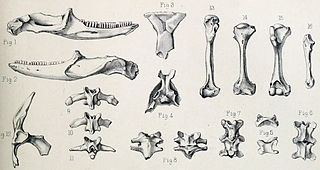
The Mauritian giant skink is a large, extinct species of skink It was found only in Mauritius. It became extinct sometime in the 17th century, likely due to human-introduced predators.
Carinascincus palfreymani, known commonly as the Pedra Branca skink, as well as the Palfreyman's window-eyed skink, the Pedra Branca cool-skink, or the red-throated skink, is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Australia, and is restricted to the windswept Pedra Branca, an island off southern Tasmania of only 2.5 ha, where it is dependent on the seabird colonies. It is the only lizard species found on the island.

The long-nosed echymipera, or long-nosed spiny bandicoot, is a species of marsupial in the family Peramelidae. It is found in Australia, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests.

Lygosominae is the largest subfamily of skinks in the family Scincidae. The subfamily can be divided into a number of genus groups. If the rarely used taxonomic rank of infrafamily is employed, the genus groups would be designated as such, but such a move would require a formal description according to the ICZN standards.

Carinascincus metallicus, the metallic cool-skink or metallic skink is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. It is endemic to Australia, found in southern Victoria, as well as in Tasmania where it is the most widespread and common lizard, occurring on many offshore islands in Bass Strait as well as the mainland. It gives birth to live young. It is highly variable in colour and pattern, and may be a complex of closely related species.
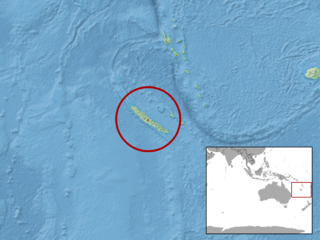
Geoscincus is a monotypic genus of skinks: the only accepted species is Geoscincus haraldmeieri.

Eugongylinae is a subfamily of skinks within the family Scincidae. The genera in this subfamily were previously found to belong the Eugongylus group in the large subfamily Lygosominae.

Eugongylus albofasciolatus, the white-striped cape skink or barred shark skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. It is found in Australia (Queensland), the Solomon Islands, New Britain, New Ireland, and Micronesia.

Phoboscincus garnieri, also known commonly as Garnier's giant skink and Garnier's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to New Caledonia.
Ctenotus rufescens, the rufous finesnout ctenotus, is a species of skink found in Western Australia.


















