
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. The organization operates in parallel with the European Union (EU), and all four member states participate in the European Single Market and are part of the Schengen Area. They are not, however, party to the European Union Customs Union.
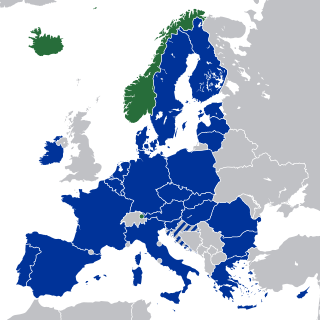
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the Agreement on the European Economic Area, an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Association. The EEA links the EU member states and three of the four EFTA states into an internal market governed by the same basic rules. These rules aim to enable free movement of persons, goods, services, and capital within the European single market, including the freedom to choose residence in any country within this area. The EEA was established on 1 January 1994 upon entry into force of the EEA Agreement. The contracting parties are the EU, its member states, and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway. New members of EFTA would not automatically become party to the EEA Agreement, as each EFTA State decides on its own whether it applies to be party to the EEA Agreement or not. According to Article 128 of the EEA Agreement, "any European State becoming a member of the Community shall, and the Swiss Confederation or any European State becoming a member of EFTA may, apply to become a party to this Agreement. It shall address its application to the EEA Council." EFTA does not envisage political integration. It does not issue legislation, nor does it establish a customs union. Schengen is not a part of the EEA Agreement. However, all of the four EFTA States participate in Schengen and Dublin through bilateral agreements. They all apply the provisions of the relevant Acquis.
The Schengen Information System (SIS) is a governmental database maintained by the European Commission. The SIS is used by 31 European countries to find information about individuals and entities for the purposes of national security, border control and law enforcement since 2001. A second technical version of this system, SIS II, went live on 9 April 2013. An upgraded Schengen Information System entered into operation on 7 March 2023.

The Dublin Regulation is a Regulation of the European Union that determines which EU member state is responsible for the examination of an application for asylum, submitted by persons seeking international protection under the Geneva Convention and the Qualification Directive, within the European Union.

The European Health Insurance Card (EHIC) is issued free of charge and allows anyone who is insured by or covered by a statutory social security scheme of the EEA countries, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom to receive medical treatment in another member state in the same way as residents of that state—i.e., free or at a reduced cost—if treatment becomes necessary during their visit, or if they have a chronic pre-existing condition which requires care such as kidney dialysis. The term of validity of the card varies according to the issuing country. Continued reciprocal healthcare access between the EU and the UK was agreed, and the UK issues a UK Global Health Insurance Card (GHIC) valid in the EU, but not other EEA countries.
The EFTA Court is a supranational judicial body responsible for the three EFTA members who are also members of the European Economic Area (EEA): Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway.
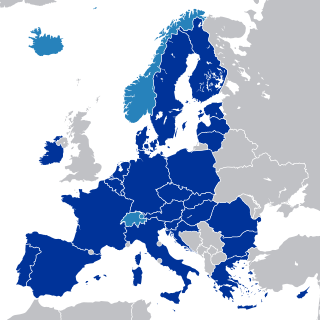
The EFTA Surveillance Authority (ESA) monitors compliance with the Agreement on the European Economic Area (EEA) in Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway (the EEA EFTA States). ESA operates independently of the States and safeguards the rights of individuals and undertakings under the EEA Agreement, ensuring free movement, fair competition, and control of state aid.

The Brussels Regime is a set of rules regulating which courts have jurisdiction in legal disputes of a civil or commercial nature between individuals resident in different member states of the European Union (EU) and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA). It has detailed rules assigning jurisdiction for the dispute to be heard and governs the recognition and enforcement of foreign judgments.

The Prüm Convention is a law enforcement treaty which was signed on 27 May 2005 by Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and Spain in the town of Prüm in Germany, and which is open to all members of the European Union, 14 of which are currently parties.
Asylum shopping is a term for the practice by some asylum seekers of applying for asylum in several states or seeking to apply in a particular state after traveling through other states. It is used mostly in the context of the European Union and the Schengen Area, but has also been used by the Federal Court of Canada.
Currently, all of the European microstates have some form of relations with the European Union (EU).

The European driving licence is a driving licence issued by the member states of the European Economic Area (EEA); all 27 EU member states and three EFTA member states; Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, which give shared features the various driving licence styles formerly in use. It is credit card-style with a photograph. They were introduced to replace the 110 different plastic and paper driving licences of the 300 million drivers in the EEA. The main objective of the licence is to reduce the risk of fraud.

The European Union itself does not issue ordinary passports, but ordinary passport booklets issued by its 27 member states share a common format. This common format features a colored cover emblazoned—in the official language(s) of the issuing country —with the title "European Union", followed by the name(s) of the member state, the heraldic "Arms" of the State concerned, the word "PASSPORT", together with the biometric passport symbol at the bottom center of the front cover.

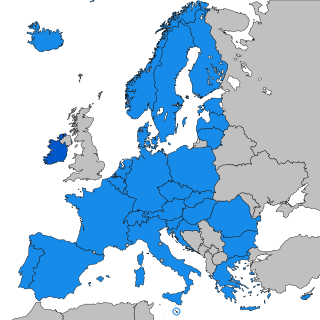
The Schengen Area is an area encompassing 29 European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union (EU), it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.

The Maintenance Regulation (EC) No 4/2009, formally the Council Regulation (EC) on jurisdiction, applicable law, recognition and enforcement of decisions and cooperation in matters relating to maintenance obligations, is a European Union Regulation on conflict of law issues regarding maintenance obligations. The regulation governs which courts have jurisdiction and which law it should apply. It further governs the recognition and enforcement of decisions. The regulation amends the Brussels Regulation, which covers jurisdiction in legal disputes of a civil or commercial nature between individuals more broadly.

The Treaties of the European Union are a set of international treaties between the European Union (EU) member states which sets out the EU's constitutional basis. They establish the various EU institutions together with their remit, procedures and objectives. The EU can only act within the competences granted to it through these treaties and amendment to the treaties requires the agreement and ratification of every single signatory.

The European Union Agency for the Operational Management of Large-Scale IT Systems in the Area of Freedom, Security and Justice (eu-LISA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) that was founded in 2011 to ensure the uninterrupted operation of large-scale IT systems within the area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ), that are instrumental in the implementation of the asylum, border management and migration policies of the EU. It began its operational activities on 1 December 2012.

Passports of the EFTA member states are passports issued by the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) member states Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. EFTA is in this article used as a common name for these countries.
The migration and asylum policy of the European Union is within the area of freedom, security and justice, established to develop and harmonise principles and measures used by member countries of the European Union to regulate migration processes and to manage issues concerning asylum and refugee status in the European Union.
















