
Human capital flight is the emigration or immigration of individuals who have received advanced training at home. The net benefits of human capital flight for the receiving country are sometimes referred to as a "brain gain" whereas the net costs for the sending country are sometimes referred to as a "brain drain". In occupations with a surplus of graduates, immigration of foreign-trained professionals can aggravate the underemployment of domestic graduates, whereas emigration from an area with a surplus of trained people leads to better opportunities for those remaining. But emigration may cause problems for the home country if the trained people are in short supply there.

Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another, with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location. The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another, but internal migration is the dominant form of human migration globally.

Foreign workers or guest workers are people who work in a country other than one of which they are a citizen. Some foreign workers use a guest worker program in a country with more preferred job prospects than in their home country. Guest workers are often either sent or invited to work outside their home country or have acquired a job before leaving their home country, whereas migrant workers often leave their home country without a specific job in prospect.

The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign financial output claimed by the residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents, minus income earned in the domestic economy by nonresidents.

International economics is concerned with the effects upon economic activity from international differences in productive resources and consumer preferences and the international institutions that affect them. It seeks to explain the patterns and consequences of transactions and interactions between the inhabitants of different countries, including trade, investment and transaction.

A migrant worker is a person who migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work. Migrant workers usually do not have an intention to stay permanently in the country or region in which they work.
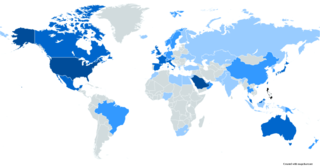
An overseas Filipino is a person of full or partial Filipino origin who trace their ancestry back to the Philippines but are living and working outside of the country. They get jobs in countries, and they move to live in countries that they get jobs in, or if they want to migrate to somewhere else, This term generally applies to both people of Filipino ancestry and citizens abroad. As of 2019, there were over 15 million Filipinos overseas.

A remittance is a non-commercial transfer of money by a foreign worker, a member of a diaspora community, or a citizen with familial ties abroad, for household income in their home country or homeland. Money sent home by migrants competes with international aid as one of the largest financial inflows to developing countries. Workers' remittances are a significant part of international capital flows, especially with regard to labor-exporting countries.

Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however.

Immigration to Greece percentage of foreign populations in Greece is 7.1% in proportion to the total population of the country. Moreover, between 9 and 11% of the registered Greek labor force of 4.4 million are foreigners. Migrants additionally make up 25% of wage and salary earners.

Circular migration or repeat migration is the temporary and usually repetitive movement of a migrant worker between home and host areas, typically for the purpose of employment. It represents an established pattern of population mobility, whether cross-country or rural-urban. There are several benefits associated with this migration pattern, including gains in financial capital, human capital, and social capital. There are also costs associated with circular migration, such as brain drain, poor working conditions, forced labor, and the inability to transfer acquired skills to home economies. Socially, there are strong connections to gender, health outcomes, development, poverty, and global immigration policy.
International migration occurs when people cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum length of the time. Migration occurs for many reasons. Many people leave their home countries in order to look for economic opportunities in another country. Others migrate to be with family members who have migrated or because of political conditions in their countries. Education is another reason for international migration, as students pursue their studies abroad, although this migration is sometimes temporary, with a return to the home country after the studies are completed.
Emigration from Colombia is a migratory phenomenon that started in the early 20th century.

Emigration from Mexico is the movement of people from Mexico to other countries. The top destination by far is the United States, by a factor of over 150 to 1 compared to the second most popular destination, Canada.
The labor migration policy of the Philippine government allows and encourages emigration. The Department of Foreign Affairs, which is one of the government's arms of emigration, grants Filipinos passports that allow entry to foreign countries. In 1952, the Philippine government formed the Philippine Overseas Employment Administration (POEA) as the agency responsible for opening the benefits of the overseas employment program. In 1995, it enacted the Migrant Workers and Overseas Filipino Act in order to "institute the policies of overseas employment and establish a higher standard of protection and promotion of the welfare of migrant workers and their families and overseas Filipinos in distress." In 2022, the Department of Migrant Workers was formed, incorporating the POEA with its functions and mandate becoming the backbone of the new executive department.
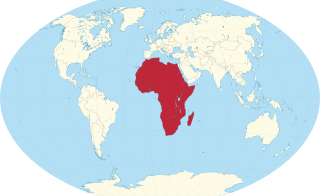
During the period of 1965 – 2021, an estimated 440,000 people per year emigrated from Africa; a total number of 17 million migrants within Africa was estimated for 2005. The figure of 0.44 million African emigrants per year pales in comparison to the annual population growth of about 2.6%, indicating that only about 2% of Africa's population growth is compensated for by emigration.
Women migrant workers from developing countries engage in paid employment in countries where they are not citizens. While women have traditionally been considered companions to their husbands in the migratory process, most adult migrant women today are employed in their own right. In 2017, of the 168 million migrant workers, over 68 million were women. The increase in proportion of women migrant workers since the early twentieth century is often referred to as the "feminization of migration".

Maya Americans are Americans of Indigenous Maya descent. Most Maya Americans originate from western Guatemala and Chiapas.
International money transfers made by migrant workers and immigrants sending a portion of their earnings to their families in their country of origin are known as remittances. Remittances are an important aspect of the global economy, totaling an estimated $601 billion (USD) for the year 2015. The United States is currently the largest source of international remittances in the world, sending a total of $148 billion in 2017. Mexico received the largest portion of these remittances, accounting for more than $30 billion USD. making the U.S.-Mexico remittance corridor one of the largest in the world. With the exception of the 2008 global financial crisis, remittances sent from the U.S. have been consistently climbing for the past half century. This major increase in remittances can be partially attributed to the larger population of immigrants and migrant workers, as well as to increasing globalization in the financial and money markets. China and India are also major recipients of U.S. remittances, and are the top two recipients of remittances globally.
A global care chain is a globalized labor market for workers who provide care-intensive labor, such as childcare, eldercare and healthcare. The term was coined by the feminist sociologist Arlie Hochschild. The movement of these workers is an important topic for research and policy development since the number of international migrants around the world has grown substantially since the 1990s.













