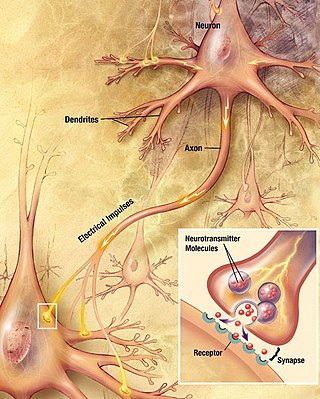
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network in the nervous system. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap.
Chemical synapses are biological junctions through which neurons' signals can be sent to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.
An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is a kind of synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron less likely to generate an action potential. The opposite of an inhibitory postsynaptic potential is an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP), which is a synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron more likely to generate an action potential. IPSPs can take place at all chemical synapses, which use the secretion of neurotransmitters to create cell-to-cell signalling. EPSPs and IPSPs compete with each other at numerous synapses of a neuron. This determines whether an action potential occurring at the presynaptic terminal produces an action potential at the postsynaptic membrane. Some common neurotransmitters involved in IPSPs are GABA and glycine.

In neuroscience, an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. This temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential, caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell, is a result of opening ligand-gated ion channels. These are the opposite of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), which usually result from the flow of negative ions into the cell or positive ions out of the cell. EPSPs can also result from a decrease in outgoing positive charges, while IPSPs are sometimes caused by an increase in positive charge outflow. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC).
In neuroscience, a silent synapse is an excitatory glutamatergic synapse whose postsynaptic membrane contains NMDA-type glutamate receptors but no AMPA-type glutamate receptors. These synapses are named "silent" because normal AMPA receptor-mediated signaling is not present, rendering the synapse inactive under typical conditions. Silent synapses are typically considered to be immature glutamatergic synapses. As the brain matures, the relative number of silent synapses decreases. However, recent research on hippocampal silent synapses shows that while they may indeed be a developmental landmark in the formation of a synapse, that synapses can be "silenced" by activity, even once they have acquired AMPA receptors. Thus, silence may be a state that synapses can visit many times during their lifetimes.
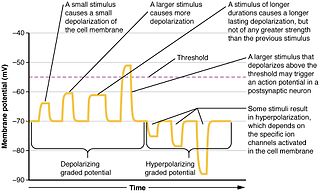
Graded potentials are changes in membrane potential that vary according to the size of the stimulus, as opposed to being all-or-none. They include diverse potentials such as receptor potentials, electrotonic potentials, subthreshold membrane potential oscillations, slow-wave potential, pacemaker potentials, and synaptic potentials. The magnitude of a graded potential is determined by the strength of the stimulus. They arise from the summation of the individual actions of ligand-gated ion channel proteins, and decrease over time and space. They do not typically involve voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels, but rather can be produced by neurotransmitters that are released at synapses which activate ligand-gated ion channels. They occur at the postsynaptic dendrite in response to presynaptic neuron firing and release of neurotransmitter, or may occur in skeletal, smooth, or cardiac muscle in response to nerve input. These impulses are incremental and may be excitatory or inhibitory.

A neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
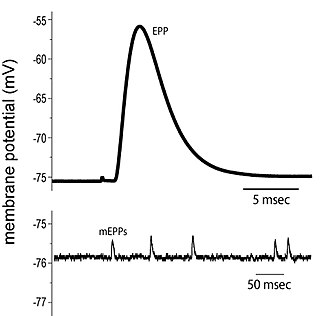
End plate potentials (EPPs) are the voltages which cause depolarization of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called "end plates" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.4mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.
Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject covers topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics and epigenetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.
The induction of NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation (LTP) in chemical synapses in the brain occurs via a fairly straightforward mechanism. A substantial and rapid rise in calcium ion concentration inside the postsynaptic cell is most possibly all that is required to induce LTP. But the mechanism of calcium delivery to the postsynaptic cell in inducing LTP is more complicated.
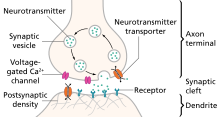
Postsynaptic potentials are changes in the membrane potential of the postsynaptic terminal of a chemical synapse. Postsynaptic potentials are graded potentials, and should not be confused with action potentials although their function is to initiate or inhibit action potentials. They are caused by the presynaptic neuron releasing neurotransmitters from the terminal bouton at the end of an axon into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic terminal, which may be a neuron, or a muscle cell in the case of a neuromuscular junction. These are collectively referred to as postsynaptic receptors, since they are on the membrane of the postsynaptic cell.

Neurotransmission is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron, and bind to and react with the receptors on the dendrites of another neuron a short distance away. A similar process occurs in retrograde neurotransmission, where the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron release retrograde neurotransmitters that signal through receptors that are located on the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, mainly at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses.

In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.

Synaptic potential refers to the potential difference across the postsynaptic membrane that results from the action of neurotransmitters at a neuronal synapse. In other words, it is the “incoming” signal that a neuron receives. There are two forms of synaptic potential: excitatory and inhibitory. The type of potential produced depends on both the postsynaptic receptor, more specifically the changes in conductance of ion channels in the post synaptic membrane, and the nature of the released neurotransmitter. Excitatory post-synaptic potentials (EPSPs) depolarize the membrane and move the potential closer to the threshold for an action potential to be generated. Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) hyperpolarize the membrane and move the potential farther away from the threshold, decreasing the likelihood of an action potential occurring. The Excitatory Post Synaptic potential is most likely going to be carried out by the neurotransmitters glutamate and acetylcholine, while the Inhibitory post synaptic potential will most likely be carried out by the neurotransmitters gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine. In order to depolarize a neuron enough to cause an action potential, there must be enough EPSPs to both depolarize the postsynaptic membrane from its resting membrane potential to its threshold and counterbalance the concurrent IPSPs that hyperpolarize the membrane. As an example, consider a neuron with a resting membrane potential of -70 mV (millivolts) and a threshold of -50 mV. It will need to be raised 20 mV in order to pass the threshold and fire an action potential. The neuron will account for all the many incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals via summative neural integration, and if the result is an increase of 20 mV or more, an action potential will occur.
Gliotransmitters are chemicals released from glial cells that facilitate neuronal communication between neurons and other glial cells. They are usually induced from Ca2+ signaling, although recent research has questioned the role of Ca2+ in gliotransmitters and may require a revision of the relevance of gliotransmitters in neuronal signalling in general.

Summation, which includes both spatial summation and temporal summation, is the process that determines whether or not an action potential will be generated by the combined effects of excitatory and inhibitory signals, both from multiple simultaneous inputs, and from repeated inputs. Depending on the sum total of many individual inputs, summation may or may not reach the threshold voltage to trigger an action potential.
Cellular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience concerned with the study of neurons at a cellular level. This includes morphology and physiological properties of single neurons. Several techniques such as intracellular recording, patch-clamp, and voltage-clamp technique, pharmacology, confocal imaging, molecular biology, two photon laser scanning microscopy and Ca2+ imaging have been used to study activity at the cellular level. Cellular neuroscience examines the various types of neurons, the functions of different neurons, the influence of neurons upon each other, and how neurons work together.

The active zone or synaptic active zone is a term first used by Couteaux and Pecot-Dechavassinein in 1970 to define the site of neurotransmitter release. Two neurons make near contact through structures called synapses allowing them to communicate with each other. As shown in the adjacent diagram, a synapse consists of the presynaptic bouton of one neuron which stores vesicles containing neurotransmitter, and a second, postsynaptic neuron which bears receptors for the neurotransmitter, together with a gap between the two called the synaptic cleft. When an action potential reaches the presynaptic bouton, the contents of the vesicles are released into the synaptic cleft and the released neurotransmitter travels across the cleft to the postsynaptic neuron and activates the receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
In neuroscience, synaptic scaling is a form of homeostatic plasticity, in which the brain responds to chronically elevated activity in a neural circuit with negative feedback, allowing individual neurons to reduce their overall action potential firing rate. Where Hebbian plasticity mechanisms modify neural synaptic connections selectively, synaptic scaling normalizes all neural synaptic connections by decreasing the strength of each synapse by the same factor, so that the relative synaptic weighting of each synapse is preserved.
Anoxic depolarization is a progressive and uncontrollable depolarization of neurons during stroke or brain ischemia in which there is an inadequate supply of blood to the brain. Anoxic depolarization is induced by the loss of neuronal selective membrane permeability and the ion gradients across the membrane that are needed to support neuronal activity. Normally, the Na+/K+-ATPase pump maintains the transmembrane gradients of K+ and Na+ ions, but with anoxic brain injury, the supply of energy to drive this pump is lost. The hallmarks of anoxic depolarization are increased concentrations of extracellular K+ ions, intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ ions, and extracellular glutamate and aspartate. Glutamate and aspartate are normally present as the brain's primary excitatory neurotransmitters, but high concentrations activate a number of downstream apoptotic and necrotic pathways. This results in neuronal dysfunction and brain death.