
The Chihuahuan Desert is a desert ecoregion designation covering parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies much of far West Texas, the middle to lower Rio Grande Valley and the lower Pecos Valley in New Mexico, and a portion of southeastern Arizona, as well as the central and northern portions of the Mexican Plateau. It is bordered on the west by the Sonoran Desert, the Colorado Plateau, and the extensive Sierra Madre Occidental range, along with northwestern lowlands of the Sierra Madre Oriental range. Its largest, continual expanse is located in Mexico, covering a large portion of the state of Chihuahua, along with portions of Coahuila, north-eastern Durango, the extreme northern part of Zacatecas, and small western portions of Nuevo León. With an area of about 501,896 km2 (193,783 sq mi), it is the largest desert in North America. The desert is fairly young, existing for only 8000 years.

Cylindropuntia fulgida, the jumping cholla, also known as the hanging chain cholla, is a cholla cactus native to Sonora and the Southwestern United States.
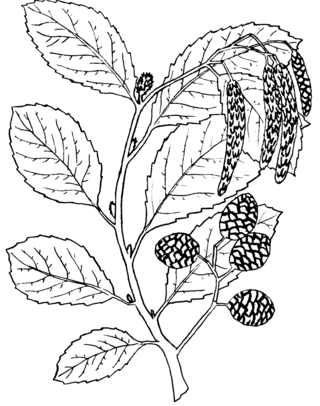
Alnus oblongifolia is a large alder growing up to 72 feet (22 m), from the southwestern United States and northern Sonora, Mexico. It grows across Arizona into western New Mexico mountain ranges. In central Arizona its range extends across the transition zone to the White Mountains region of eastern Arizona–western New Mexico border.

Fraxinus velutina, the velvet ash, Arizona ash or Modesto ash, is a species of Fraxinus native to southwestern North America, in the United States from southern California east to Texas, and in Mexico from northern Baja California east to Coahuila and Nuevo León.

Psorothamnus spinosus, or Delea spinosa, is a perennial legume tree of the deserts in North America. Common names include smokethorn, smoketree, smoke tree, smokethorn dalea, and corona de Cristo.

Olneya tesota is a perennial flowering tree of the family Fabaceae, legumes, which is commonly known as ironwood, desert ironwood, or palo fierro in Spanish. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Olneya. This tree is part of the western Sonoran Desert complex in the Southwestern United States.

Condalia globosa, also called bitter condalia, or bitter snakewood, is a perennial shrub, small tree of the family Rhamnaceae.

Nolina bigelovii is a flowering plant native to the Southwestern United States, California, and northwest Mexico. It grows in the driest desert areas and at elevations up to 1,500 metres (4,900 ft).

The Lower Colorado River Valley (LCRV) is the river region of the lower Colorado River of the southwestern United States in North America that rises in the Rocky Mountains and has its outlet at the Colorado River Delta in the northern Gulf of California in northwestern Mexico, between the states of Baja California and Sonora. This north–south stretch of the Colorado River forms the border between the U.S. states of California/Arizona and Nevada/Arizona, and between the Mexican states of Baja California/Sonora.

Koeberlinia spinosa is a species of flowering plant native to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico known by several common names, including crown of thorns, allthorn, and crucifixion thorn. It is one of two species of the genus Koeberlinia, which is sometimes considered to be the only genus in the plant family Koeberliniaceae. Alternately it is treated as a member of the caper family. This is a shrub of moderate to large size, sprawling to maximum heights over 4 m (13 ft). It is entirely green while growing and is made up of tangling straight stems which branch many times. The tip of each rigid stem branch tapers into a long, sharp spine. Leaves are mainly rudimentary, taking the form of tiny deciduous scales. Most of the photosynthesis occurs in the green stem branches. The shrub blooms abundantly in white to greenish-white flowers. The fruits are shiny black berries each a few millimeters long; they are attractive to birds.

Celtis reticulata, with common names including netleaf hackberry, western hackberry, Douglas hackberry, netleaf sugar hackberry, palo blanco, and acibuche, is a small- to medium-sized deciduous tree native to western North America.

Yucca faxoniana is a bladed evergreen shrub of the genus Yucca. It is known by the common names Faxon yucca,Spanish dagger, and giant dagger.

Yucca × schottii is a plant species in the genus Yucca, native to southern Arizona, southwestern New Mexico, and the northern parts of Sonora and Chihuahua. The common names are Schott's yucca, hoary yucca, and mountain yucca. The "×" in the name indicates that this is a nothospecies, regarded as being a natural hybrid between two other species. In this case, Yucca × schottii is believed to have originated as a hybrid between Y. baccata and Y. madrensis. Yucca × schottii is firmly established and does reproduce freely in the wild.

Arbutus arizonica, commonly known as Arizona madrone, is a tree species in the heath family that is native to the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. Its range extends along the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera from the Madrean Sky Islands of southeastern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico south as far as Jalisco. It has been found in Sonora, Chihuahua, Durango, and Sinaloa, with one isolated population in Tamaulipas.

Salix taxifolia, the yewleaf or yew-leaf willow, is a species of willow native to all of southern Mexico, also Pacific Coast regions, north to Sinaloa, and in the south Pacific Coast of Mexico into central Guatemala. Scattered populations are also reported from northern Mexico and from the US states of Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona.

Salix bonplandiana, , is a perennial species of willow tree native to southern and southwest Mexico and extending into central Guatemala; in western Mexico it is a tree of the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera, but also occurring in other small locales, for example Baja California Sur, northern Sonora, San Luis Potosi, etc. A core disjunct area occurs in central and southeast Arizona, in advantageous locales, especially associated with higher elevations and water.

Purshia mexicana is a species of perennial flowering small tree in the rose family known by the common name Mexican cliffrose. It is native to western-northern Mexico, the region of the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera.

Eysenhardtia texana, commonly known as Texas kidneywood, bee-brush, or vara dulce, is a species of small flowering tree in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is found from south-central Texas south to northern San Luis Potosí in the Rio Grande Valley region of south Texas–Northeastern Mexico, and the species ranges into the eastern Chihuahuan Desert areas of Coahuila.

Platanus wrightii, the Arizona sycamore, is a sycamore tree native to Arizona and New Mexico with its range extending south into the Mexican states of Sonora, Chihuahua, and Sinaloa.

Frangula betulifolia, the birchleaf buckthorn, is a shrub or small tree in the buckthorn family, Rhamnaceae. It is native in northern Mexico in the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera, and mountainous, desert regions of the Southwestern United States of Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, and far west Texas; besides being found in Sonora, Chihuahua and Durango of the Occidental cordillera, a large species locale occurs to the east in Nuevo León.



















