Pago Pago is the capital of American Samoa. It is in Maoputasi County on Tutuila, which is American Samoa's main island.

Tutuila is the largest and most populous island of American Samoa and is part of the archipelago of the Samoan Islands. It is the third largest island in the Samoan Islands chain of the Central Pacific. It is located roughly 4,000 kilometers (2,500 mi) northeast of Brisbane, Australia and lies over 1,200 kilometers (750 mi) to the northeast of Fiji. It contains a large, natural harbor, Pago Pago Harbor, where Pago Pago, the capital of American Samoa, is situated. Pago Pago International Airport is also located on Tutuila. The island's land expanse is about 68% of the total land area of American Samoa. With 56,000 inhabitants, it is also home to 95% of the population of American Samoa. The island has six terrestrial and three marine ecosystems.

Fagatogo is the downtown area of Pago Pago. Located in the low grounds at the foot of Matafao Peak, it was the location of the first American settlement on Tutuila Island. It includes the sub-village of Malaloa. Today, Fagatogo is the government, commercial, financial, and shipping center of Tutuila. It is also the administrative capital of American Samoa. It is the location of the American Samoa Fono (legislature), and is listed in the Constitution of American Samoa as the territory's official seat of government. Its population is 1,737.

Poloa is a village in American Samoa. It is located at the west side of Tutuila in the Alataua District. The village has 193 residents in 2010. The main denominations in the area are Methodist and Christian. Poloa has one elementary school. It is located in Lealataua County.
The Eastern District is one of the primary districts of American Samoa. It consists of the eastern portion of Tutuila, American Samoa's largest island, plus the island of Aunu'u. The district has a land area of 67.027 km2 and a 2010 census population of 23,030. It contains 34 villages plus a portion of Nuʻuuli village. Among these are Pago Pago, Fagatogo, and Utulei.

Fatu Rock is a natural landmark and offshore islet of American Samoa. It is located near the entrance of Pago Pago Harbor, close to the village of Fatumafuti. Fatu and nearby Futi are also known as Flowerpot Rock.

Leone is the second-largest city on Tutuila Island's west coast. The village is on the south-west coast of Tutuila Island, American Samoa. Leone was the ancient capital of Tutuila Island. Leone was also where the Samoan Islands’ first missionary, John Williams, visited on October 18, 1832. A monument in honor of Williams has been erected in front of Zion Church. Its large church was the first to be built in American Samoa. It has three towers, a carved ceiling and stained glass. Until steamships were invented, Leone was the preferred anchorage of sailing ships which did not risk entering Pago Pago Harbor. Much early contact between Samoans and Europeans took place in Leone.

Tafuna is a village in Tualauta County, Western District, American Samoa. It is the most populous village in American Samoa, with a population of 7,988 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, and is the center of nightlife on island.

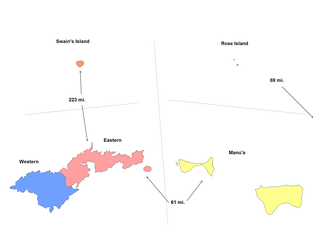
American Samoa is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Centered on 14.3°S 170.7°W, it is east of the International Date Line and the Wallis and Futuna Islands, west of the Cook Islands, north of Tonga, and some 500 kilometers (310 mi) south of Tokelau. American Samoa is the southernmost territory of the United States and one of two U.S. territories south of the Equator, along with the uninhabited Jarvis Island.
Afao is a village in southwest Tutuila Island, American Samoa. It is located on the island's short southwestern coast, between 'Amanave and Leone, to the southwest of Pago Pago. It includes the settlement of Atauloma. Afao is home to two places listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places: Afao Beach Site and Atauloma Girls School.

Afono is a village on the northeast coast of Tutuila Island, American Samoa. One of the island's more populous villages, it is located on the edge of Afono Bay, at the eastern edge of the National Park of American Samoa. It is connected by Highway 6 to Vatia, which lies along the coast to the northwest, and to Aua, on the edge of Pago Pago Harbor to the south via a winding stretch of highway which crosses the spine of the island.

Alega is a village on the southeast coast of Tutuila Island, American Samoa. One of the island's least populous villages, it is located to the east of Pago Pago Harbor and to the west of Faga'itua Bay. Alega, with a population of 29 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, is one of the smallest villages in American Samoa, surpassing only Maloata and Sili in population.

Aʻoloau is a village in the west of Tutuila Island, American Samoa. It is located inland, 5 miles (8 km) southwest of Pago Pago. It is also known as Aʻoloaufou, which means "New Aʻolou". An abandoned area in town by Aʻoloau Bay is known as Aʻoloautuai, which means "Old Aʻoloau". Aʻoloau's nickname is Nuu Puaolele which means the Fog Village.
Aʻumi is a village on the central south coast of Tutuila Island, American Samoa.

Pago Pago Harbor on Tutuila Island in American Samoa is one of the world's largest natural harbors. The capital, Pago Pago is located on the inner reaches of the harbor, close to its northwesternmost point. It has the highest annual rainfall of any harbor in the world. It is also considered one of the best and deepest deepwater harbors in the South Pacific Ocean or in Oceania as a whole. Pago Pago Bay is over 400 feet (120 m) deep and two miles (3.2 km) long. As part of the Pago Volcano caldera, the harbor is 50% landlocked.
Fagaʻalu is a village in central Tutuila Island, American Samoa. It is also known as Fagaʻalo. It is located on the eastern shore of Pago Pago Harbor, to the south of Pago Pago. American Samoa's lone hospital, Lyndon B. Johnson Tropical Medical Center, is located in Fagaʻalu. The village is centered around Fagaalu Stream.

Vatia is a village on Tutuila Island in American Samoa. It is a north shore village located on Vatia Bay. The road to Vatia, American Samoa Highway 006, is the only road going through National Park of American Samoa. Vatia is a scenic community at the foot of Pola Ridge and surrounded by the national park. It is only reached by Route 6 which traverses the national park before reaching Vatia. There was once a hiking trail over Maugaloa Ridge from Leloaloa, but since the completion of Route 6, this trail is now overgrown. It is home to a beach, and panoramic views of jungle-covered peaks surround the village on all sides. Vatia is the center of the Tutuila-section of National Park of American Samoa. It is located in Vaifanua County.

Fagasā is a village in the Eastern District of Tutuila Island in American Samoa. The village lies by Fagasa Bay, on the north shore of the island. Its name is Samoan and translates to "Forbidden Bay." The village borders the Tutuila-section of National Park of American Samoa. The trailhead to Mount ʻAlava is located near the village by Fagasa Pass.
Saʻilele is a village on the north shore in the Eastern District of Tutuila Island in American Samoa. It is reached from a cross-island road which leads north from the village of Fagaʻitua. On a track east of the village is a burial ground where some aliʻi were buried.