
The politics of Haiti takes place in the framework of a unitary semi-presidential republic, where the president is the head of state and the prime minister is the head of government. The politics of Haiti are considered historically unstable due to various coups d'état, regime changes, military juntas and internal conflicts. After Jean-Bertrand Aristide was deposed, Haitian politics became relatively stable. The Economist Intelligence Unit rated Haiti an "authoritarian regime" in 2022. According to the V-Dem Democracy indices Haiti is 2023 the 4th least electoral democratic country in Latin America.

Fanmi Lavalas is a social-democratic political party in Haiti. Its leader is former Haitian President Jean-Bertrand Aristide. It has been a powerful force in Haitian politics since 1991. Fanmi Lavalas governments advocate a policy of "growth with equity" based on Western European social democratic principles. Fanmi Lavalas governments have emphasised investment in education and health care as their priorities and have refused International Monetary Fund austerity measures.

The Constitution of Haiti provides for the election of the President, Parliament, and members of local governing bodies. The 2015–16 Haitian parliamentary election was held. The February 2016 Haitian presidential election was held following annulment of the February 2016 Haitian presidential election.

Elections in Lithuania are held to select members of the parliament, the president, members of the municipal councils and mayors, as well as delegates to the European Parliament. Lithuanian citizens can also vote in mandatory or consultative referendums.

Jocelerme Privert is a Haitian accountant and bureaucrat who served as the interim President of Haiti from 2016 to 2017.

General elections were held in Haiti on 7 February 2006 to elect the replacements for the interim government of Gérard Latortue, which had been put in place after the 2004 Haiti rebellion. The elections were delayed four times, having originally been scheduled for October and November 2005. Voters elected a president, all 99 seats in the Chamber of Deputies of Haiti and all 30 seats in the Senate of Haiti. Voter turnout was around 60%. Run-off elections for the Chamber of Deputies of Haiti were held on 21 April, with around 28% turnout.

Michel Joseph Martelly is a Haitian musician and politician who served as the 42nd president of Haiti from May 2011 until February 2016. On August 20, 2024, the United States sanctioned the former president for trafficking drugs, in particular cocaine, into the United States, and for sponsoring several gangs based in Haiti.
General elections were held in Haiti on 28 November 2010, having originally been scheduled for 28 February. Ten senators and all 99 deputies were to be elected.

General elections were held in the Central African Republic on 30 December 2015 to elect the president and National Assembly. As no presidential candidate received more than 50% of the vote, and following the annulling of the results of the National Assembly elections by the Transitional Constitutional Court, a second round of the presidential elections and a re-run of the parliamentary elections were held on 14 February 2016, with second round run-offs for the parliamentary elections on 31 March.

This national electoral calendar for 2016 lists the national/federal elections held in 2016 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

Presidential elections were held in Haiti on 25 October 2015, alongside local elections and the second round of the legislative elections. Incumbent President Michel Martelly was constitutionally barred from running. As no candidate received a majority of the vote in the first round, a runoff was to be held on 27 December 2015. On 22 December the Conseil Electoral Provisoire (CEP) announced that the runoff has been postponed indefinitely. However, on 1 January 2016 President Michel Martelly announced that the runoff would be held on 17 January, but on 7 January the President changed the date to 24 January. On 20 January, Jude Célestin issued a statement that calls "whatever the person who will participate in this January 24 [runoff], is a traitor to the Nation". Because of rioting and electoral violence, on 22 January the CEP decided to postpone the second round again, with no specific date given, even after President Michel Martelly confirmed the previous day in a nationwide speech that the election should still take place. The run-off date was later agreed to take place on 24 April 2016.

Parliamentary elections were held in Haiti on 9 August 2015, with a second round initially planned for 25 October. Two-thirds of the Senate and all members of the Chamber of Deputies were up for election. International observers reported that early rounds of voting have experienced significant fraud, including people voting more than once due to failure of indelible ink, vote buying due to lack of secrecy, poor training of election workers, poor tracking of political parties, and other problems. This has resulted in the nullification of some results and rescheduling of re-runs. The second round of the parliamentary elections that had been scheduled for October 2015 was postponed to October 2016, along with the first round for a third of the Senate and the first round of a new presidential election.

Jovenel Moïse was a Haitian politician and entrepreneur who served as the 43rd president of Haiti from 2017 until his assassination in 2021. He assumed the presidency in February 2017 after winning the November 2016 election. During his term, Haiti experienced widespread protests. In the early morning of 7 July 2021, Moïse was assassinated and his wife Martine was injured during an attack on their private residence in Pétion-Ville.

Cholzer Chancy is a Haitian politician. He was President of the Haitian Chamber of Deputies between 11 January 2016 and 11 January 2018. He is a member of the political party Haiti in Action.

Presidential elections were held in Haiti on 20 November 2016 after having been postponed several times. The elections were overseen by the Provisional Electoral Council (CEP), and were held using the two-round system, with a second round scheduled for 29 January 2017 if no candidate received an absolute majority of the votes in the first round. However, on 27 November election officials announced that, according to preliminary results, Jovenel Moïse had won the election in the first round with more than 50% of the vote. Voter turnout, in the election held 6 weeks after Hurricane Matthew hit Haiti, was reported to be 21%. Jovenel Moïse assumed office on 7 February 2017, and was assassinated on 7 July 2021.

The president of France is elected by direct popular vote to a five-year term. If the office falls vacant before the end of five years, an election to a new five-year term is held, generally within 20 to 35 days of the vacancy.

General elections are due to be held in Haiti in February 2026. The parliamentary elections had originally been scheduled for 27 October 2019, but were postponed to 26 September 2021, and then again to 7 November 2021, when wider elections were planned to elect the president and Parliament, alongside a constitutional referendum. However, in September 2021 they were postponed again following the dismissal of the members of the Provisional Electoral Council by acting prime minister Ariel Henry. Henry later stated that he hoped to hold the elections in early 2022. On 8 February 2022, he called for renewed efforts to organize elections. In December 2022, he signed an agreement to hold the elections in 2023, but stated in February 2024 that they will be held once the security situation was under control. Henry later committed to hold the elections by August 2025, but resigned in April 2024 to make way for a Transitional Presidential Council, which is expected to hold the presidential election in early 2026.
Ukrainian presidential elections determine who will serve as the President of Ukraine for the next five years.
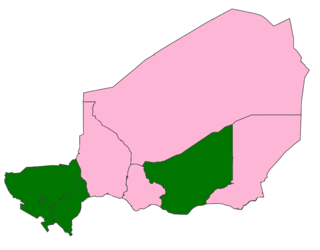
General elections were held in Niger on 27 December 2020 to elect the President and National Assembly. With incumbent president Mahamadou Issoufou stepping down following his two terms constitutional limit, new presidential candidates competed for office. As no presidential candidate received a majority of the vote on the first round, a second round was held on 21 February 2021. The ruling Nigerien Party for Democracy and Socialism (PNDS) candidate Mohamed Bazoum was declared the winner, beating Mahamane Ousmane in the second round with 56% of the vote. In the National Assembly elections the PNDS won 79 of the 166 seats, falling just short of a majority.

A constitutional referendum was planned to be held in Haiti in 2023. It is the first referendum in the country since 1987, and was unilaterally proposed by the administration of Jovenel Moïse. Originally set to be held on 27 June 2021, the referendum was postponed to 26 September 2021, on the same day as the presidential and parliamentary elections. The referendum was again postponed to 7 November. Acting Prime Minister Ariel Henry later postponed it first to February 2022 and then 2023.














