
Cedrus libani, commonly known as cedar of Lebanon or Lebanese cedar, is a species of tree in the genus Cedrus, a part of the pine family, native to the mountains of the Eastern Mediterranean basin. It is a large evergreen conifer that has great religious and historical significance in the cultures of the Middle East, and is referenced many times in the literature of ancient civilisations. It is the national emblem of Lebanon and is widely used as an ornamental tree in parks and gardens.

Western white pine, also called silver pine and California mountain pine, is a species of pine in the family Pinaceae. It occurs in mountain ranges of northwestern North America and is the state tree of Idaho.

Mount Cameroon is an active volcano in the South West region of Cameroon next to the city of Buea near the Gulf of Guinea. Mount Cameroon is also known as Cameroon Mountain or Fako or by its indigenous name Mongo ma Ndemi. Mount Cameroon is ranked 22nd by topographic isolation.

The mountain gorilla is one of the two subspecies of the eastern gorilla. It is listed as endangered by the IUCN as of 2018.

Abies × borisii-regis is a hybrid species of fir native to the mountains of the Balkan Peninsula in Bulgaria, northern Greece, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Albania and Serbia. It occurs at altitudes of 800–1,800 m (2,600–5,900 ft), on mountains with an annual rainfall of over 1,000 mm (39 in).

Virunga National Park is a national park in the Albertine Rift Valley in the eastern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was created in 1925. In elevation, it ranges from 680 m (2,230 ft) in the Semliki River valley to 5,109 m (16,762 ft) in the Rwenzori Mountains. From north to south it extends approximately 300 km (190 mi), largely along the international borders with Uganda and Rwanda in the east. It covers an area of 8,090 km2 (3,120 sq mi).

Abies pinsapo, Spanish fir, is a species of tree in the family Pinaceae, native to southern Spain and northern Morocco. Related to other species of Mediterranean firs, it appears at altitudes of 900–1,800 metres (3,000–5,900 ft) in the Sierra de Grazalema in the Province of Cádiz and the Sierra de las Nieves and Sierra Bermeja, both near Ronda in the province of Málaga. In Morocco, it is limited to the Rif Mountains at altitudes of 1,400–2,100 metres (4,600–6,900 ft) on Jebel Tissouka and Jebel Tazaot.

Snub-nosed monkeys are a group of Old World monkeys and make up the entirety of the genus Rhinopithecus. The genus is rare and not fully researched. Some taxonomists group snub-nosed monkeys together with the genus Pygathrix.

Picea engelmannii, with the common names Engelmann spruce, white spruce, mountain spruce, and silver spruce, is a species of spruce native to western North America. It is mostly a high-elevation mountain tree but also appears in watered canyons.
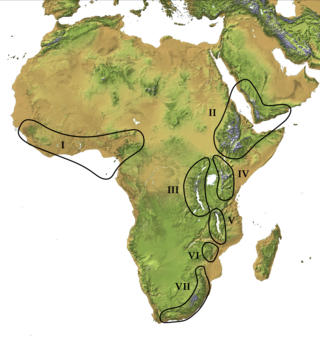
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.
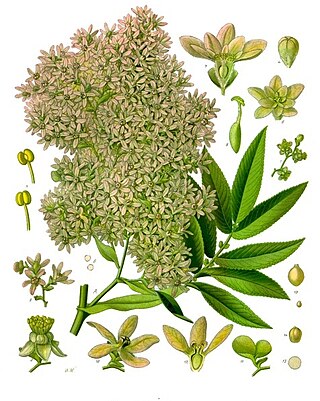
Hagenia is a monotypic genus of flowering plant with the sole species Hagenia abyssinica, native to the high-elevation Afromontane regions of central and eastern Africa. It also has a disjunct distribution in the high mountains of East Africa from Sudan and Ethiopia in the north, through Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo, and Tanzania, to Malawi and Zambia in the south. A member of the rose family, its closest relative is the Afromontane genus Leucosidea.

The silver-throated tanager is a species of passerine bird in the tanager family Thraupidae. It is found in Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador, and northeastern Peru. It inhabits mossy forests, montane evergreen forests, tropical lowland evergreen forests and forest edges, along with tall secondary forests and disturbed habitat with remnant trees and forest. It is 13 centimetres (5.1 in) long and weighs 22 grams (0.78 oz) on average, and shows slight sexual dimorphism, with duller female plumage. Adult males are mainly bright yellow, with a silvery-white throat bordered above with a black stripe on the cheeks, black streaking on the back, and green edges to the wings and tail. Juveniles are duller and greener.

The collared grosbeak is a species of finch in the family Fringillidae. Its range encompasses the northern regions of the Indian Subcontinent, mainly the Himalayas, along with some adjoining regions. It is found in Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal and Thailand. Its natural habitat is mountainous deciduous or mixed forests.

The rufous-gaped hillstar, formerly included in the white-tailed hillstar, is a species of hummingbird in the "brilliants", tribe Heliantheini in subfamily Lesbiinae. It is found in Colombia and Ecuador.
Leptopelis karissimbensis is a species of frog in the family Arthroleptidae. It is found in the highlands of western Rwanda and southwestern Uganda and in the adjacent eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is very similar to Leptopelis kivuensis and has been confused with that species. Common names Karissimbi forest treefrog and Karissimbi tree frog have been coined for it.

The black imperial pigeon, also known as the Bismarck imperial pigeon, is a species of bird in the pigeon family, Columbidae. First described by English zoologist Philip Sclater in 1878, it is endemic to the Bismarck Archipelago, where it mainly inhabits rainforest and cloud forest in mountain areas above 500 m (1,600 ft). It is a large, heavily built imperial pigeon, with a length of 38–43 cm (15–17 in) and a weight of 661–665 g (23.3–23.5 oz). Adults are almost entirely black, except for the dark chestnut undertail coverts, the silvery-grey underside of the tail, and a pale grey scaly pattern on the wings and back. Both sexes look alike. Juveniles differ from adults in having paler undertail coverts.

The Sumatran green pigeon is a species of bird in the pigeon family, Columbidae. First described by the Dutch zoologist Coenraad Jacob Temminck in 1823, it is endemic to Indonesia, where it is found in Sumatra and western Java. It inhabits the canopy of dense hill and montane forest and has been recorded at elevations of 350 to 1,800 m on Sumatra and 600 to 3,000 m on Java. The Sumatran green pigeon is a relatively slender species with a long wedge-shaped tail and an adult length of 29.0–34.1 cm (11.4–13.4 in) in males and 27.7–29.0 cm (10.9–11.4 in) in females. Adult males have a dark green head and body, bright yellow lower belly and undertail-coverts, dark grey tail, and bluish-green unfeathered patches on the face. Adult females are duller and have no grey on the back of the neck, a fainter orange wash on the breast, and no orange markings on the crown or the bend of the wing.

The tyrannine woodcreeper is a species of bird in subfamily Dendrocolaptinae of the ovenbird family Furnariidae. It is found in Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela.
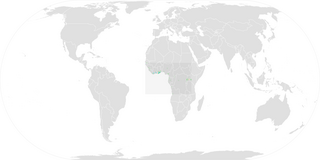
The buff-spotted woodpecker is a species of bird in the family Picidae. It is native to large parts of tropical central Africa. It has an extremely wide range and is an uncommon species, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".

Disperis nitida is a species of orchid endemic to Cameroon. Described in 1942, D. nitida is now considered a vulnerable species.



















