
Geranium robertianum, commonly known as herb-robert, or Robert's geranium, is a species of cranesbill that is widespread throughout the northern hemisphere and introduced to some countries in the southern. It is common in woods, hedges, gardens, and on waste ground, and can also be found on shingle beaches and limestone pavements. It is not rare or threatened, but in some places, it is considered to be invasive.

Salix purpurea, the purple willow, purpleosier willow, or purple osier, is a species of willow native to most of Europe and western Asia north to the British Isles, Poland, and the Baltic States.

Fumaria is a genus of about 60 species of annual flowering plants in the family Papaveraceae. The genus is native to Europe, Africa and Asia, most diverse in the Mediterranean region, and introduced to North, South America and Australia. Fumaria species are sometimes used in herbal medicine. Fumaria indica contains the alkaloids fuyuziphine and alpha-hydrastine. Fumaria indica may have anti-inflammatory and analgesic potential.

The Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland (BSBI) is a scientific society for the study of flora, plant distribution and taxonomy relating to Great Britain, Ireland, the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man. The society was founded as the Botanical Society of London in 1836, and became the Botanical Society of the British Isles, eventually changing to its current name in 2013. It includes both professional and amateur members and is the largest organisation devoted to botany in the British Isles. Its history is recounted in David Allen's book The Botanists.

Fumaria officinalis, the common fumitory, drug fumitory or earth smoke, is a herbaceous annual flowering plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It is the most common species of the genus Fumaria in Western and Central Europe.

Senecio cambrensis, the Welsh groundsel or Welsh ragwort, is a flowering plant of the family Asteraceae. It is endemic to Great Britain and currently known only from North Wales. It is a recently evolved plant that arose as a result of hybridization between two related species.

Calystegia silvatica is the largest species of bindweed and is a strong rampant climber. It is native to southern Europe but has been introduced to many other areas because it is an attractive garden plant. Calystegia silvatica subsp. fraterniflora(Mack. & Bush) Brummitt is native to North America.
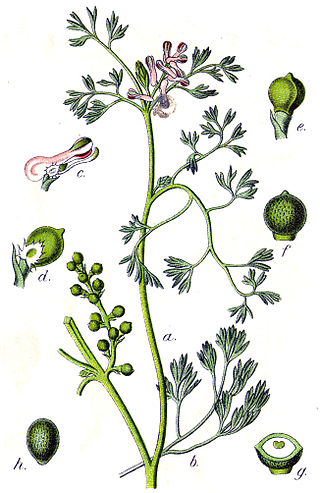
Fumaria parviflora is a species of flowering plant known by the common names fineleaf fumitory, fine-leaved fumitory and Indian fumitory. It is native to Europe, Asia, and Africa, but it is common and widely distributed in many other parts of the world. It is sometimes weedy. The small flowers are dull white with purple tips. The fruit is a rounded nutlet with a central crest.

Fumaria muralis, known as common ramping-fumitory or wall fumitory, is a flowering herbaceous plant in the poppy family (Papaveraceae) native to western Europe and northwestern Africa.

Potamogeton compressus is a species of aquatic plant known by the common names grass-wrack pondweed, flatstem pondweed and eel-grass pondweed.

Stellaria neglecta, greater chickweed, is an annual to short-lived herbaceous perennial flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae. It is native to Europe and Asia, where it grows in hedges and woodland margins on neutral to slightly acid, damp soils, and is widespread but rarely abundant. It has been introduced to North America, where it has been spreading in recent decades.

Stellaria apetala, lesser chickweed, is an annual herbaceous plant in the flowering plant family Caryophyllaceae. It occurs in short, sandy grassland by the sea and, less often, in similar habitat inland. It is native to Europe and is well established as an introduced species worldwide.

Veronica anagallis-aquatica is a species of flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae known by the common names water speedwell, blue water-speedwell,brook pimpernel.

William Hunt Painter was an English botanist who made a significant contribution to the science of Derbyshire vascular plant flora. He was a keen and wide-ranging collector of plant specimens, and was a member of the Botanical Exchange Club. In 1889 he published the first in a series of four books, all by different authors and spanning 120 years, all called The Flora of Derbyshire.

Rubia peregrina, the common wild madder, is a herbaceous perennial plant species belonging to the bedstraw and coffee family Rubiaceae.

Fumaria capreolata, the white ramping fumitory or climbing fumitory, is an herbaceous annual plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It is native to Europe, western Asia and northern Africa and naturalised in southern Australia, New Zealand, and southern South America. Common names include also ramping fumitory, white fumitory, and white-flower fumitory.
Fumaria occidentalis, the western ramping-fumitory, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Fumaria that is endemic to Cornwall. It is the largest of the British fumitories, and was discovered in 1904.
Potamogeton × griffithii is a hybrid pondweed between Potamogeton alpinus and Potamogeton praelongus. It occurs in oligotrophic, moderate alkalinity lakes.

Dactylorhiza francis-drucei subsp. traunsteinerioides, known as the narrow-leaved marsh-orchid and Pugsley's marsh orchid, is a subspecies of Dactylorhiza francis-drucei found only in Great Britain and Ireland. It is also treated as the species Dactylorhiza traunsteinerioides.

Oenanthe aquatica, fine-leaved water-dropwort, is an aquatic flowering plant in the carrot family. It is widely distributed from the Atlantic coast of Europe to central Asia.




















