
Norbert Wiener was an American computer scientist, mathematician and philosopher. He became a professor of mathematics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). A child prodigy, Wiener later became an early researcher in stochastic and mathematical noise processes, contributing work relevant to electronic engineering, electronic communication, and control systems.
In business and engineering, product development or new product development covers the complete process of bringing a new product to market, renewing an existing product and introducing a product in a new market. A central aspect of NPD is product design, along with various business considerations. New product development is described broadly as the transformation of a market opportunity into a product available for sale. The products developed by an organisation provide the means for it to generate income. For many technology-intensive firms their approach is based on exploiting technological innovation in a rapidly changing market.
Rapid application development (RAD), also called rapid application building (RAB), is both a general term for adaptive software development approaches, and the name for James Martin's method of rapid development. In general, RAD approaches to software development put less emphasis on planning and more emphasis on an adaptive process. Prototypes are often used in addition to or sometimes even instead of design specifications.

Brainstorming is a creativity technique in which a group of people interact to suggest ideas spontaneously in response to a prompt. Stress is typically placed on the volume and variety of ideas, including ideas that may seem outlandish or "off-the-wall". Ideas are noted down during the activity, but not assessed or critiqued until later. The absence of criticism and assessment is intended to avoid inhibiting participants in their idea production. The term was popularized by advertising executive Alex Faickney Osborn in the classic work Applied Imagination (1953).
Scenario planning, scenario thinking, scenario analysis, scenario prediction and the scenario method all describe a strategic planning method that some organizations use to make flexible long-term plans. It is in large part an adaptation and generalization of classic methods used by military intelligence.

In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bringing about a certain goal, like acquiring knowledge or verifying knowledge claims. This normally involves various steps, like choosing a sample, collecting data from this sample, and interpreting the data. The study of methods concerns a detailed description and analysis of these processes. It includes evaluative aspects by comparing different methods. This way, it is assessed what advantages and disadvantages they have and for what research goals they may be used. These descriptions and evaluations depend on philosophical background assumptions. Examples are how to conceptualize the studied phenomena and what constitutes evidence for or against them. When understood in the widest sense, methodology also includes the discussion of these more abstract issues.

Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks to complex issues in business and technical fields. The former is an example of simple problem solving (SPS) addressing one issue, whereas the latter is complex problem solving (CPS) with multiple interrelated obstacles. Another classification of problem-solving tasks is into well-defined problems with specific obstacles and goals, and ill-defined problems in which the current situation is troublesome but it is not clear what kind of resolution to aim for. Similarly, one may distinguish formal or fact-based problems requiring psychometric intelligence, versus socio-emotional problems which depend on the changeable emotions of individuals or groups, such as tactful behavior, fashion, or gift choices.
A technology roadmap is a flexible planning schedule to support strategic and long-range planning, by matching short-term and long-term goals with specific technology solutions. It is a plan that applies to a new product or process and may include using technology forecasting or technology scouting to identify suitable emerging technologies. It is a known technique to help manage the fuzzy front-end of innovation. It is also expected that roadmapping techniques may help companies to survive in turbulent environments and help them to plan in a more holistic way to include non-financial goals and drive towards a more sustainable development. Here roadmaps can be combined with other corporate foresight methods to facilitate systemic change.
Futures techniques used in the multi-disciplinary field of futurology by futurists in Americas and Australasia, and futurology by futurologists in EU, include a diverse range of forecasting methods, including anticipatory thinking, backcasting, simulation, and visioning. Some of the anticipatory methods include, the delphi method, causal layered analysis, environmental scanning, morphological analysis, and scenario planning.
ion is a term originally used to describe a software development process pioneered and deployed during the mid-1970s by the New York Telephone Company's Systems Development Center under the direction of Dan Gielan. Following a series of implementations of this methodology, Gielan lectured extensively in various forums on the methodology and its practices. Arnie Lind, then a Senior Systems Engineer at IBM Canada in Regina, Saskatchewan created and named joint application design in 1974. Existing methods, however, entailed application developers spending months learning the specifics of a particular department or job function, and then developing an application for the function or department. In addition to development backlog delays, this process resulted in applications taking years to develop, and often not being fully accepted by the application users.
Backcasting is a planning method that starts with defining a desirable future and then works backwards to identify policies and programs that will connect that specified future to the present. The fundamentals of the method were outlined by John B. Robinson from the University of Waterloo in 1990. The fundamental question of backcasting asks: "if we want to attain a certain goal, what actions must be taken to get there?"

The issue-based information system (IBIS) is an argumentation-based approach to clarifying wicked problems—complex, ill-defined problems that involve multiple stakeholders. Diagrammatic visualization using IBIS notation is often called issue mapping.

Cybernetics is a field of systems theory that studies circular causal systems whose outputs are also inputs, such as feedback systems. It is concerned with the general principles of circular causal processes, including in ecological, technological, biological, cognitive and social systems and also in the context of practical activities such as designing, learning, and managing.
SAP implementation refers to the name of the German company SAP SE, and is the whole of processes that defines a method to implement the SAP ERP enterprise resource planning software in an organization. The SAP implementation method described in this entry is a generic method and not a specific implementation method as such. It is based on best practices and case studies from various literature sources and presents a collection of processes and products that make up a complete implementation method to allow any organization to plan and execute the implementation of SAP software.
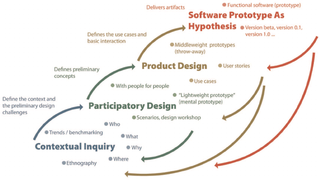
The research-based design process is a research process proposed by Teemu Leinonen, inspired by several design theories. It is strongly oriented towards the building of prototypes and it emphasizes creative solutions, exploration of various ideas and design concepts, continuous testing and redesign of the design solutions.
Design fiction is a design practice aiming at exploring and criticising possible futures by creating speculative, and often provocative, scenarios narrated through designed artifacts. It is a way to facilitate and foster debates, as explained by futurist Scott Smith: "... design fiction as a communication and social object creates interactions and dialogues around futures that were missing before. It helps make it real enough for people that you can have a meaningful conversation with".

The term serious play refers to an array of playful inquiry and innovation methods that serve as vehicles for complex problem-solving, typically in work-related contexts. Lego Serious Play is one of the best known examples; however, serious play methods also include improv theater, role play exercises, low fidelity prototyping, as well as certain simulations and gamification interventions, etc.
Advanced Innovation Design Approach (AIDA) is a holistic approach for enhancing the innovative and competitive capabilities of industrial companies. The name Advanced Innovation Design Approach (AIDA) was proposed in the research project "Innovation Process 4.0" run at the University of Applied Sciences Offenburg, Germany in co-operation with 10 German industrial companies in 2015–2019. AIDA can be considered as a pioneering mindset, an individually adaptable range of strong innovation techniques such as comprehensive front-end innovation process, advanced innovation methods, best tools and methods of the theory of inventive problem solving TRIZ, organisational measures for accelerating innovation, IT-solutions for Computer-Aided Innovation, and other tools for new product development, elaborated in the recent decade in the industry and academia.
Horizon scanning (HS) or horizon scan is a method from futures studies, sometimes regarded as a part of foresight. It is the early detection and assessment of emerging technologies or threats for mainly policy makers in a domain of choice. Such domains include agriculture, environmental studies, health care, biosecurity, and food safety.
Speculative design is a design practice concerned with future design proposals of a critical nature. The term was popularised by Anthony Dunne and Fiona Raby as a subsidiary of critical design. The aim is not to present commercially-driven design proposals but to design proposals that identify and debate crucial issues that might happen in the future. Speculative design is concerned with future consequences and implications of the relationship between science, technology, and humans. It problematizes this relation by proposing provocative future design scenarios where technology and design implications are accentuated. These design proposals are meant to trigger debates about the future rather than marketing products.







