Related Research Articles
Oligonucleotidase is an exoribonuclease derived from Flammulina velutipes. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Arabinogalactan, also known as galactoarabinan, larch arabinogalactan, and larch gum, is a biopolymer consisting of arabinose and galactose monosaccharides. Two classes of arabinogalactans are found in nature: plant arabinogalactan and microbial arabinogalactan. In plants, it is a major component of many gums, including gum arabic and gum ghatti. It is often found attached to proteins, and the resulting arabinogalactan protein (AGP) functions as both an intercellular signaling molecule and a glue to seal plant wounds.

Flammulina velutipes is a species of gilled mushroom in the family Physalacriaceae. In the UK, it has been given the recommended English name of velvet shank. The species occurs in Europe and North America. Until recently Flammulina velutipes was considered to be conspecific with the Asian Flammulina filiformis, cultivated for food as "enokitake" or "golden needle mushroom", but DNA sequencing has shown that the two are distinct.
Arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs) are highly glycosylated proteins (glycoproteins) found in the cell walls of plants. Each one consists of a protein with sugar molecules attached. They are members of the wider class of hydroxyproline (Hyp)-rich cell wall glycoproteins, a large and diverse group of glycosylated wall proteins.

Baccatin III is an isolate from the yew tree. Baccatin III is a precursor to the anti-cancer drug paclitaxel (Taxol).

In molecular biology, Glycoside hydrolase family 16 is a family of glycoside hydrolases.

In molecular biology, Glycoside hydrolase family 17 is a family of glycoside hydrolases. It folds into a TIM barrel.

In molecular biology, the glycoside hydrolase family 53 is a family of glycoside hydrolases EC 3.2.1., which are a widespread group of enzymes that hydrolyse the glycosidic bond between two or more carbohydrates, or between a carbohydrate and a non-carbohydrate moiety. A classification system for glycoside hydrolases, based on sequence similarity, has led to the definition of >100 different families. This classification is available on the CAZy web site, and also discussed at CAZypedia, an online encyclopedia of carbohydrate active enzymes.
In molecular biology, glycoside hydrolase family 26 is a family of glycoside hydrolases.
Rhamnopyranosyl-N-acetylglucosaminyl-diphospho-decaprenol beta-1,3/1,4-galactofuranosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-alpha-D-galactofuranose:alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-diphospho-trans,octacis-decaprenol 3-beta/4-beta-galactofuranosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Endo-1,3(4)-β-glucanase -β-D-glucan 3(4)-glucanohydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name 3(or 4)-β-D-glucan 3(4)-glucanohydrolase. It catalyses the following chemical reaction
endo-1,3-β-Xylanase, EC 3.2.1.32 [xylanase (ambiguous), endo-1,3-β-xylosidase, 1,3-β-xylanase, 1,3-xylanase, β-1,3-xylanase, endo-β-1,3-xylanase, 1,3-β-D-xylan xylanohydrolase, xylan endo-1,3-β-xylosidase (misleading)] is an enzyme with systematic name 3-β-D-xylan xylanohydrolase. It catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Glucan endo-1,3-β-D-glucosidase is an enzyme with systematic name 3-β-D-glucan glucanohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Arabinogalactan endo-β-1,4-galactanase is an enzyme with systematic name arabinogalactan 4-β-D-galactanohydrolase. It specifically catalyses the hydrolysis (1→4)-β-D-galactosidic linkages in type I arabinogalactans.
Blood-group-substance endo-1,4-β-galactosidase is an enzyme with systematic name blood-group-substance 4-β-D-galactanohydrolase. It catalyses endohydrolysis of (1→4)-β-D-galactosidic linkages in blood group A and B substances.
Keratan-sulfate endo-1,4-β-galactosidase is an enzyme with systematic name keratan-sulfate 4-β-D-galactanohydrolase. It catalyses endohydrolysis of (1→4)-β-D-galactosidic linkages in keratan sulfate.
Galactan 1,3-beta-galactosidase is an enzyme with systematic name galactan 3-beta-D-galactosidase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Galactan endo-1,6-beta-galactosidase is an enzyme with systematic name endo-beta-(1->6)-galactanase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Medicinal fungi are fungi that contain metabolites or can be induced to produce metabolites through biotechnology to develop prescription drugs. Compounds successfully developed into drugs or under research include antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, cholesterol and ergosterol synthesis inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, immunosuppressants and fungicides.
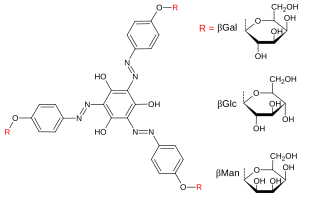
Yariv reagent is a glycosylated phenolic compound that binds strongly to galactans and arabinogalactan proteins. It can therefore be used in their detection, quantification, precipitation, isolation, staining, and interfere with their function. It was initially synthesised in 1962 as an antigen for carbohydrate-binding antibodies but has subsequently become more broadly used. There are many variants of Yariv reagents which vary in the glycosyl groups on the outside of the structure, typically glucose, galactose, and mannose.
References
- ↑ Kotake T, Hirata N, Degi Y, Ishiguro M, Kitazawa K, Takata R, Ichinose H, Kaneko S, Igarashi K, Samejima M, Tsumuraya Y (August 2011). "Endo-beta-1,3-galactanase from winter mushroom Flammulina velutipes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 286 (31): 27848–54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m111.251736 . PMC 3149374 . PMID 21653698.