
A turbocharger, colloquially known as a turbo, is a turbine-driven, forced induction device that increases an internal combustion engine's efficiency and power output by forcing extra compressed air into the combustion chamber. This improvement over a naturally aspirated engine's power output is due to the fact that the compressor can force more air—and proportionately more fuel—into the combustion chamber than atmospheric pressure alone.

The Fiat Croma is the name used for two different large family cars produced by Italian automaker Fiat, one a five door liftback built from 1985 to 1996, and the other a crossover station wagon built from 2005 to 2010.

The Nissan S130 is a sports coupé produced by Nissan in Japan from 1978 to 1983. It was sold as the Datsun 280ZX, Nissan Fairlady Z and Nissan Fairlady 280Z, depending on the market. In Japan, it was exclusive to Nissan Bluebird Store locations. It was the second generation Z-car, replacing the Nissan S30 in late 1978. The 280ZX was the first time the "by Nissan" subscript was badged alongside the Datsun logo, along with Nissan trucks. The 280ZX was Motor Trend's import car of the year for 1979. The 280ZX was replaced by the Nissan 300ZX in 1984.

The Shelby CSX was a limited-production high performance automobile based on the turbocharged intercooled Dodge Shadow and Plymouth Sundance. These cars were offered by Shelby Automobiles Inc. from 1987 through 1989.

The Saab B engine is an inline four-cylinder car petrol engine developed by Saab Automobile. A redesign of the Triumph slant-four engine, the B engine displaced 2.0 L and first appeared in 1972. The B engine was used in the Saab 99 and 900 models. Saab began to phase the engine out in 1981.
A wastegate is a valve that diverts exhaust gases away from the turbine wheel in a turbocharged engine system.

Variable-geometry turbochargers (VGTs), occasionally known as variable-nozzle turbines (VNTs), are a type of turbochargers, usually designed to allow the effective aspect ratio of the turbocharger to be altered as conditions change. This is done because the optimum aspect ratio at low engine speeds is very different from that at high engine speeds.

The Toyota Fortuner , also known as the Toyota SW4, is a mid-size SUV manufactured by Toyota. The Fortuner is built on the Hilux pickup truck platform. It features three rows of seats and is available in rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive configuration. The Fortuner is part of Toyota's IMV project in Thailand, which also includes the Hilux and the Kijang Innova. Developed in large part by Toyota's Thai operations, the Fortuner has piggybacked the success of the Hilux and is now built in a number of countries including Egypt, India, Indonesia, Argentina and Pakistan.
A boost controller is a device to control the boost level produced in the intake manifold of a turbocharged or supercharged engine by affecting the air pressure delivered to the pneumatic and mechanical wastegate actuator.

Turbo-diesel, also written as turbodiesel and turbo diesel, refers to any Diesel engine equipped with a turbocharger. As per other engine types, turbocharging a diesel engine can greatly increase its power output.
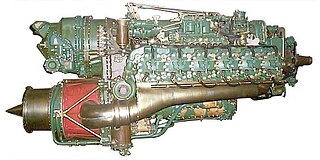
A turbo-compound engine is a reciprocating engine that employs a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust gases. Instead of using that energy to drive a turbocharger as found in many high-power aircraft engines, the energy is instead sent to the output shaft to increase the total power delivered by the engine. The turbine is usually mechanically connected to the crankshaft, as on the Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, but electric and hydraulic power recovery systems have been investigated as well.

The YD engine is a 2.2 and 2.5 L Inline-4 diesel engine from Nissan. It has a cast-iron block and aluminium head with chain driven DOHC. The engine shares much of its architecture with the QR petrol engine.
Garrett AiResearch was a manufacturer of turboprop engines and turbochargers, and a pioneer in numerous aerospace technologies. It was previously known as Aircraft Tool and Supply Company, Garrett Supply Company, AiResearch Manufacturing Company, or simply AiResearch. In 1964, Garrett AiResearch merged with Signal Oil & Gas to form a company renamed in 1968 to Signal Companies, which in 1985 merged with Allied Corp. into AlliedSignal. In 1999 AlliedSignal acquired Honeywell and adopted the Honeywell name.
Gale Banks is an American hot rodder, drag racer, engineer, and entrepreneur who grew up in Lynwood, California. His company, Gale Banks Engineering, sells performance parts for automotive and marine engines. It specializes in diesel engines, and high end cutting edge equipment, performance parts, and auxiliaries. The company has approximately 100+ employees.
Gale Banks Engineering and its four divisions, Banks Power, Banks Technology, Banks Marine, and Banks Racing, are companies created by Southern California hot rodder and automobile engineer Gale Banks. These companies design, engineer, and build high performance parts for the automobile and marine aftermarket and military customers. Located in Azusa, California, the company develops technology and components for both gasoline and diesel-powered vehicles, but is best known for advancing development of the turbocharger and ultra high performance diesel engines for racing and street purposes.
An electric supercharger is a specific type of supercharger for internal combustion engines that uses an electrically powered forced-air system that contains an electric motor to pressurize the intake air. By pressurizing the air available to the engine intake system, the air becomes more dense, and is matched with more fuel, producing the increased horsepower to the wheels.
Turbochargers have been used on various petrol engines since 1962, in order to obtain greater power or torque output for a given engine displacement.

An Electric Turbo Compound (ETC) system is defined where a turbine coupled to a generator (turbogenerator) is located in the exhaust gas flow of a reciprocating engine to harvest waste heat energy and convert it into electrical power. An example of an ETC system is where a turbogenerator is located downstream of a turbocharger turbine of an Internal Combustion Engine (ICE). The power generated from the ETC system can be used to feed into an electrical grid or provide power to local electrical loads such as engine auxiliaries.
Per Sune Evaldsson Gillbrand was a Swedish automobile engineer. Born in Tidaholm, Gillbrand is best known for his contribution to the development of several engines for Saab, and in particular their turbocharged engines.
The Audi RC8 2.0 TFSI is a mass-produced four-stroke 2.0-litre single-turbocharged inline-4 gasoline racing engine, developed and produced by Audi Sport GmbH for Deutsche Tourenwagen Masters. The RC8 2.0 TFSI engine is commonly based on Audi 2.0 R4 16v TSI/TFSI (EA888) road car engine. Audi RC8 TFSI was shakedowned on 15 November 2018 and later made public unveil on 20 March 2019 after more engine dyno test. Audi RC8 TFSI is the first-ever turbocharged DTM engine to date, replacing the aging Audi DTM V8 engine after nineteen-years of service which conform the "Class One" regulations that shared with Japanese Super GT.















