
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root brak. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it is damaging to the environment.

An ecoregion is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation . Ecoregions are also known as "ecozones", although that term may also refer to biogeographic realms.

A snail is a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name snail is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gastropoda that have a coiled shell that is large enough for the animal to retract completely into. When the word "snail" is used in this most general sense, it includes not just land snails but also numerous species of sea snails and freshwater snails. Gastropods that naturally lack a shell, or have only an internal shell, are mostly called slugs, and land snails that have only a very small shell are often called semi-slugs.

Dhilba Guuranda–Innes National Park, formerly Innes National Park, is an IUCN-designated protected area in the Australian state of South Australia located on the southwest tip of Yorke Peninsula about 300 kilometres (190 mi) west of the state capital of Adelaide. It is a popular destination for camping, bushwalking, fishing, surfing and scuba diving.

Gastropods, commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda.
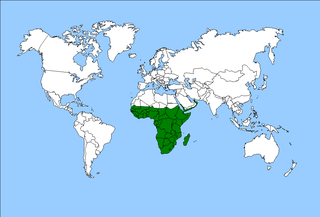
The Afrotropical realm is one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Sub-Saharan Africa, the southern Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, and the islands of the western Indian Ocean. It was formerly known as the Ethiopian Zone or Ethiopian Region.

Great Smoky Mountains National Park is an American national park in the southeastern United States, with parts in North Carolina and Tennessee. The park straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, which are a division of the larger Appalachian Mountain chain. The park contains some of the highest mountains in eastern North America, including Clingmans Dome, Mount Guyot, and Mount Le Conte. The border between the two states runs northeast to southwest through the center of the park. The Appalachian Trail passes through the center of the park on its route from Georgia to Maine. With 13 million visitors in 2023, the Great Smoky Mountains National Park is the most visited national park in the United States.

Lake Mead National Recreation Area is a U.S. national recreation area in southeastern Nevada and northwestern Arizona. Operated by the National Park Service, Lake Mead NRA follows the Colorado River corridor from the westernmost boundary of Grand Canyon National Park to just north of the cities of Laughlin, Nevada and Bullhead City, Arizona. It includes all of the eponymous Lake Mead as well as the smaller Lake Mohave – reservoirs on the river created by Hoover Dam and Davis Dam, respectively – and the surrounding desert terrain and wilderness.
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws.
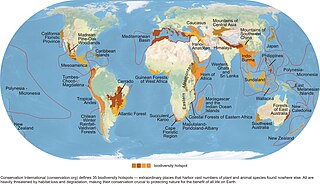
Habitat destruction occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved to elsewhere or are dead, leading to a decrease in biodiversity and species numbers. Habitat destruction is in fact the leading cause of biodiversity loss and species extinction worldwide.

Male is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs.

Carex is a vast genus of over 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as caricology.

Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land, as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water, and semiaquatic animals, which rely on both aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Some groups of insects are terrestrial, such as ants, butterflies, earwigs, cockroaches, grasshoppers and many others, while other groups are partially aquatic, such as mosquitoes and dragonflies, which pass their larval stages in water.

The Natal multimammate mouse is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is also known as the Natal multimammate rat, the common African rat, or the African soft-furred mouse. The Natal multimammate rat is the natural host of the Lassa fever virus.

A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the sea snails and freshwater snails. Land snail is the common name for terrestrial gastropod mollusks that have shells. However, it is not always easy to say which species are terrestrial, because some are more or less amphibious between land and fresh water, and others are relatively amphibious between land and salt water.

Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland and Wales. With an area of 209,331 km2 (80,823 sq mi), it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The island of Ireland, with an area 40 per cent that of Great Britain, is to the west—these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago.

A love dart is a sharp, calcareous or chitinous dart which some hermaphroditic land snails and slugs create. Love darts are both formed and stored internally in a dart sac. These darts are made in sexually mature animals only, and are used as part of the sequence of events during courtship, before actual mating takes place. Darts are quite large compared to the size of the animal: in the case of the semi-slug genus Parmarion, the length of a dart can be up to one fifth that of the semi-slug's foot.

Freshwater snails are gastropod mollusks that live in fresh water. There are many different families. They are found throughout the world in various habitats, ranging from ephemeral pools to the largest lakes, and from small seeps and springs to major rivers. The great majority of freshwater gastropods have a shell, with very few exceptions. Some groups of snails that live in freshwater respire using gills, whereas other groups need to reach the surface to breathe air. In addition, some are amphibious and have both gills and a lung. Most feed on algae, but many are detritivores and some are filter feeders.

The Otay Mountain Wilderness is a U.S. Wilderness Area located in San Diego County, California, 12 miles east of the community of Otay Mesa and just north of the Mexican border. Some parts of the wilderness area rise quickly from sea level, reaching a peak of just over 3,500 feet (1,100 m) at the summit of Otay Mountain.

Saddle Peak Hills Wilderness is the smallest designated wilderness area created by the California Desert Protection Act of 1994.



















